|
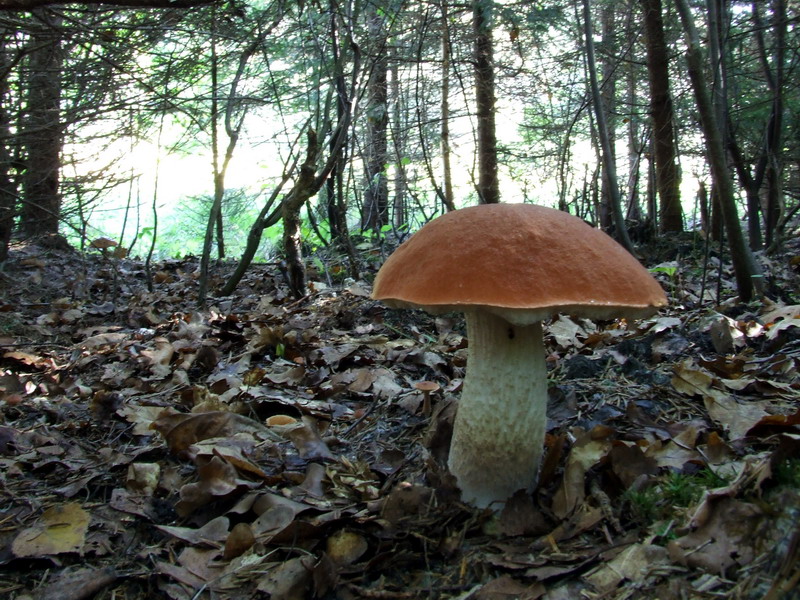
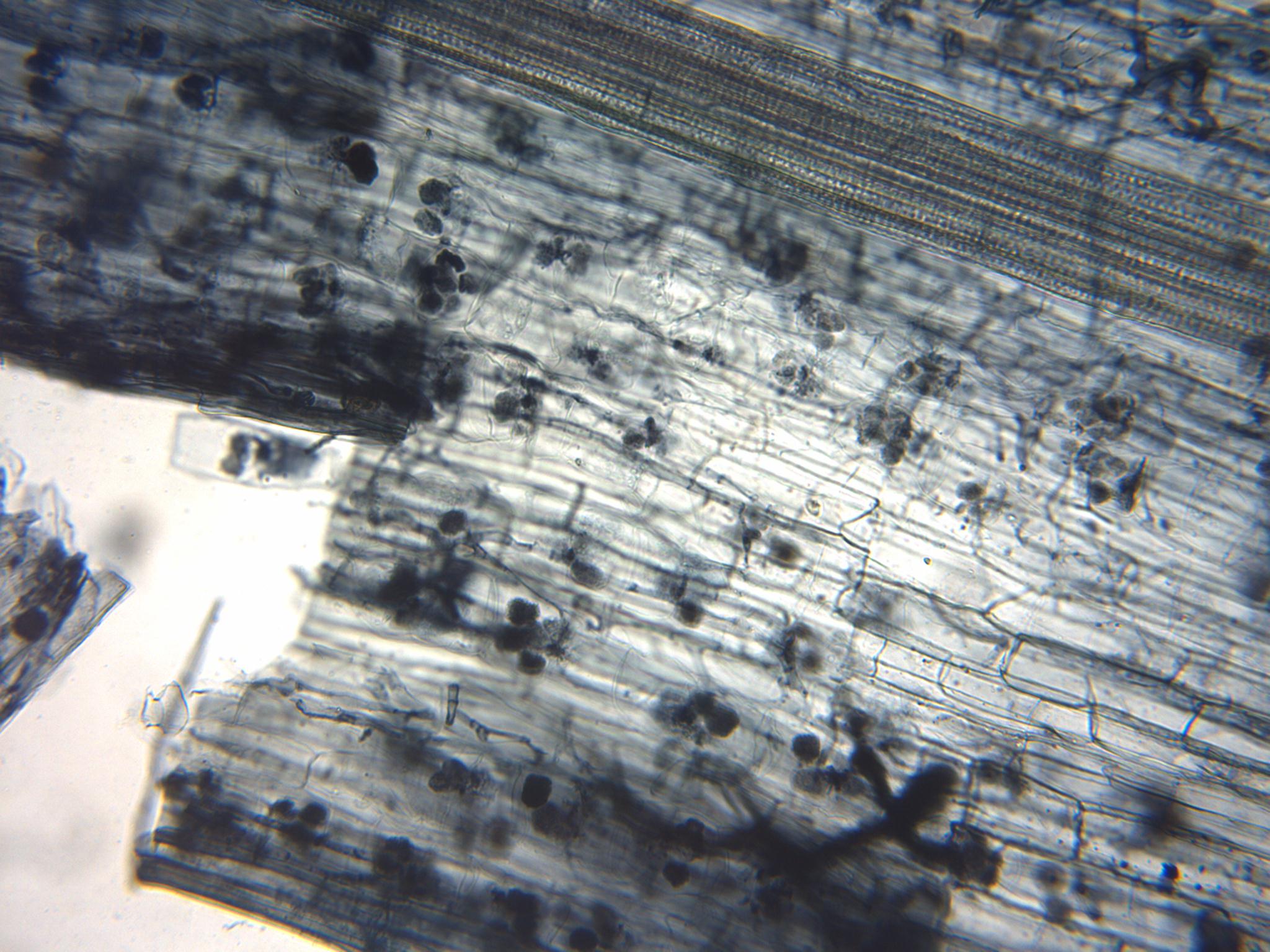
Arum Type
Arum-type refers to the morphology of fungal hyphae living in, or around plant root cells. *Forms in arbuscular or tree-like fashion, branching off dichotomously at predetermined junctions. This is a type of mycorrhizal infection whereby the fungus in question invaginates the cell membrane of a plant cell, and branches in arbuscular manner. Arum-type growth of hyphae is used in endomycorrhizal symbiosis with a plant. *Often, but not always, accompanied by intercellular hyphal growth. See also *Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'', a.k.a. ''endomycorrhiza'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''AM fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. (N ... * Paris type References *C.J. Alexopolous, Charles W. Mims, M. Blackwell et al., ''Introductory Mycology, 4th ed.'' (John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken NJ, 2004) Fungal morphology and anatomy {{mycolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Friedrich Burdach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbuscular Mycorrhiza
An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'', a.k.a. ''endomycorrhiza'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''AM fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. (Not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza or ericoid mycorrhiza.) Arbuscular mycorrhizae are characterized by the formation of unique structures, arbuscules and vesicles, by Glomeromycota and Mucoromycota, sister clades of the more well-known and diverse dikaryan fungi (all three are together called "symbiomycota"). AM fungi help plants to capture nutrients such as phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen and micronutrients from the soil. It is believed that the development of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis played a crucial role in the initial colonisation of land by plants and in the evolution of the vascular plants. It has been said that it is quicker to list the plants that do not form endomycorrhizae than those that do. This symbiosis is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichotomous
A dichotomy is a partition of a whole (or a set) into two parts (subsets). In other words, this couple of parts must be * jointly exhaustive: everything must belong to one part or the other, and * mutually exclusive: nothing can belong simultaneously to both parts. If there is a concept A, and it is split into parts B and not-B, then the parts form a dichotomy: they are mutually exclusive, since no part of B is contained in not-B and vice versa, and they are jointly exhaustive, since they cover all of A, and together again give A. Such a partition is also frequently called a bipartition. The two parts thus formed are complements. In logic, the partitions are opposites if there exists a proposition such that it holds over one and not the other. Treating continuous variables or multicategorical variables as binary variables is called dichotomization. The discretization error inherent in dichotomization is temporarily ignored for modeling purposes. Etymology The term ''di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycorrhizal
A mycorrhiza (from Greek μύκης ', "fungus", and ῥίζα ', "root"; pl. mycorrhizae, mycorrhiza or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, its root system. Mycorrhizae play important roles in plant nutrition, soil biology, and soil chemistry. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungus colonizes the host plant's root tissues, either intracellularly as in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF or AM), or extracellularly as in ectomycorrhizal fungi. The association is sometimes mutualistic. In particular species or in particular circumstances, mycorrhizae may have a parasitic association with host plants. Definition A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a green plant and a fungus. The plant makes organic molecules such as sugars by photosynthesis and supplies them to the fungus, and the fungus supplies to the plant water and mineral nutrients, such as phos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invaginate
Invagination is the process of a surface folding in on itself to form a cavity, pouch or tube. In developmental biology, invagination is a mechanism that takes place during gastrulation. This mechanism or cell movement happens mostly in the vegetal pole. Invagination consists of the folding of an area of the exterior sheet of cells towards the inside of the blastula. In each organism, the complexity will be different depending on the number of cells. Invagination can be referenced as one of the steps of the establishment of the body plan. The term, originally used in embryology, has been adopted in other disciplines as well. There is more than one type of movement for invagination. Two common types are axial and orthogonal. The difference between the production of the tube formed in the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix. Axial can be formed at a single point along the axis of a surface. Orthogonal is linear and trough. Biology * Invagination is the morphogenetic processes by wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Cell
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capability to perform photosynthesis and store starch, a large vacuole that regulates turgor pressure, the absence of flagella or centrioles, except in the gametes, and a unique method of cell division involving the formation of a cell plate or phragmoplast that separates the new daughter cells. Characteristics of plant cells * Plant cells have cell walls, constructed outside the cell membrane and composed of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. Their composition contrasts with the cell walls of fungi, which are made of chitin, of bacteria, which are made of peptidoglycan and of archaea, which are made of pseudopeptidoglycan. In many cases lignin or suberin are secreted by the protoplast as secondary wall layers inside the primary cell wall. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endomycorrhizae
A mycorrhiza (from Greek μύκης ', "fungus", and ῥίζα ', "root"; pl. mycorrhizae, mycorrhiza or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, its root system. Mycorrhizae play important roles in plant nutrition, soil biology, and soil chemistry. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungus colonizes the host plant's root tissues, either intracellularly as in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF or AM), or extracellularly as in ectomycorrhizal fungi. The association is sometimes mutualistic. In particular species or in particular circumstances, mycorrhizae may have a parasitic association with host plants. Definition A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a green plant and a fungus. The plant makes organic molecules such as sugars by photosynthesis and supplies them to the fungus, and the fungus supplies to the plant water and mineral nutrients, such as phosph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. The organisms, each termed a symbiont, must be of different species. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term was subject to a century-long debate about whether it should specifically denote mutualism, as in lichens. Biologists have now abandoned that restriction. Symbiosis can be obligatory, which means that one or more of the symbionts depend on each other for survival, or facultative (optional), when they can generally live independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. When symbionts form a single body it is called conjunctive symbiosis, while all other arrangements are called disjunctive symbiosis."symbiosis." Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |