|
Astragalus Arenarius
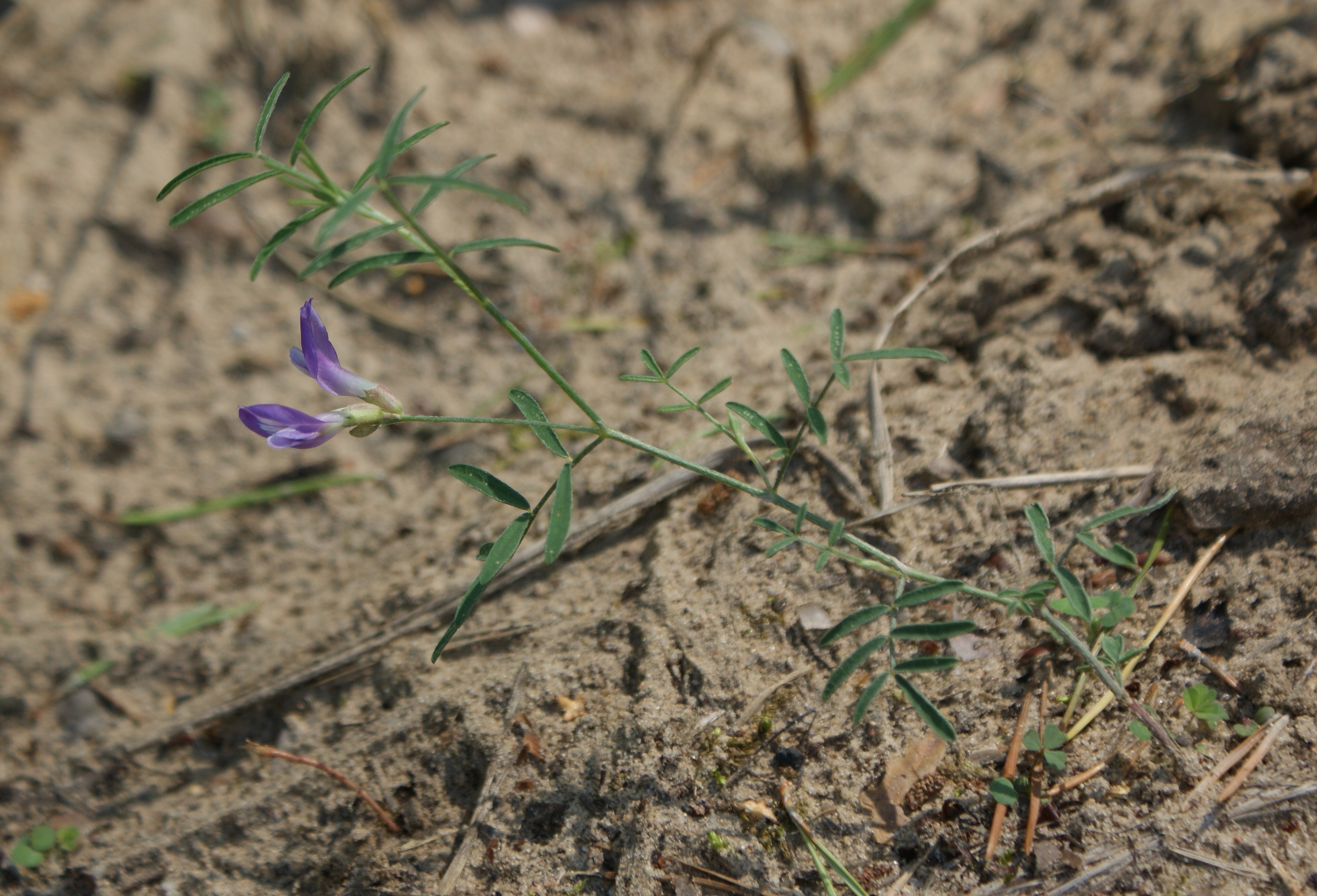
''Astragalus arenarius'', the sand milk-vetch or sand milkvetch, is a species of milkvetch mostly found in Central and Eastern Europe, with populations in Russia stretching perhaps as far as the Urals, and a few instances in Sweden, Finland, and perhaps Denmark. The center of diversity appears to be in Central Russia. Its chromosome number is 2n=16. Description The somewhat recumbent ''A. arenarius'' has slender branched stems from 10 to 40cm long, and typically reaches30 cm tall. It can be distinguished from its congeners by its having leaflets grouped in 2 to 6 pairs, 2 to 4mm wide by 10 to 20mm long; calyces that are characterized by having mostly strongly asymmetric bifurcate hairs; a standard (the large posterior petal seen in legume flowers) 15 to 17mm long; and legumes that 12 to 20 mmlong. Its petals range in color from light purple to lilac, and rarely can be white. The flowering time is from June to July. Ecology As the specific name implies it grows in sandy or gravel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk Vetch
''Astragalus'' is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Common names include milkvetch (most species), locoweed (in North America, some species) and goat's-thorn ( ''A. gummifer'', ''A. tragacantha''). Some pale-flowered vetches (''Vicia'' spp.) are similar in appearance, but they are more vine-like than ''Astragalus''. Description Most species in the genus have pinnately compound leaves. There are annual and perennial species. The flowers are formed in clusters in a raceme, each flower typical of the legume family, with three types of petals: banner, wings, and keel. The calyx is tubular or bell-shaped. Ecology ''Astragalus'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including many case-bearing moths of the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of Diversity
A center of origin is a geographical area where a group of organisms, either domesticated or wild, first developed its distinctive properties. They are also considered centers of diversity. Centers of origin were first identified in 1924 by Nikolai Vavilov. Plants Locating the origin of crop plants is basic to plant breeding. This allows one to locate wild relatives, related species, and new genes (especially dominant genes, which may provide resistance to diseases). Knowledge of the origins of crop plants is important in order to avoid genetic erosion, the loss of germplasm due to the loss of ecotypes and landraces, loss of habitat (such as rainforests), and increased urbanization. Germplasm preservation is accomplished through gene banks (largely seed collections but now frozen stem sections) and preservation of natural habitats (especially in centers of origin). Vavilov centers A Vavilov Center (of Diversity) is a region of the world. First indicated by Nikolai Vavilov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astragalus Arenarius Kz1
''Astragalus'' is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Common names include milkvetch (most species), locoweed (in North America, some species) and goat's-thorn ( ''A. gummifer'', ''A. tragacantha''). Some pale-flowered vetches ('' Vicia'' spp.) are similar in appearance, but they are more vine-like than ''Astragalus''. Description Most species in the genus have pinnately compound leaves. There are annual and perennial species. The flowers are formed in clusters in a raceme, each flower typical of the legume family, with three types of petals: banner, wings, and keel. The calyx is tubular or bell-shaped. Ecology ''Astragalus'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including many case-bearing moths of the genus '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleophora Gallipennella
