|
Artesunate Mefloquine
Artesunate (AS) is a medication used to treat malaria. The intravenous form is preferred to quinine for severe malaria. Often it is used as part of combination therapy, such as artesunate plus mefloquine. It is not used for the prevention of malaria. Artesunate can be given by injection into a vein, injection into a muscle, by mouth, and by rectum. The most common side effects include kidney failure requiring dialysis, hemoglobinuria (the presence of hemoglobin in urine) and jaundice. Artesunate is generally well tolerated. Side effects may include a slow heartbeat, allergic reaction, dizziness, and low white blood cell levels. During pregnancy it appears to be a safer option, even though animal studies have found harm to the baby. Use is likely fine during breastfeeding. It is in the artemisinin class of medication. Artesunate was developed by Liu Xu in 1977. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It was approved for medical use in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweet Wormwood
''Artemisia annua'', also known as sweet wormwood, sweet annie, sweet sagewort, annual mugwort or annual wormwood (), is a common type of wormwood native to temperate Asia, but naturalized in many countries including scattered parts of North America. An extract of ''A. annua'', called artemisinin (or artesunate), is a medication used to treat malaria. Discovery of artemisinin and its antimalarial properties by the Chinese scientist, Tu Youyou, led to award of the 2011 Lasker Prize and 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Description ''Artemisia annua'' belongs to the plant family of ''Asteraceae'' and is an annual short-day plant. Its stem is erect brownish or violet brown. The plant itself is hairless and naturally grows from 30 to 100 cm tall, although in cultivation it is possible for plants to reach a height of 200 cm. The leaves of ''A. annua'' have a length of 3–5 cm and are divided by deep cuts into two or three small leaflets. The intensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP2A6
Cytochrome P450 2A6 (abbreviated CYP2A6) is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP2A6 is the primary enzyme responsible for the oxidation of nicotine and cotinine. It is also involved in the metabolism of several pharmaceuticals, carcinogens, and a number of coumarin-type alkaloids. CYP2A6 is the only enzyme in the human body that appreciably catalyzes the 7-hydroxylation of coumarin, such that the formation of the product of this reaction, 7-hydroxycoumarin, is used as a probe for CYP2A6 activity. The CYP2A6 gene is part of a large cluster of cytochrome P450 genes from the CYP2A, CYP2B and CYP2F subfamilies on chromosome 19q. The gene was formerly referred to as CYP2A3; however, it has been renamed CYP2A6. Interactive pathway map Distribution CYP2A6 localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and is found predominantly in the liver. Variability Significant interindividual variability in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
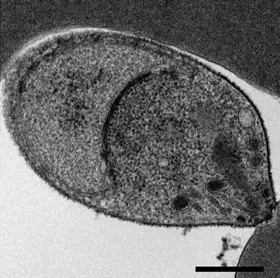
Hemolysis
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in vivo or in vitro. One cause of hemolysis is the action of hemolysins, toxins that are produced by certain pathogenic bacteria or fungi. Another cause is intense physical exercise. Hemolysins damage the red blood cell's cytoplasmic membrane, causing lysis and eventually cell death. Etymology From hemo- + -lysis, from , "blood") + , "loosening"). Inside the body Hemolysis inside the body can be caused by a large number of medical conditions, including some parasites (''e.g.'', ''Plasmodium''), some autoimmune disorders (''e.g.'', autoimmune haemolytic anaemia, drug-induced hemolytic anemia, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS)), some genetic disorders (''e.g.'', Sickle-cell disease or G6PD deficiency), or blood with too low a solute conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticulocyte
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs). In the process of erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation), reticulocytes develop and mature in the bone marrow and then circulatory system, circulate for about a day in the blood stream before developing into mature red blood cells. Like mature red blood cells, in mammals, reticulocytes do not have a cell nucleus. They are called reticulocytes because of a reticular (mesh-like) network of ribosome, ribosomal RNA that becomes visible under a microscope with certain staining, stains such as new methylene blue and Romanowsky stain. Clinical significance To accurately measure reticulocyte counts, automated flow cytometry, counters use a combination of laser excitation, detectors and a fluorophore, fluorescent dye that marks RNA and DNA (such as titan yellow or polymethine). Reticulocytes appear slightly bluer than other red cells when looked at with the normal Romanowsky stain. Reticulocytes are also relatively large, a character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. The WHO was established on 7 April 1948. The first meeting of the World Health Assembly (WHA), the agency's governing body, took place on 24 July of that year. The WHO incorporated the assets, personnel, and duties of the League of Nations' Health Organization and the , including the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Its work began in earnest in 1951 after a significant infusion of financial and technical resources. The WHO's mandate seeks and includes: working worldwide to promote health, keeping the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. It advocates that a billion more people should have: universal health care coverag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
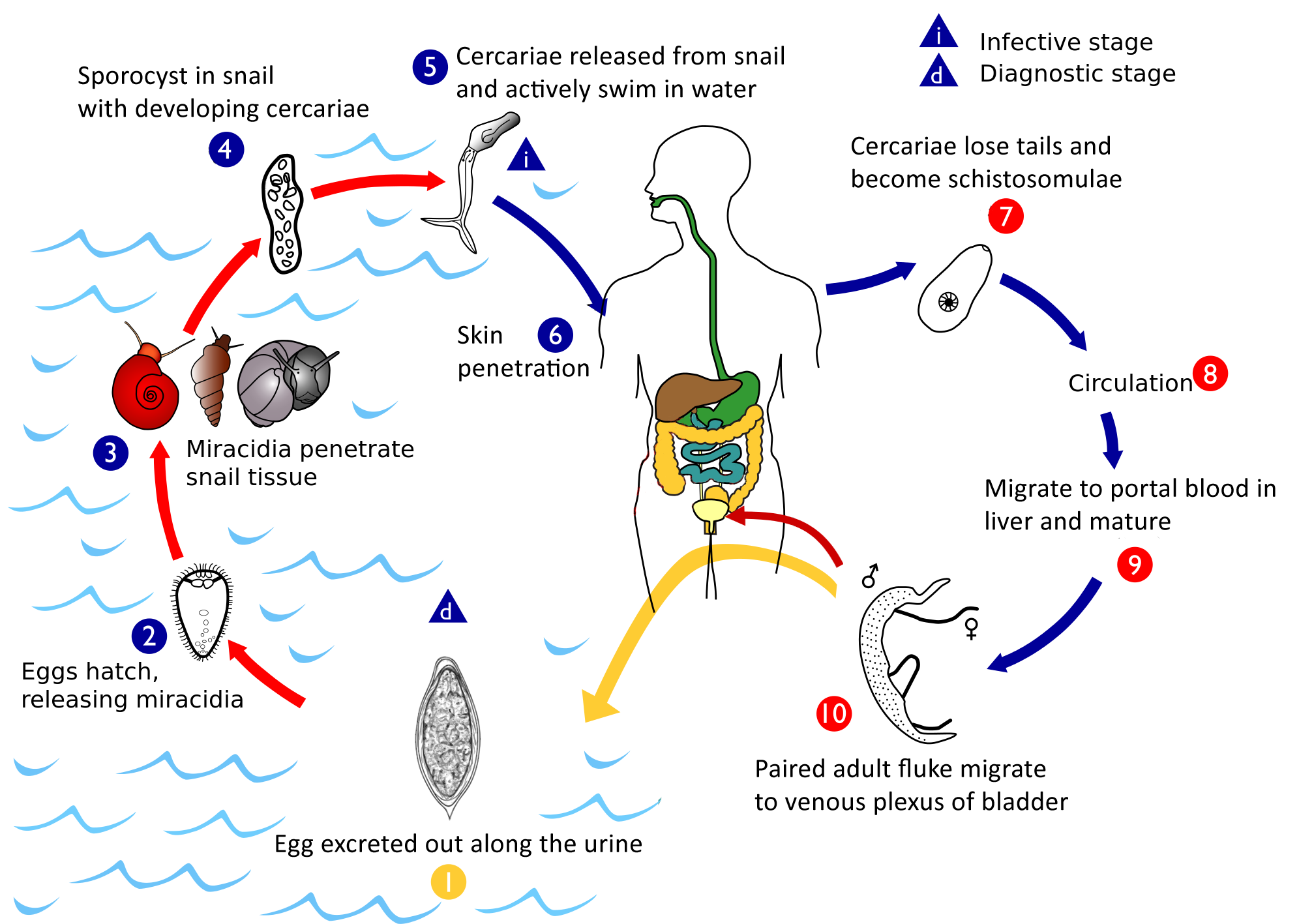
Schistosoma Haematobium
''Schistosoma haematobium'' (urinary blood fluke) is a species of digenetic trematode, belonging to a group (genus) of blood flukes (''Schistosoma''). It is found in Africa and the Middle East. It is the major agent of schistosomiasis, the most prevalent parasitic infection in humans. It is the only blood fluke that infects the urinary tract, causing urinary schistosomiasis, and is the leading cause of bladder cancer (only next to tobacco smoking). The diseases are caused by the eggs. Adults are found in the venous plexuses around the urinary bladder and the released eggs travels to the wall of the urine bladder causing haematuria and fibrosis of the bladder. The bladder becomes calcified, and there is increased pressure on ureters and kidneys otherwise known as hydronephrosis. Inflammation of the genitals due to ''S. haematobium'' may contribute to the propagation of HIV. ''S. haematobium'' was the first blood fluke discovered. Theodor Bilharz, a German surgeon working in Cair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine
Sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine, sold under the brand name Fansidar, is a combination medication used to treat malaria. It contains sulfadoxine (a sulfonamide) and pyrimethamine (an antiprotozoal). For the treatment of malaria it is typically used along with other antimalarial medication such as artesunate. In areas of Africa with moderate to high rates of malaria, three doses are recommended during the second and third trimester of pregnancy. Side effects include diarrhea, rash, itchiness, headache, and hair loss. Rarely a severe allergic reaction or rash such as toxic epidermal necrolysis, may occur. It is not generally recommended in people with a sulfonamide allergy or significant liver or kidney disease. It works by blocking malaria's ability to use folinic acid. Sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine was initially approved for medical use in the United States in 1981. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is not commercially available in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium Knowlesi
''Plasmodium knowlesi'' is a parasite that causes malaria in humans and other primates. It is found throughout Southeast Asia, and is the most common cause of human malaria in Malaysia. Like other ''Plasmodium'' species, ''P. knowlesi'' has a life cycle that requires infection of both a mosquito and a warm-blooded host. While the natural warm-blooded hosts of ''P. knowlesi'' are likely various Old World monkeys, humans can be infected by ''P. knowlesi'' if they are fed upon by infected mosquitoes. ''P. knowlesi'' is a eukaryote in the phylum Apicomplexa, genus ''Plasmodium'', and subgenus ''Plasmodium''. It is most closely related to the human parasite ''Plasmodium vivax'' as well as other ''Plasmodium'' species that infect non-human primates. Humans infected with ''P. knowlesi'' can develop uncomplicated or severe malaria similar to that caused by ''Plasmodium falciparum''. Diagnosis of ''P. knowlesi'' infection is challenging as ''P. knowlesi'' very closely resembles other spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium Malariae
''Plasmodium malariae'' is a parasitic protozoan that causes malaria in humans. It is one of several species of ''Plasmodium'' parasites that infect other organisms as pathogens, also including ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and ''Plasmodium vivax'', responsible for most malarial infection. Found worldwide, it causes a so-called "benign malaria", not nearly as dangerous as that produced by ''P. falciparum'' or ''P. vivax''. The signs include fevers that recur at approximately three-day intervals – a ''quartan fever'' or ''quartan malaria'' – longer than the two-day (tertian) intervals of the other malarial parasites. History Malaria has been recognized since the Greek and Roman civilizations over 2,000 years ago, with different patterns of fever described by the early Greeks. In 1880, Alphonse Laveran discovered that the causative agent of malaria is a parasite. Detailed work of Golgi in 1886 demonstrated that in some patients there was a relationship between the 72-hour life c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemether
Artemether is a medication used for the treatment of malaria. The injectable form is specifically used for severe malaria rather than quinine. In adults, it may not be as effective as artesunate. It is given by injection in a muscle. It is also available by mouth in combination with lumefantrine, known as artemether/lumefantrine. Artemether causes relatively few side effects. An irregular heartbeat may rarely occur. While there is evidence that use during pregnancy may be harmful in animals, there is no evidence of concern in humans. The World Health Organization (WHO) therefore recommends its use during pregnancy. It is in the artemisinin class of medication. Artemether has been studied since at least 1981, and been in medical use since 1987. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Artemether is an antimalarial drug for uncomplicated malaria caused by '' P. falciparum'' (and chloroquine-resistant '' P. falciparum'') or chloroqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)