|
Aspidophytine
Aspidophytine is an indole alkaloid that has attracted a lot of attention from synthetic chemists.''"A Concise Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Aspidophytine" ''Nicolaou, K. C., Dalby, S. M., Majumder, U. ''J. Am. Chem. Soc.'' 2008, ''130(45)'', 14942–14943 () An extract of the cockroach plant, aspidophytine is an insecticidal substance particularly effective against cockroaches. It is one of the two components of the dimer haplophytine.Column: Totally Synthetic by Paul Docherty, at the ; published October 9, 2009; retrieved October 3, 2014 In his suicide note, Harvard doctoral student |
Jason Altom
Jason Altom (6 October 1971 – 15 August 1998) was an American PhD student working in the research group of Nobel laureate Elias James Corey at Harvard University. He killed himself by taking potassium cyanide in 1998, citing in his suicide note "abusive research supervisors" as one reason for taking his life. Altom was studying a complex natural product and felt enormous pressure to finish the molecule before starting his academic career. Altom's suicide highlighted the pressures on PhD students, problems of isolation in graduate school, and sources of tension between graduate mentors and their students. His case prompted many US universities to insist that PhD students have an advisory committee in addition to a supervisor, to whom they might turn for support: James Anderson, who became Harvard Chemistry Department Chairman, stated that "Jason's death prompted an examination of the role the department should play in graduate students' lives". Anderson went on to promise that st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C8 H7 N. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indole is widely distributed in the natural environment and can be produced by a variety of bacteria. As an intercellular signal molecule, indole regulates various aspects of bacterial physiology, including spore formation, plasmid stability, resistance to drugs, biofilm formation, and virulence. The amino acid tryptophan is an indole derivative and the precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin. General properties and occurrence Indole is a solid at room temperature. It occurs naturally in human feces and has an intense fecal odor. At very low concentrations, however, it has a flowery smell, and is a constituent of many perfumes. It also occurs in coal tar. The corresponding substituent is called indolyl. Indole undergoes electrophilic substitution, mainly at position 3 (see diagra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , Medicinal plant, plants, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockroach Plant
''Haplophyton crooksii'' is a plant species native to Arizona, New Mexico, Texas, and northern Mexico Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema .... It is an herb up to 60 cm tall, with showy yellow flowers, found on rocky slopes in desert scrub and desert grassland.L.D. Benson. 1943. American Journal of Botany 30(8): 630. 