|
Aster (cell Biology)
An aster is a cellular structure shaped like a star, consisting of a centrosome and its associated microtubules during the early stages of mitosis in an animal cell. Asters do not form during mitosis in plants. Astral rays, composed of microtubules, radiate from the centrosphere and look like a cloud. Astral rays are one variant of microtubule which comes out of the centrosome; others include kinetochore microtubules and polar microtubules. During mitosis, there are five stages of cell division: Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase. During prophase, two aster-covered centrosomes migrate to opposite sides of the nucleus in preparation of mitotic spindle formation. During prometaphase there is fragmentation of the nuclear envelope and formation of the mitotic spindles. During metaphase, the kinetochore microtubules extending from each centrosome connect to the centromeres of the chromosomes. Next, during anaphase, the kinetochore microtubules pull the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spindle Apparatus
In cell biology, the spindle apparatus refers to the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. It is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitosis, a process that produces genetically identical daughter cells, or the meiotic spindle during meiosis, a process that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Besides chromosomes, the spindle apparatus is composed of hundreds of proteins. Microtubules comprise the most abundant components of the machinery. Spindle structure Attachment of microtubules to chromosomes is mediated by kinetochores, which actively monitor spindle formation and prevent premature anaphase onset. Microtubule polymerization and depolymerization dynamic drive chromosome congression. Depolymerization of microtubules generates tension at kinetochores; bipolar attachment of sister kinetochores to microtubules emanating from opposite ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomes
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division (where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form). Before this happens, each chromosome is duplicated (S phase), and both copies are joined by a centromere, resulting either in an X-shaped structure (pictured above), if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-arm structure, if the centromere is located distally. The joined copies are now called s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fields ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division (where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form). Before this happens, each chromosome is duplicated (S phase), and both copies are joined by a centromere, resulting either in an X-shaped structure (pictured above), if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-arm structure, if the centromere is located distally. The joined copies are now ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centriole
In cell biology a centriole is a cylindrical organelle composed mainly of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are found in most eukaryotic cells, but are not present in conifers ( Pinophyta), flowering plants ( angiosperms) and most fungi, and are only present in the male gametes of charophytes, bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, cycads, and '' Ginkgo''. A bound pair of centrioles, surrounded by a highly ordered mass of dense material, called the pericentriolar material (PCM), makes up a structure called a centrosome. Centrioles are typically made up of nine sets of short microtubule triplets, arranged in a cylinder. Deviations from this structure include crabs and '' Drosophila melanogaster'' embryos, with nine doublets, and ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' sperm cells and early embryos, with nine singlets. Additional proteins include centrin, cenexin and tektin. The main function of centrioles is to produce cilia during interphase and the aster and the spindle du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosome
In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum 'center' + Greek sōma 'body') (archaically cytocentre) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center (MTOC) of the animal cell, as well as a regulator of cell-cycle progression. The centrosome provides structure for the cell. The centrosome is thought to have evolved only in the metazoan lineage of eukaryotic cells. Fungi and plants lack centrosomes and therefore use other structures to organize their microtubules. Although the centrosome has a key role in efficient mitosis in animal cells, it is not essential in certain fly and flatworm species. Centrosomes are composed of two centrioles arranged at right angles to each other, and surrounded by a dense, highly structured mass of protein termed the pericentriolar material (PCM). The PCM contains proteins responsible for microtubule nucleation and anchoring — including γ-tubulin, pericentrin and ninein. In general, each centriole of the centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APC (protein)
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 (DP2.5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APC'' gene. The APC protein is a negative regulator that controls beta-catenin concentrations and interacts with E-cadherin, which are involved in cell adhesion. Mutations in the ''APC'' gene may result in colorectal cancer. ''APC'' is classified as a tumor suppressor gene. Tumor suppressor genes prevent the uncontrolled growth of cells that may result in cancerous tumors. The protein made by the ''APC'' gene plays a critical role in several cellular processes that determine whether a cell may develop into a tumor. The APC protein helps control how often a cell divides, how it attaches to other cells within a tissue, how the cell polarizes and the morphogenesis of the 3D structures, or whether a cell moves within or away from tissue. This protein also helps ensure that the chromosome number in cells produced through cell division is correct. The A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAPRE1
Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MAPRE1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene was first identified by its binding to the APC ( Adenomatous polyposis coli) protein which is often mutated in familial and sporadic forms of colorectal cancer. Immunofluorescence has demonstrated that EB1 localizes to the centrosome, mitotic spindle, and distal tips of cytoplasmic microtubules. Throughout the cell cycle, EB1 proteins situate on the microtubule plus ends, which is why EB1 is categorized as a microtubule plus end tracking protein(+TIP protein). The protein also associates with components of the dynactin complex and the intermediate chain of cytoplasmic dynein. Because of these associations, it is thought that this protein is involved in the regulation of microtubule structures and chromosome stability. This gene is a member of the RP/EB family. Interactions MAPRE1 has been shown to interact with T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spindle Apparatus
In cell biology, the spindle apparatus refers to the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. It is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitosis, a process that produces genetically identical daughter cells, or the meiotic spindle during meiosis, a process that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Besides chromosomes, the spindle apparatus is composed of hundreds of proteins. Microtubules comprise the most abundant components of the machinery. Spindle structure Attachment of microtubules to chromosomes is mediated by kinetochores, which actively monitor spindle formation and prevent premature anaphase onset. Microtubule polymerization and depolymerization dynamic drive chromosome congression. Depolymerization of microtubules generates tension at kinetochores; bipolar attachment of sister kinetochores to microtubules emanating from opposite ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis () is the part of the cell division process during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytoplasmic division begins during or after the late stages of nuclear division in mitosis and meiosis. During cytokinesis the spindle apparatus partitions and transports duplicated chromatids into the cytoplasm of the separating daughter cells. It thereby ensures that chromosome number and complement are maintained from one generation to the next and that, except in special cases, the daughter cells will be functional copies of the parent cell. After the completion of the telophase and cytokinesis, each daughter cell enters the interphase of the cell cycle. Particular functions demand various deviations from the process of symmetrical cytokinesis; for example in oogenesis in animals the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles. This leaves very little for the resulting polar bodies, which in most species die without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
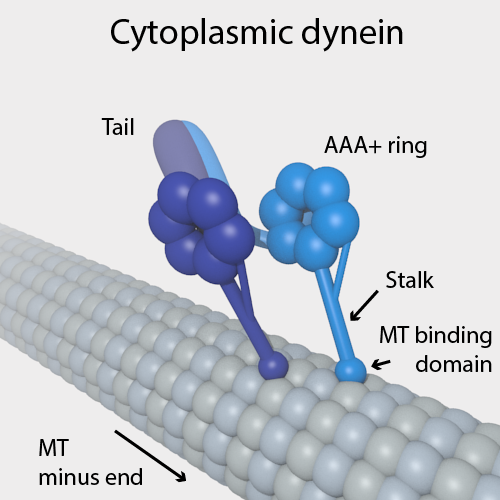
Dynein
Dyneins are a family of cytoskeletal motor proteins that move along microtubules in cells. They convert the chemical energy stored in ATP to mechanical work. Dynein transports various cellular cargos, provides forces and displacements important in mitosis, and drives the beat of eukaryotic cilia and flagella. All of these functions rely on dynein's ability to move towards the minus-end of the microtubules, known as retrograde transport; thus, they are called "minus-end directed motors". In contrast, most kinesin motor proteins move toward the microtubules' plus-end, in what is called anterograde transport. Classification Dyneins can be divided into two groups: cytoplasmic dyneins and axonemal dyneins, which are also called ciliary or flagellar dyneins. * cytoplasmic ** heavy chain: DYNC1H1, DYNC2H1 ** intermediate chain: DYNC1I1, DYNC1I2 ** light intermediate chain: DYNC1LI1, DYNC1LI2, DYNC2LI1 ** light chain: DYNLL1, DYNLL2, DYNLRB1, DYNLRB2, DYNLT1, DYN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |