|
Asghar The Murderer
Ali Asghar Borujerdi ( fa, علیاصغر بروجردی; 18936 July 1934), better known as Asghar the Murderer (, ''Asghar-e Ghatel'') was the first Iranian serial killer and rapist reported in the 20th century. Asghar-e Ghatel was born in Iran and moved to Iraq as a child with his family. He began assaulting, raping, and later murdering, adolescent boys in Baghdad when he was fourteen years old. Escaping back to Iran in 1933, he continued his murders in Tehran where he was eventually arrested and executed. Asghar-e Ghatel was convicted of raping and killing 33 young adults, eight in Tehran and the rest in Baghdad. Early life Ali Asghar Borujerdi was born in 1893 in Borujerd. He had 2 brothers named Reza and Taghi, and one sister. Asghar grew up in a family which had a history of various criminal activities, including theft, murder, and defamation. His grandfather, Zulfali, was a bandit who robbed caravans in the cities of Borujerd, Malayer, and Arak, sometimes murdering th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
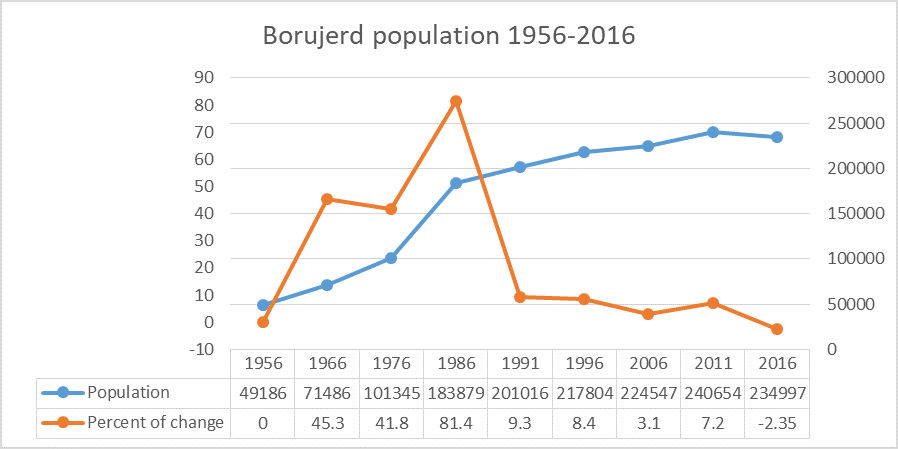
Borujerd
Borujerd ( fa, بروجرد ''Borūjerd'') is a city and the capital of Borujerd County, Lorestan Province in western Iran. At the 2016 census, its population was 234,997 persons. Among the existing modern cities in Iran, Borujerd is one of the oldest reported at least since the 9th century. In Sassanid Empire, Borujerd was a small town and region neighboring Nahavand. Gaining more attention during Great Seljuq Empire in the 9th and 10th centuries, Borujerd stood as an industrial, commercial and strategic city in Zagros Mountains until the 20th century. In its golden ages, Borujerd was selected as the state capital of Lorestan and Khuzestan region during Qajar dynasty in the 18th and 19th centuries. Due to the existence of a large number of production and industrial units and the supply of their products in the domestic and foreign markets, Borujerd is considered the industrial hub of Lorestan province. Geography and climate Borujerd city is located approximately 1670 meters ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Cossack Brigade
, image = Persian Cossack Brigade.jpg , caption = Persian Cossack Brigade in Tabriz in 1909 , dates = 1879–1921 , disbanded = 6 December 1921 , country = Persia , allegiance = (1879–1917) White movement (1917–1920) (1921) , branch = Persian Army , type = Cavalry , role = Special operations , size = , command_structure = , garrison = Tehran, Tabriz, Isfahan, Mashhad, Ardabil, Hamadan , Urmia, Mazandaran and Gilan , battles = , notable_commanders = Col. Vladimir Liakhov BG Reza Khan BG Martiros Khan Davidkhanian BG Alexander Khan Setkhanian The Persian Cossack Brigade or Iranian Cossack Brigade ( fa, بریگاد قزاق, Berīgād-e qazzāq) was a Cos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah-Abdol-Azim Shrine
The Shāh Abdol-Azīm Shrine ( fa, شاه عبدالعظیم), also known as Shabdolazim, located in Rey, Iran, contains the tomb of ‘Abdul ‘Adhīm ibn ‘Abdillāh al-Hasanī (aka Shah Abdol Azim). Shah Abdol Azim was a fifth generation descendant of Hasan ibn ‘Alī and a companion of Muhammad al-Taqī. He was entombed here after his death in the 9th century. Adjacent to the shrine, within the complex, include the mausolea of Imamzadeh Tahir (son of the fourth Shia Imam Sajjad) and Imamzadeh Hamzeh (brother of the eighth Twelver Imām - Imām Reza). Background Abdol Azim migrated to Rayy out of persecution and subsequently died there. A piece of paper was found in his pocket outlining his ancestry as being: ‘Abdul ‘Adhīm son of ‘Abdillāh son of ‘Alī son of Husayn son of Zayd son of Hasan ibn ‘Alī. Shah Abdol Azim was sent to Rayy ( Modern day Tehran) by Imam Reza. His journey was full of hardships but he successfully reached there and delivered the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okra
Okra or Okro (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in many English-speaking countries as ladies' fingers or ochro, is a flowering plant in the mallow family. It has edible green seed pods. The geographical origin of okra is disputed, with supporters of West African, Ethiopian, Southeast Asian, and South Asian origins. Cultivated in tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions around the world, okra is used in the cuisines of many countries. Etymology ''Abelmoschus'' is New Latin from Arabic أَبُو المِسْك (ʾabū l-misk, “father of musk”), while ''esculentus'' is Latin for being fit for human consumption. The first use of the word ''okra'' (alternatively; ''okro'' or ''ochro'') appeared in 1679 in the Colony of Virginia, deriving from the Igbo word . The word ''gumbo'' was first used in American vernacular around 1805, deriving from Louisiana Creole, but originates from either the Umbundu word ''ochinggômbo'' or the Kimbundu word ''ki-ngombo.'' Despi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qanat
A qanat or kārīz is a system for transporting water from an aquifer or water well to the surface, through an underground aqueduct; the system originated approximately 3,000 BC in what is now Iran. The function is essentially the same across North Africa and the Middle East but the system operates under a variety of regional names: ''qanat'' or kārīz in Iran, ''foggara'' in Algeria, ''khettara'' in Morocco, ''falaj'' in Oman, ''karez'' in Afghanistan, ''auyoun'' in Saudi Arabia, et al. The largest extant and functional qanat systems are located in Iran, Afghanistan, Oman, the oases of Turfan region of China, Algeria, and Pakistan. This is a system of water supply that allows water to be transported over long distances in hot dry climates without loss of much of the water to evaporation. The system has the advantage of being resistant to natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods, and to deliberate destruction in war. Furthermore, it is almost insensitive to the level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qarat