1943.McLaughliln, S.P. 1993. Apocynaceae A.L. Juss., Dogbane Family. Journal of the Arizona-Nevada Academy of Science 27:164-168. The plant is commonly called the cockroach plant (or ''hierba de la cucaracha'') because of its insecticidal properties. References Rauvolfioideae Flora of Chihuahua (state) Flora of Sonora Flora of Mexico Flora of New Mexico Flora of Arizona Flora of Texas {{Apocynaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to be a major factor behind the increase in the 20th-century's agricultural productivity. Nearly all insecticides have the potential to significantly alter ecosystems; many are toxic to humans and/or animals; some become concentrated as they spread along the food chain. Insecticides can be classified into two major groups: systemic insecticides, which have residual or long term activity; and contact insecticides, which have no residual activity. The mode of action describes how the pesticide kills or inactivates a pest. It provides another way of classifying insecticides. Mode of action can be important in understanding whether an insecticide will be toxic to unrelated species, such as fish, birds and mammals. Insecticides may be repellent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockroach
Cockroaches (or roaches) are a paraphyletic group of insects belonging to Blattodea, containing all members of the group except termites. About 30 cockroach species out of 4,600 are associated with human habitats. Some species are well-known as pests. The cockroaches are an ancient group, with their ancestors, known as " roachoids", originating during the Carboniferous period, some 320 million years ago. Those early ancestors, however, lacked the internal ovipositors of modern roaches. Cockroaches are somewhat generalized insects lacking special adaptations (such as the sucking mouthparts of aphids and other true bugs); they have chewing mouthparts and are probably among the most primitive of living Neopteran insects. They are common and hardy insects capable of tolerating a wide range of climates, from Arctic cold to tropical heat. Tropical cockroaches are often much larger than temperate species. Modern cockroaches are not considered to be a monophyletic group, as it has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimer (chemistry)
A dimer () ('' di-'', "two" + ''-mer'', "parts") is an oligomer consisting of two monomers joined by bonds that can be either strong or weak, covalent or intermolecular. Dimers also have significant implications in polymer chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and biochemistry. The term ''homodimer'' is used when the two molecules are identical (e.g. A–A) and ''heterodimer'' when they are not (e.g. A–B). The reverse of dimerization is often called dissociation. When two oppositely charged ions associate into dimers, they are referred to as ''Bjerrum pairs'', after Niels Bjerrum. Noncovalent dimers Anhydrous carboxylic acids form dimers by hydrogen bonding of the acidic hydrogen and the carbonyl oxygen. For example, acetic acid forms a dimer in the gas phase, where the monomer units are held together by hydrogen bonds. Under special conditions, most OH-containing molecules form dimers, e.g. the water dimer. Excimers and exciplexes are excited structures with a short lifetime. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 34,000 in the UK and a further 8,000 abroad. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
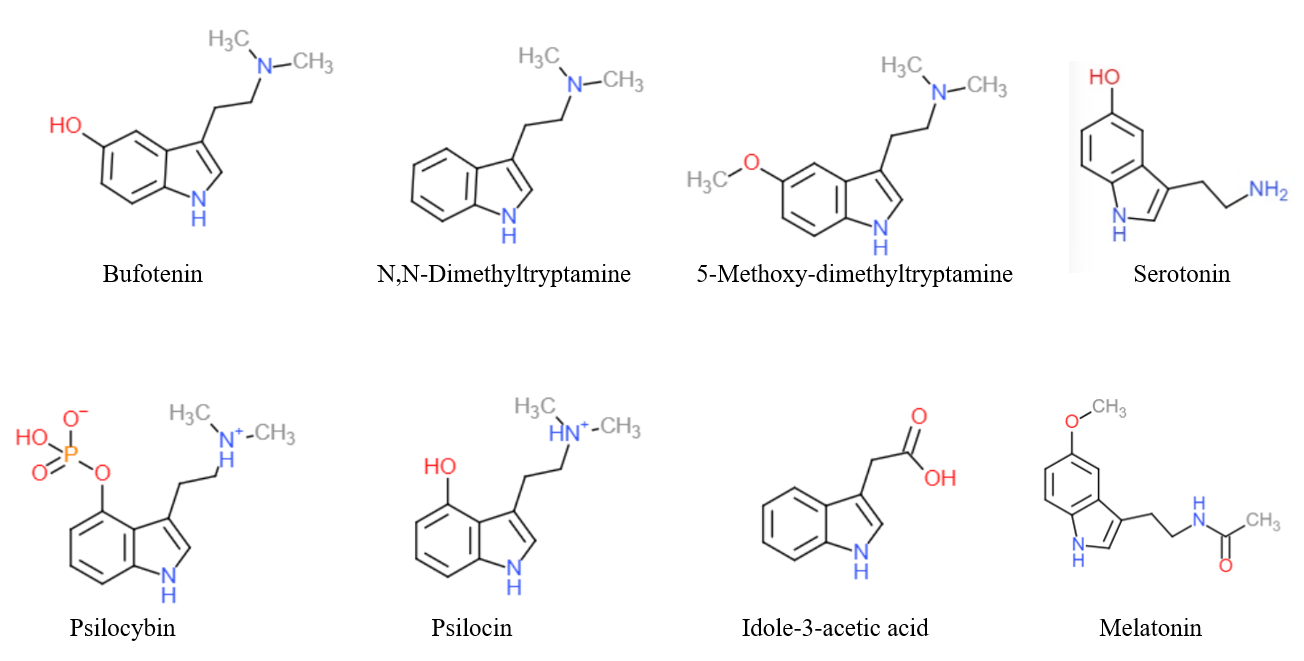
Tryptamine Alkaloids
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloids Found In Apocynaceae
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , |
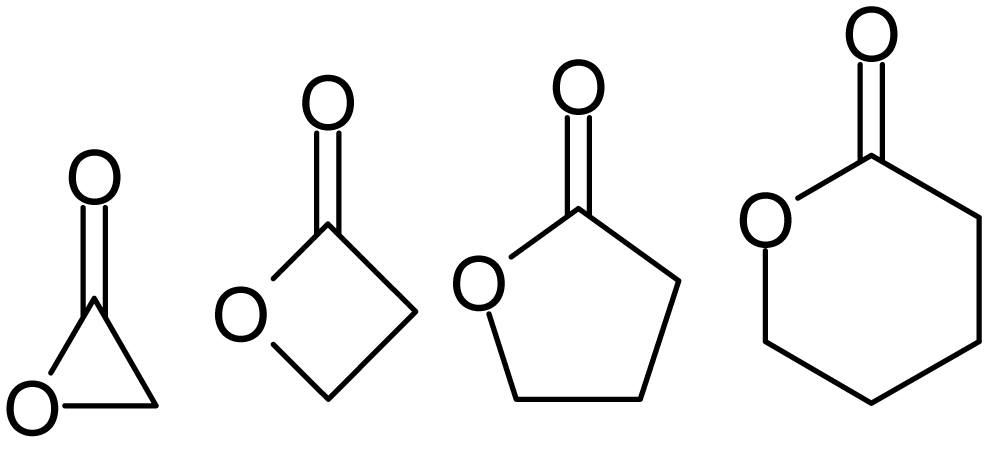
Lactones
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)