''Coleophora gallipennella'' is a moth of the family Coleophoridae. It is found in most of Europe (except the Iberian Peninsula, most of the Balkan Peninsula, Ireland, Great Britain and the Netherlands). It is also found in Asia Minor. The wingspan is . Adults are on wing in June and July. The larvae feed on '' Astragalus arenarius'' and ''Astragalus glycyphyllos ''Astragalus glycyphyllos'' (liquorice milkvetch, wild liquorice, wild licorice) is a flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to Europe. It is a perennial herbaceous Herbaceous plants are vascular plants that have no persistent woody ...''. They feed on the generative organs of their host plant. References gallipennella Moths described in 1796 Moths of Europe Moths of Asia {{Coleophoridae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleophora Onobrychiella
''Coleophora onobrychiella'' is a moth of the family Coleophoridae. It is found from Sweden to the Pyrenees, Italy and Greece and from France to Romania. It is also found in China. The wingspan is 14–15 mm. The larvae feed on '' Astragalus arenarius'', '' Astragalus hamosus'', ''Astragalus onobrychis'', '' Genista tincoria'', '' Hippocrepis comosa'', '' Onobrychis sativa'', '' Onobrychis saxatilis'', '' Onobrychis supina'' and ''Onobrychis viciifolia ''Onobrychis viciifolia'', also known as ''O. sativa'' or common sainfoin () has been an important forage legume in temperate regions until the 1950s. During the Green Revolution it was replaced by high yielding alfalfa and clover species. Due ...''. They create a straw-coloured lobe case of 8–10 mm. It has a mouth angle of 55-60°. The shape of the case is exceptionally variable. The mouth opening is shifted to the side of the case, causing the case to lie on its side on the leaf. Larvae can be found from autumn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleophora Polonicella
''Coleophora polonicella'' is a moth of the family Coleophoridae. It is found in Lithuania, Poland and Romania. The wingspan The wingspan (or just span) of a bird or an airplane is the distance from one wingtip to the other wingtip. For example, the Boeing 777–200 has a wingspan of , and a wandering albatross (''Diomedea exulans'') caught in 1965 had a wingspan of ... is 9–10 mm. Adults are on wing in June and July. References polonicella Moths of Europe Moths described in 1865 {{Coleophoridae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncopacma Albifrontella
''Syncopacma albifrontella'' is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It was described by Hermann von Heinemann in 1870. It is found in Great Britain, France, Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Italy, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Romania, Latvia, Lithuania, Ukraine and Russia. The wingspan is about 10 mm. The larvae have been recorded feeding on ''Astragalus arenarius ''Astragalus arenarius'', the sand milk-vetch or sand milkvetch, is a species of milkvetch mostly found in Central and Eastern Europe, with populations in Russia stretching perhaps as far as the Urals, and a few instances in Sweden, Finland, and ...'', but probably also feed on other '' Astragalus'' species. References Moths described in 1870 Syncopacma {{Anacampsini-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astragalus
''Astragalus'' is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Common names include milkvetch (most species), locoweed (in North America, some species) and goat's-thorn ( ''A. gummifer'', ''A. tragacantha''). Some pale-flowered vetches (''Vicia'' spp.) are similar in appearance, but they are more vine-like than ''Astragalus''. Description Most species in the genus have pinnately compound leaves. There are annual and perennial species. The flowers are formed in clusters in a raceme, each flower typical of the legume family, with three types of petals: banner, wings, and keel. The calyx is tubular or bell-shaped. Ecology ''Astragalus'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including many case-bearing moths of the genus ''Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Middle Europe
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Eastern Europe
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Northern Europe
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms ''gut flora'' or '' skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de Phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)