|
Astronomical Seeing
In astronomy, seeing is the degradation of the image of an astronomical object due to turbulence in the atmosphere of Earth that may become visible as blurring, twinkling or variable distortion. The origin of this effect are rapidly changing variations of the optical refractive index along the light path of the object. Seeing is a major limitation to the angular resolution in astronomical observations with telescopes that would otherwise be limited through diffraction by the size of the telescope aperture. Today, many large scientific ground-based optical telescopes include adaptive optics to overcome seeing. The strength of seeing is often characterized by the angular diameter of the long-exposure image of a star (''seeing disk'') or by the Fried parameter ''r''0. The diameter of the seeing disk is the full width at half maximum of its optical intensity. An exposure time of several tens of milliseconds can be considered ''long'' in this context. The Fried parameter des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmos Struct Imaging
Atmos may refer to: * An abbreviation for the Earth's atmosphere * The atmosphere (unit), a unit of pressure Atmos may also refer to: * ATMOS (festival), The Technical Festival of BITS Pilani Hyderabad Campus * Atmos Energy Corporation, a U.S. energy company * Atmos clock, a clock manufactured by Jaeger-LeCoultre, which runs on changes in ambient temperature * Oric Atmos, a home computer first marketed in 1984 * Ambience (sound recording), sounds of a given location or space * Dolby Atmos, surround sound format * ATMOS Software, an Australian computer and video game company * Atmos (character), a minor character in the 30th century DC Universe * Atmos Heating Systems, a British supplier of industrial and domestic heaters * ATMOS (ATMospheric Omission System), fictional technology in the 2008 ''Doctor Who'' two-part serial " The Sontaran Stratagem" / " The Poison Sky" * ATMOS 2000 ATMOS (Autonomous Truck Mounted howitzer System) is a 155 mm/52 calibre self-propelled gun sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Width At Half Maximum
In a distribution, full width at half maximum (FWHM) is the difference between the two values of the independent variable at which the dependent variable is equal to half of its maximum value. In other words, it is the width of a spectrum curve measured between those points on the ''y''-axis which are half the maximum amplitude. Half width at half maximum (HWHM) is half of the FWHM if the function is symmetric. The term full duration at half maximum (FDHM) is preferred when the independent variable is time. FWHM is applied to such phenomena as the duration of pulse (signal processing), pulse waveforms and the spectral width of sources used for optical telecommunication, communications and the resolution of spectrometers. The convention of "width" meaning "half maximum" is also widely used in signal processing to define bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth as "width of frequency range where less than half the signal's power is attenuated", i.e., the power is at least half the max ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoplanetic Patch
The isoplanetic patch is defined as an arbitrary area of the sky over which the path length of incoming electromagnetic waves (such as light or radio waves) only varies by a relatively small amount relative to their wavelength. Typically this area is measured by angular size. Poor seeing or a larger telescope aperture will decrease the size of a patch. Thus, the patch size varies inversely with the Fried parameter and the telescope's angular resolution. In order to correct for atmospheric distortion, telescopes fitted with adaptive optics use a bright light source such as a laser to identify the properties of a patch in the area of interest. See also * optical resolution Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail, in the object that is being imaged. An imaging system may have many individual components, including one or more lenses, and/or recording and display components. ... References Further reading * Birney S, Gonzalez G, Oesper D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
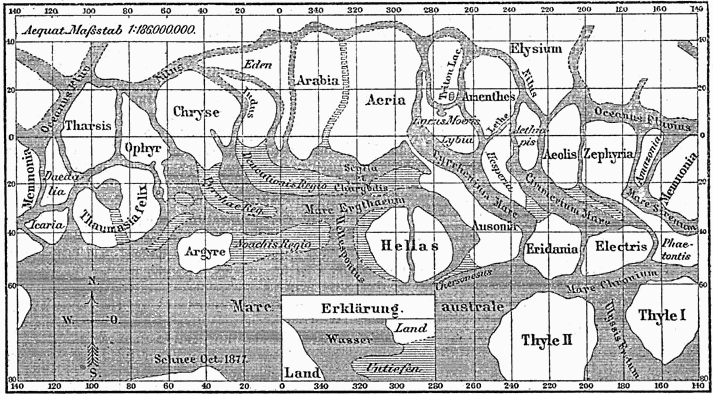
Martian Canals
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, it was erroneously believed that there were "canals" on the planet Mars. These were a network of long straight lines in the equatorial regions from 60° north to 60° south latitude on Mars, observed by astronomers using early telescopes without photography. They were first described by the Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli during the opposition of 1877, and confirmed by later observers. Schiaparelli called these ''canali'' ("channels"), which was mis-translated into English as "canals". The Irish astronomer Charles E. Burton made some of the earliest drawings of straight-line features on Mars, although his drawings did not match Schiaparelli's. Around the turn of the century there was even speculation that they were engineering works, irrigation canals constructed by a civilization of intelligent aliens indigenous to Mars. By the early 20th century, improved astronomical observations revealed the "canals" to be an optical ill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Interferometer
An astronomical interferometer or telescope array is a set of separate telescopes, mirror segments, or radio telescope antenna (radio), antennas that work together as a single telescope to provide higher resolution images of astronomical objects such as stars, nebulas and galaxy, galaxies by means of interferometry. The advantage of this technique is that it can theoretically produce images with the angular resolution of a huge telescope with an aperture equal to the separation between the component telescopes. The main drawback is that it does not collect as much light as the complete instrument's mirror. Thus it is mainly useful for fine resolution of more luminous astronomical objects, such as close binary stars. Another drawback is that the maximum angular size of a detectable emission source is limited by the minimum gap between detectors in the collector array. Interferometry is most widely used in radio astronomy, in which signals from separate radio telescopes are combi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scintillation (astronomy)
Twinkling, also called scintillation, is a generic term for variations in apparent brightness, colour, or position of a distant luminous object viewed through a medium.Wang, Ting-I; Williams, Donn"Scintillation technology bests NIST" , ''InTech'', May 1, 2005. If the object lies outside the Earth's atmosphere, as in the case of stars and planets, the phenomenon is termed ''astronomical scintillation''; for objects within the atmosphere, the phenomenon is termed ''terrestrial scintillation''. As one of the three principal factors governing astronomical seeing (the others being light pollution and cloud cover), atmospheric scintillation is defined as variations in illuminance only. In simple terms, twinkling of stars is caused by the passing of light through different layers of a turbulent atmosphere. Most scintillation effects are caused by anomalous atmospheric refraction caused by small-scale fluctuations in air density usually related to temperature gradients. Scintillation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speckle Imaging
Speckle imaging describes a range of high-resolution astronomical imaging techniques based on the analysis of large numbers of short exposures that freeze the variation of atmospheric turbulence. They can be divided into the shift-and-add ("''image stacking''") method and the speckle interferometry methods. These techniques can dramatically increase the resolution of ground-based telescopes, but are limited to bright targets. Explanation The principle of all the techniques is to take very short exposure images of astronomical targets, and then process those so as to remove the effects of astronomical seeing. Use of these techniques led to a number of discoveries, including thousands of binary stars that would otherwise appear as a single star to a visual observer working with a similar-sized telescope, and the first images of sunspot-like phenomena on other stars. Many of the techniques remain in wide use today, notably when imaging relatively bright targets. The resolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airy Disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best- focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy. The diffraction pattern resulting from a uniformly illuminated, circular aperture has a bright central region, known as the Airy disk, which together with the series of concentric rings around is called the Airy pattern. Both are named after George Biddell Airy. The disk and rings phenomenon had been known prior to Airy; John Herschel described the appearance of a bright star seen through a telescope under high magnification for an 1828 article on light for the '' Encyclopedia Metropolitana'': Airy wrote the first full theoretical treatment explaining the phenomenon (his 1835 "On the Diffraction of an Object-glass with Circular Aperture"). Mathematically, the diffraction pattern is characterized by the waveleng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Source
A point source is a single identifiable ''localised'' source of something. A point source has negligible extent, distinguishing it from other source geometries. Sources are called point sources because in mathematical modeling, these sources can usually be approximated as a mathematical point to simplify analysis. The actual source need not be physically small, if its size is negligible relative to other length scales in the problem. For example, in astronomy, stars are routinely treated as point sources, even though they are in actuality much larger than the Earth. In three dimensions, the density of something leaving a point source decreases in proportion to the inverse square of the distance from the source, if the distribution is isotropic, and there is no absorption or other loss. Mathematics In mathematics, a point source is a singularity from which flux or flow is emanating. Although singularities such as this do not exist in the observable universe, mathematical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Bootis Short Exposure
Zeta (, ; uppercase Ζ, lowercase ζ; grc, ζῆτα, el, ζήτα, label=Demotic Greek, classical or ''zē̂ta''; ''zíta'') is the sixth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 7. It was derived from the Phoenician letter zayin . Letters that arose from zeta include the Roman Z and Cyrillic З. Name Unlike the other Greek letters, this letter did not take its name from the Phoenician letter from which it was derived; it was given a new name on the pattern of beta, eta and theta. The word ''zeta'' is the ancestor of ''zed'', the name of the Latin letter Z in Commonwealth English. Swedish and many Romanic languages (such as Italian and Spanish) do not distinguish between the Greek and Roman forms of the letter; "''zeta''" is used to refer to the Roman letter Z as well as the Greek letter. Uses Letter The letter ζ represents the voiced alveolar fricative in Modern Greek. The sound represented by zeta in Greek before 40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roque De Los Muchachos Observatory
Roque de los Muchachos Observatory ( es, Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos, ORM) is an astronomical observatory located in the municipality of Garafía on the island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, Spain. The observatory site is operated by the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, based on nearby Tenerife. ORM is part of the European Northern Observatory. The seeing statistics at ORM make it the second-best location for optical and infrared astronomy in the Northern Hemisphere, after Mauna Kea Observatory, Hawaii. The site also has some of the most extensive astronomical facilities in the Northern Hemisphere; its fleet of telescopes includes the 10.4 m Gran Telescopio Canarias, the world's largest single-aperture optical telescope as of July 2009, the William Herschel Telescope (second largest in Europe), and the adaptive optics corrected Swedish 1-m Solar Telescope. The observatory was established in 1985, after 15 years of international work and co-operation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |