|
Arnold V, Count Of Looz
Arnold V de Looz, (died August 22, 1327) was Count of Loon from 1279 to 1323 and Count of Chiny (Arnulf III) from 1299 to 1310. He was the son of John I, Count of Looz and Mathilde Jülich. Biography He helped Richardis Gelderland, his widow maternal grandfather, Henri, Count of Luxembourg and Renaud I, Count of Gelderland, fight Siegfried von Westerburg, archbishop of Cologne. Taken prisoner, he had to pay a ransom to be freed. He was forced to deal with Isabelle de Conde, widow of his father in 1281 and had to assign a dower, and give Warcq, Agimont and Givet to his half-brothers John and Jacquemin. In turn, they give up their rights to the county of Loon. This is the only condition that the parents of Marguerite one hand, and his uncle Nicolas II de Conde on the other hand, consent to marriage. In 1288, he commanded a corps of the army of John I, Duke of Brabant, and contributed much to the victory on June 5 in the famous Battle of Worringen (on the Rhine), which ended t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
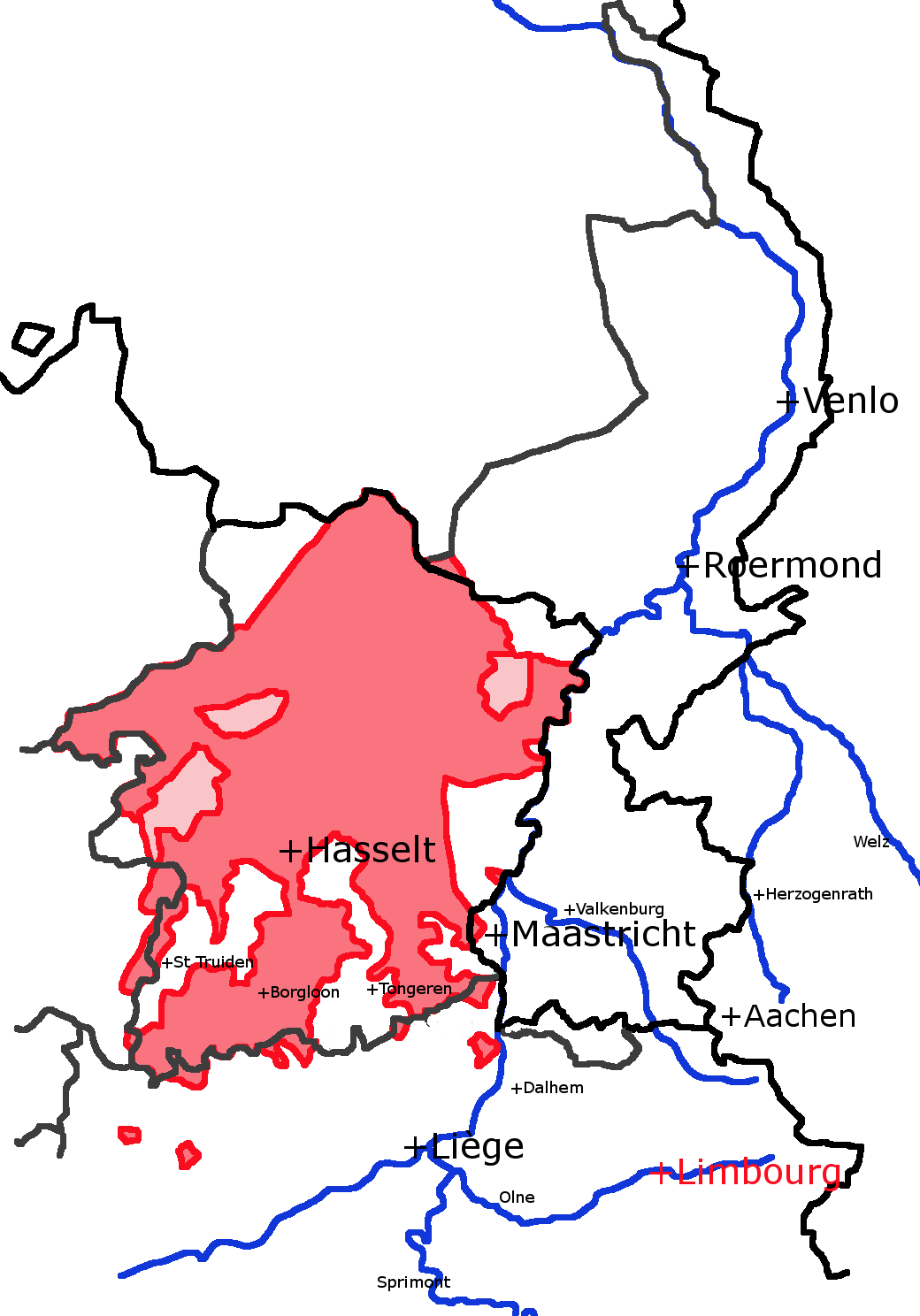
County Of Loon
The County of Loon ( , , ) was a county in the Holy Roman Empire, which corresponded approximately with the Belgian province of Limburg. It was named after the original seat of its count, Loon, which is today called Borgloon. During the middle ages the counts moved their court to a more central position in Kuringen, which is today a part of Hasselt, the modern capital of the region. From its beginnings, Loon was associated with the Prince-bishop of Liège and by 1190 the count had come under the bishop's overlordship. In the fourteenth century the male line ended for a second time, at which point the prince-bishops themselves took over the county directly. Loon approximately represented the Dutch-speaking (archaic ) part of the princedom. All of the Dutch-speaking towns in the Prince-Bishopric, with the status of being so-called "Good Cities" (french: bonnes villes), were in Loon, and are in Belgian Limburg today. These were Beringen, Bilzen, Borgloon, Bree, Hamont, Hassel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Limburg Succession
The War of the Limburg Succession, was a series of conflicts between 1283 and 1289 for the succession in the Duchy of Limburg. The cause of the War of the Limburg Succession was the death of Waleran IV, Duke of Limburg in 1280, and his only daughter Ermengarde of Limburg in 1283. Waleran IV had no sons and Ermengarde had no children. Ermergarde had married Reginald I of Guelders, who now claimed the Duchy of Limburg. However, Waleran's nephew Adolf VIII of Berg, son of his elder brother Adolf VII of Berg, also claimed the Duchy. Unable to assert his claims, he sold them in 1283 to the mighty John I, Duke of Brabant. Between 1283 and 1288, several smaller confrontations occurred between both sides, none of them decisive. Meanwhile, most of the other local powers chose sides. Siegfried II of Westerburg, the Archbishop of Cologne and ruler of the Electorate of Cologne, traditional enemy of the Duke of Brabant, forged an alliance with Reginald I, joined by Henry VI, Count of Luxembour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theobald (bishop Of Liège)
Theobald of Bar (Thibaut of Bar, Thiébaut de Bar) was the third surviving son of Theobald II of Bar and Jeanne de Toucy. He was prince-bishop of Liège from 1302 until his death in 1312, while serving in the retinue of Henri VII of Luxembourg. Life In 1296, on the death of Bouchard d'Avesnes, bishop of Metz, he was one of the candidates in competition with , bishop of Orléans. In the end Gérard de Rhéninghe was chosen. Adolph of Waldeck, prince-bishop of Liège, died at the end of 1302. Of three candidate, Guillaume d'Arras was elected. He, however, turned down the position, claiming his background was too humble, and designated Theobald. Theobald's election gained papal approval 13 March 1303; Theobald was then in fact in Rome. He allied himself with Philip IV of France, in 1304. Two years later his relative Henri VII of Luxembourg became King of the Romans; Theobald was a close adviser. When Henry went to Rome in 1312 to be consecrated as Holy Roman Emperor, Theobald acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolph II De La Marck (Bishop)
Adolph II von der Mark (English: Adolph II of the Mark) (August 1288 – Clermont-sur-Meuse, 3 November 1344) was the Prince-Bishop of Liège from 1313 until his death in 1344. Adolph was the third son of Count Eberhard I of the Mark and Mary of Loon. Aged only 25, but through the influence of King Philip IV of France, he became Prince-Bishop of Liège in 1313. The people of the Prince-Bishopric opposed his authoritarian way of ruling. In 1316, he was forced to sign the Peace of Fexhe, which has been compared to ''Magna Carta'' and which limited his powers. When he tried to revert the treaty, he was forced to flee from Liège to Huy at the end of 1324. From here, he placed Liège under interdict. In 1333, he sold the Lordship of Mechelen to the Count of Flanders. He intervened in the War of Awans and Waroux and participated in the 1334 siege of Maastricht. When Louis VI of Loon died in 1336 without an heir, he tried to annex the County of Loon, but without success. In 1343, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Of Chalon (archbishop Of Besançon)
Hugo III of Chalon (c. 1260 – c. 1312) was a cleric from Free County of Burgundy. Hugues was a son of Jean "the old" of Chalon (1190–1267), Sire of Salins and his third wife Laura of Commercy (d. 1275), sister of Simon IV, Count of Saarbrücken. His nephew Jean of Châlon (1300 – c.1334), son of Jean I, Seigneur of Châlon-Arlay, the Bishop of Basel, and Bishop of Langres and Peer of France. He studied theology in Paris and was an archdeacon in Laon. From 1295 to 1301 he was prince-bishop of Liège, appointed by Pope Boniface VIII. Jean played a role in the conflict between Awans and Waroux (fr) (1297–1335), and supported with the siege of Awans until their surrender. Hugues could not prevent military action from both sides and the war continued for decades. There were other conflicts around Liège too, with the Count of Namur and rebels on one side, and the Duke of Brabant and the Count of Loon on the other side with the bishop. In 1300 he defended himself before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awans
Awans (; wa, Awan) is a municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Liège, Belgium. On January 1, 2006, Awans had a total population of 8,696. The total area is 27.16 km² which gives a population density of 320 inhabitants per km². The municipality consists of the following districts A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...: Awans, Fooz, Hognoul, Othée, and Villers-l'Évêque. File:Awans - Eglise Sainte-Agathe.jpg, St. Agathe File:Othée - Eglise Saint-Pierre et Paul.jpg, Church Saint-Peter-and-Paul in Othée File:20120424 othee14.JPG, Old mill in Othée See also * List of protected heritage sites in Awans References External links * Municipalities of Liège Province {{Liege-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biographie Nationale De Belgique
The ''Biographie nationale de Belgique'' ( French; "National Biography of Belgium") is a biographical dictionary of Belgium. It was published by the Royal Academy of Belgium in 44 volumes between 1866 and 1986. A continuation series, entitled the ''Nouvelle Biographie Nationale'' ("New National Biography"), has been published by the Royal Academy of Science, Letters and Fine Arts of Belgium since 1988. Both the ''Biographie nationale'' and ''Nouvelle biographie nationale'' were digitised by the Fonds InBev-Baillet Latour and can be freely consulted at the Academy's website. A parallel biographical dictionary has been produced in Dutch since 1964, entitled the ''Nationaal Biografisch Woordenboek'' ("National Biographical Dictionary"). It places more emphasis on figures important to the history and culture of Flanders and is published by the Royal Flemish Academy of Belgium for Science and the Arts (with the co-operation of the Royal Academy of Dutch language and literature and the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Worringen
The Battle of Worringen was fought on 5 June 1288 near the town of Worringen (also spelled Woeringen), which is now the northernmost borough of Cologne. It was the decisive battle of the War of the Limburg Succession, fought for the possession of the Duchy of Limburg between on one side the Archbishop Siegfried II of Cologne and Count Henry VI of Luxembourg, and on the other side, Duke John I of Brabant. It was one of the largest battles in Europe in the Middle Ages. Prelude The conflict arose after Duke Waleran IV of Limburg, a scion of the Lotharingian Ardennes-Verdun dynasty, had died without male heirs in 1279. His duchy was inherited by his daughter Ermengarde, who had married Count Reginald I of Guelders about 1270. Her husband claimed the Limburg heritage and in 1282 had his ducal title recognized by the German king Rudolf I. The marriage of Reginald and Ermengarde, however, remained childless and when she died in 1283, Count Adolf VIII of Berg, Duke Waleran's neph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counts Of Chiny
The counts of Chiny were part of the nobility of Lotharingia that ruled from the 9th to the 14th century in what is now part of Belgium. It has been proposed that the County of Chiny was created in the early 10th century out of the ancient county of Ivois. The county now forms part of the province of Luxembourg in present-day Belgium. The county of Chiny included the present-day cantons of Virton, Etalle, Florenville, Neufchâteau, Montmédy and Carignan, as well as the castles of Warcq on the Meuse, which was built in 971 by Otto, ancestor of the later Counts of Chiny. It has also been proposed that there is a close relationship between the counts of Chiny and the early counts of Looz, the counts of Verdun and the bishops of Verdun.Jeantin, J. François Louis. (185859)Histoire du comté de Chiny et des pays haut-wallons Paris: J. Tardieu. The family of the counts of Chiny merged with the family of the counts of Looz. The final count of Chiny, Arnold IV de Rumingy, sold the coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Cologne
The Archbishop of Cologne is an archbishop governing the Archdiocese of Cologne of the Catholic Church in western North Rhine-Westphalia and is also a historical state in the Rhine holding the birthplace of Beethoven and northern Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany and was ''ex officio'' one of the Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire, the Elector of Cologne, from 1356 to 1801. Since the early days of the Catholic Church, there have been ninety-four bishops and archbishops of Cologne. Seven of these ninety-four retired by resignation, including four resignations which were in response to impeachment. Eight of the bishops and archbishops were coadjutor bishops before they took office. Seven individuals were appointed as coadjutors freely by the Pope. One of the ninety-four moved to the Curia, where he became a cardinal. Additionally, six of the archbishops of Cologne were chairmen of the German Bishops' Conference. Cardinal Rainer Woelki has been the Archbishop of Cologne since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegfried II Of Westerburg
Siegfried (or Sigfrid) II of Westerburg (before 1260 – 7 April 1297, in Bonn) was Archbishop of Cologne from 1275 to 1297. Siegfried was the second son of Siegfried IV, Count of Runkel in Westerburg (died 1266). His older brother was Henry (''Heinrich'') I of Westerburg (who would be killed at the Battle of Worringen in 1288).. Retrieved on 2009-02-10. Siegfried was consecrated Archbishop of Cologne in March 1275 in Lyon. The city of Cologne since 1268 had been under excommunication, and was therefore deemed an unsuitable place for consecration. In July 1275, as the new Archbishop of Cologne, Siegfried lifted the city’s excommunication and signed a friendship treaty with the city. In October 1279 in Pingsheim (now part of Nörvenich), he concluded the Peace of Pingsheim with the Counts of Duchy of Jülich, Jülich. On 27 April 1285 he awarded Brühl, North Rhine-Westphalia, Brühl, situated south of Cologne, German town law, town and market rights. Around 1283, Siegfried took ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |