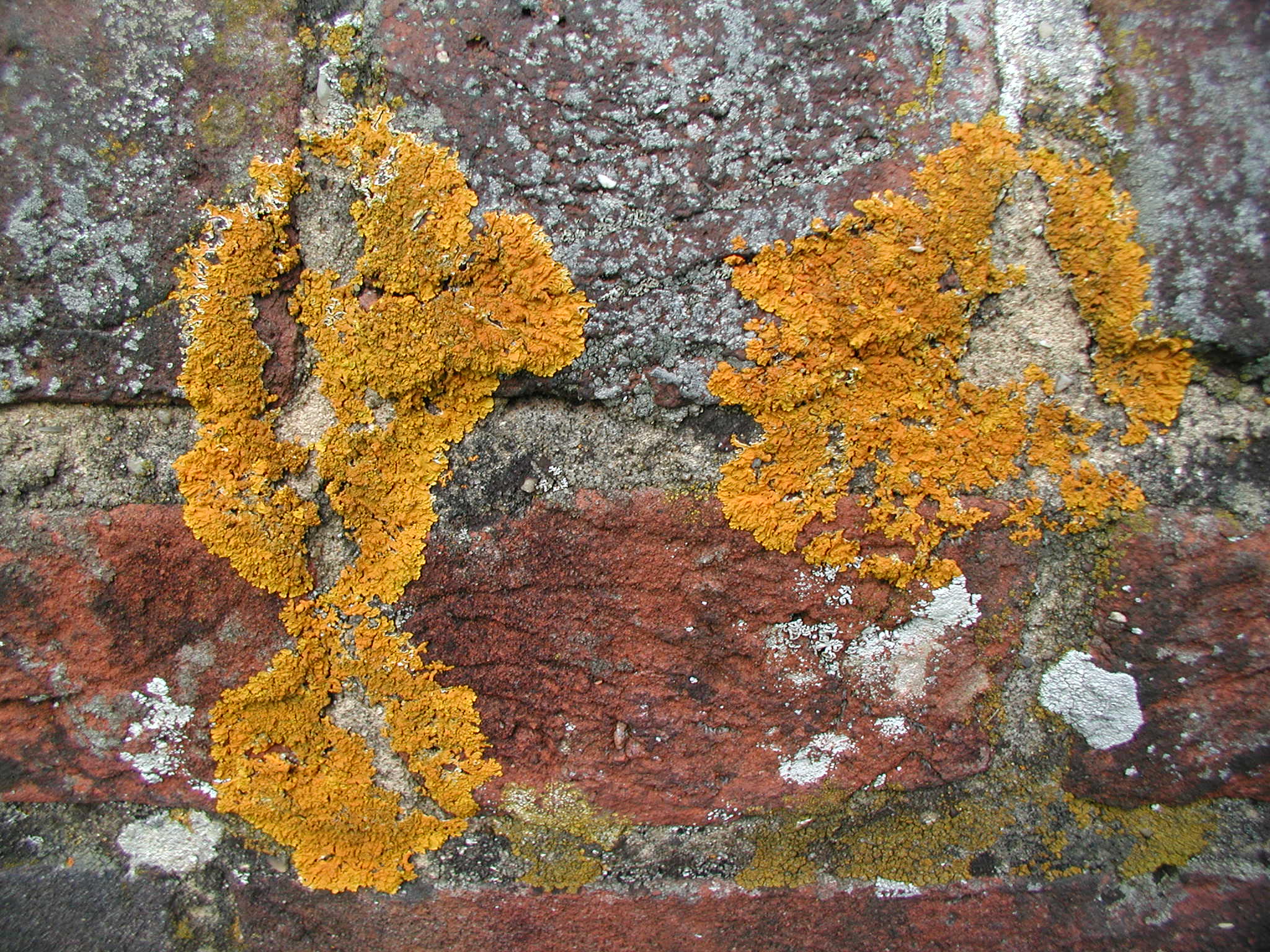|
Aspicilia Humida
''Aspicilia humida'' is a species of saxicolous (rock-dwelling) and crustose lichen in the family Megasporaceae. As a member of the ''Aspicilia cinerea'' species group, it is most closely related to that lichen as well as '' A. dudinensis'', '' A. laevata'', and '' A. indissimilis''. Found in South Korea, it was formally described as a new species in 2022 by Beeyoung Gun Lee. The type specimen was collected in a forest wetland in Hoenggye-ri ( Daegwallyeong-myeon, Gangwon Province) at an altitude of ; here it was found growing on siliceous rock. The lichen is only known to occur at the type locality. The specific epithet In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ... ''humida'' refers to the lichen's habitat, humid wetlands. Similar species include '' A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxicolous Lichen
A saxicolous lichen is a lichen that grows on rock. The prefix "sax" from the Latin means "rock" or "stone". Characteristics Saxicolous lichens exhibit very slow growth rates. They may develop on rock substrates for long periods of time, given the absence of external disturbances. The importance of the mineral composition of the rock substrate, as well as the elemental geochemistry Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing the e ... is also important to the distribution of saxicolous lichens, but the relationship between the substrate influence on lichens, either chemical or textural, is still obscure. Communities of saxicolous lichens are often species-rich in terms of number. References Lichenology {{lichen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangwon Province (South Korea)
Gangwon Province is a province of South Korea, with its capital at Chuncheon. It is bound on the east by the Sea of Japan, and borders Gyeonggi Province to its west, North Gyeongsang Province and North Chungcheong Province to its south, and the Military Demarcation Line to the north, separating it from North Korea's Kangwŏn Province. Before the division of Korea in 1945 Gangwon and Kangwŏn Provinces formed a single province. Pyeongchang County in Gangwon hosted the 2018 Winter Olympics and 2018 Winter Paralympics, with Gangwon hosting the 2024 Winter Youth Olympics. History Gangwon-do was one of the Eight Provinces of Korea during the Joseon Dynasty, formed in 1395, deriving its name from the names of the principal cities of Gangneung () and the provincial capital Wonju (). In 1895 Gangwon-do was replaced by the Districts of Chuncheon (''Chuncheon-bu;'' ) in the west and Gangneung (''Gangneung-bu;'' ) in the east, with Wonju becoming a part of Chungju District. In 1896 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen Species
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (); flat leaf-like structures ( |
Pertusariales
The Pertusariales are an order of fungi in the class Lecanoromycetes. It contains the following families: Agyriaceae The Agyriaceae are a family of lichenized fungi in the order Pertusariales. It contains two genera: ''Agyrium ''Agyrium'' is a genus of saprophytic fungi in the family Agyriaceae. It probably evolved from a lichen ancestor, as it is clos ..., Coccotremataceae, Icmadophilaceae, Megasporaceae, Microcaliciaceae, Ochrolechiaceae, Pertusariaceae, Varicellariaceae, and Variolariaceae. Many of these fungi form lichens. Gallery Image:Pertusaria_paratuberculifera_(EU).jpg, '' Pertusaria paratuberculifera'' (2 verrucae) Image:Pertusaria_paratuberculifera_(EU1).jpg, '' Pertusaria paratuberculifera'' (8 spores per ascus) References Lichen orders Lecanoromycetes orders Taxa named by David Leslie Hawksworth Taxa named by Maurice Choisy Taxa described in 1986 {{Pertusariales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspicilia Pseudovulcanica
''Aspicilia'' (sunken disk lichen) is a genus of mostly crustose areolate lichens that grow on rock. Most members have black apothecia discs that are slightly immersed in the areolas, hence the common name.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, Most of the species of this genus grow on calcareous and acidic rocks and most of the taxa prefer temperate and arctic habitats. Some members of the genus ''Aspicilia'' are pioneer species on granite and other hard rock, after which members of other lichen species may grow on them, such as members of '' Acarospora''.ACAROPSPORA, Lichen Flora of the Greater Sonoran Desert Region. Vol 3., Nash, T.H., Ryan, B.D., Gries, C., Bugartz, F., (eds.) 2001/ref> Description Members of this genus are weakly cracked to distinctly areolate, with a scattered to whole thallus, thalli. Some of the species of this genus are disc-shaped with plicate lobes at the circumference; these lobes may appear chalky white, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspicilia Vulcanica
''Aspicilia'' (sunken disk lichen) is a genus of mostly crustose areolate lichens that grow on rock. Most members have black apothecia discs that are slightly immersed in the areolas, hence the common name.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, Most of the species of this genus grow on calcareous and acidic rocks and most of the taxa prefer temperate and arctic habitats. Some members of the genus ''Aspicilia'' are pioneer species on granite and other hard rock, after which members of other lichen species may grow on them, such as members of ''Acarospora''.ACAROPSPORA, Lichen Flora of the Greater Sonoran Desert Region. Vol 3., Nash, T.H., Ryan, B.D., Gries, C., Bugartz, F., (eds.) 2001/ref> Description Members of this genus are weakly cracked to distinctly areolate, with a scattered to whole thallus, thalli. Some of the species of this genus are disc-shaped with plicate lobes at the circumference; these lobes may appear chalky white ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspicilia Aquatica
''Aspicilia'' (sunken disk lichen) is a genus of mostly crustose lichen, crustose areolate lichen, areolate lichens that grow on rock. Most members have black apothecia discs that are slightly immersed in the areolas, hence the List of common names of lichen genera, common name.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, Most of the species of this genus grow on calcareous and acidic rocks and most of the taxa prefer temperate and arctic habitats. Some members of the genus ''Aspicilia'' are pioneer species on granite and other hard rock, after which members of other lichen species may grow on them, such as members of ''Acarospora''.ACAROPSPORA, Lichen Flora of the Greater Sonoran Desert Region. Vol 3., Nash, T.H., Ryan, B.D., Gries, C., Bugartz, F., (eds.) 2001/ref> Description Members of this genus are weakly cracked to distinctly areolate, with a scattered to whole thallus, thalli. Some of the species of this genus are disc-shaped with p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Name
A botanical name is a formal scientific name conforming to the '' International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN) and, if it concerns a plant cultigen, the additional cultivar or Group epithets must conform to the ''International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants'' (ICNCP). The code of nomenclature covers "all organisms traditionally treated as algae, fungi, or plants, whether fossil or non-fossil, including blue-green algae ( Cyanobacteria), chytrids, oomycetes, slime moulds and photosynthetic protists with their taxonomically related non-photosynthetic groups (but excluding Microsporidia)." The purpose of a formal name is to have a single name that is accepted and used worldwide for a particular plant or plant group. For example, the botanical name ''Bellis perennis'' denotes a plant species which is native to most of the countries of Europe and the Middle East, where it has accumulated various names in many languages. Later, the plant was intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Locality (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siliceous Rock
Siliceous rocks are sedimentary rocks that have silica (SiO2) as the principal constituent. The most common siliceous rock is chert; other types include diatomite. They commonly form from silica-secreting organisms such as radiolarians, diatoms, or some types of sponges Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through .... References Sedimentary rocks {{Petrology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daegwallyeong-myeon
Daegwallyeong-myeon () is a Myeon (administrative division), myeon (township) in the county of Pyeongchang County, Pyeongchang in the province of Gangwon Province (South Korea), Gangwon-do, South Korea. It is located in the northeastern part of the county. The total area of Daegwallyeong-myeon is , and, as of 2008, the population was 6,162 people. The myeon was named Doam-myeon () until 2007. Daegwallyeong-myeon is named after the important mountain pass of Daegwallyeong. It has the coldest average temperature in South Korea. Climate Attractions *Yongpyong Ski Resort: largest ski resort in South Korea, venue of 2018 Winter Olympics *Alpensia Resort: main venue of 2018 Winter Olympics *Daegwallyeong Sheep husbandry, Sheep Farm *Pyeongchang Olympic Stadium: venue for the opening and closing ceremonies of the 2018 Winter Olympics. References External links Official Homepage [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustose Lichen
Crustose lichens are lichens that form a crust which strongly adheres to the Substrate (biology), substrate (soil, rock, tree bark, etc.), making separation from the substrate impossible without destruction. The basic structure of crustose lichens consists of a cortex (botany), cortex layer, an algal layer, and a medulla. The upper cortex layer is differentiated and is usually pigmented. The algal layer lies beneath the cortex. The medulla fastens the lichen to the substrate and is made up of Fungus, fungal hyphae. The surface of crustose lichens is characterized by branching cracks that periodically close in response to climatic variations such as alternate wetting and drying regimes. Subtypes * Powdery – considered as the simplest subtype due to the absence of an organized thallus. :The thallus appears powdery. :E.g. Genera ''Lepraria'', ''Vezdaea'' * Endolithic – grows inside the rock, usually in interstitial spaces between mineral grains. The :upper cortex is usually d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)