The Erbil Citadel, locally called Qelat ( ku, قەڵای ھەولێر ) is a tell or occupied mound, and the historical city centre of Erbil in the Kurdistan Region. The citadel has been inscribed on the World Heritage List since 21 June 2014. The earliest evidence for occupation of the citadel mound dates to the 5th millennium BC, and possibly earlier. It appears for the first time in historical sources in the Ebla tablets around 2,300 BC, and gained particular importance during the Neo-Assyrian period. During the Sassanian period and the Abbasid Caliphate, Erbil was an important centre for Christianity. After the Mongols captured the citadel in 1258, the importance of Erbil declined. During the 20th century, the urban structure was significantly modified, as a result of which a number of houses and public buildings were destroyed. In 2007, the High Commission for Erbil Citadel Revitalization (HCECR) was established to oversee the restoration of the citadel. In the same year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dowlatabad, Isfahan
Dowlatabad ( fa, دولت آباد, also Romanized as Dowlatābād and Daulatābād) is a city and capital of Borkhar County, Isfahan Province, Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni .... At the 2006 census, its population was 33,941, in 8,661 families. References Populated places in Borkhar County Cities in Isfahan Province {{Borkhar-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amirabad District
Amirabad District ( fa, بخش امیرآباد) is a district (bakhsh) in Damghan County, Semnan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 9,026, in 2,717 families. The District has one city: Amiriyeh. The District has three rural districts (''dehestan''): Qohab-e Rastaq Rural District , native_name_lang = fa , settlement_type = Rural District , image_skyline = , imagesize = , image_alt = , image_caption = , image_flag = , flag_alt ..., Qohab-e Sarsar Rural District, and Tuyehdarvar Rural District. References Districts of Semnan Province Damghan County {{Damghan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laleh Park
Laleh Park (Pârk-e Laleh, formerly called Park-e Farah after Farah Diba), is a large recreation area of the Iranian capital Tehran. ''Laleh'' (لاله) is the Persian word for tulip, which is also a popular symbol in Iranian culture. The park is well-kept and has green areas adjacent to Keshavarz Boulevard in the south, The Ministry of Agriculture in the east, Iran's National Carpet Museum to the northwest, and the Tehran Museum of Contemporary Art in the west. This park (one of c. 800 parks in Tehran) lies in central Tehran and north of Tehran University The University of Tehran (Tehran University or UT, fa, دانشگاه تهران) is the most prominent university located in Tehran, Iran. Based on its historical, socio-cultural, and political pedigree, as well as its research and teaching p .... Laleh Park is one of the biggest parks in Tehran. Laleh Park provides pathways for walking and shade for picnics and relaxation. The park has become a popular meeting place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Najafabad
Najafabad ( fa, نجفآباد, also Romanized as Najafābād) is a city and capital of Najafabad County, Isfahan Province, Iran. At the 2016 census, its population was 293,275, in 90,158 families. It is located west of Isfahan and is increasingly becoming a part of the Isfahan Metropolitan area. The city serves as a trade center for agricultural products in the region, and is noted for its pomegranates and almonds. One of the attractions of Najafabad is the "Arg-e Sheykh Bahaie" that has recently been repaired. Najafabad was home to several gang activities, weapon sales and drug distribution systems controlled by notorious and unknown criminal system still being investigated by the authorities; their secrecy and network is still one of the most mysterious criminal organisations in Iran. In 2019 by the help of Irgc, Basij Mobilisation and security forces and Police some of the criminals were hunted down and executed but still not much informations is in hand about them. Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qaleh Kharabeh, Fars
Qaleh Kharabeh ( fa, قلعه خرابه, also Romanized as Qal‘eh Kharābeh; also known as Deh Kharābeh) is a village in Hamaijan Rural District, Hamaijan District, Sepidan County, Fars Province, Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni .... At the 2006 census, its population was 245, in 54 families. References Populated places in Sepidan County {{Sepidan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minudasht, Qazvin
Minudasht ( fa, مينودشت, also Romanized as Mīnūdasht) is a village in Alamut-e Bala Rural District, Rudbar-e Alamut District, Qazvin County, Qazvin Province, Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni .... At the 2006 census, its population was 183, in 58 families. References Populated places in Qazvin County {{QazvinCounty-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |