|
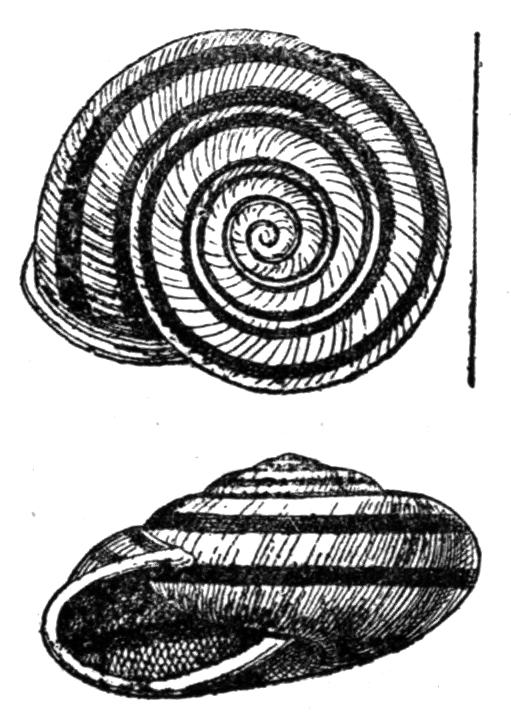
Ariophanta Laevipes
''Ariophanta laevipes'' is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc in the family Ariophantidae. ''Ariophanta laevipes'' is the type species of the genus ''Ariophanta''. Shell description The shell of this species is left-handed (sinistral). The shell is depressed, rather thin, obliquely striated and decussated with fine spiral lines above, smooth beneath. The shell color is white or whitish with three spiral chestnut bands. The spire is low and conoidal, with 5 slightly convex whorls. The body whorl is rounded beneath but angulate at the periphery, the angulation generally disappearing near the mouth. Blanford W. T. & Godwin-Austen H. H. 1908''Mollusca. Testacellidae and Zonitidae'' Taylor & Francis, Londonpage 25€“30. The aperture is lunate and diagonal. The peristome is in one plane, simple above, slightly thickened and reflected below. The width of the shell is 23–28 mm. The height is 15 mm. There is a large flat v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Peter Müller
Johannes Peter Müller (14 July 1801 – 28 April 1858) was a German physiologist, comparative anatomy, comparative anatomist, ichthyology, ichthyologist, and herpetology, herpetologist, known not only for his discoveries but also for his ability to synthesize knowledge. The paramesonephric duct (Müllerian duct) was named in his honor. Life Early years and education Müller was born in Koblenz, Coblenz. He was the son of a poor shoemaker, and was about to be apprenticed to a saddler when his talents attracted the attention of his teacher, and he prepared himself to become a Roman Catholic Priest. During his Secondary school, college course in Koblenz, he devoted himself to the classics and made his own translations of Aristotle. At first, his intention was to become a priest. When he was eighteen, his love for natural science became dominant, and he turned to medicine, entering the University of Bonn in 1819. There he received his Doctor of Medicine, M.D. in 1822. He then studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Thomas Blanford
William Thomas Blanford (7 October 183223 June 1905) was an English geologist and naturalist. He is best remembered as the editor of a major series on ''The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma''. Biography Blanford was born in London to William Blanford and Elizabeth Simpson. His father owned a factory next to their house on Bouverie street, Whitefriars. He was educated in private schools in Brighton (until 1846) and Paris (1848). He joined his family business in carving and gilding and studied at the School of Design in Somerset House. Suffering from ill health, he spent two years in a business house at Civitavecchia owned by a friend of his father. His initial aim was to enter a mercantile career. On returning to England in 1851 he was induced to enter the newly established Royal School of Mines (now part of Imperial College London), which his younger brother Henry F. Blanford (1834–1893), afterwards head of the Indian Meteorological Department, had alrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surat
Surat is a city in the western Indian state of Gujarat. The word Surat literally means ''face'' in Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of the river Tapti near its confluence with the Arabian Sea, it used to be a large seaport. It is now the commercial and economic center in South Gujarat, and one of the largest urban areas of western India. It has well-established diamond and textile industry, and is a major supply centre for apparels and accessories. About 90% of the world's diamonds supply are cut and polished in the city. It is the second largest city in Gujarat after Ahmedabad and the eighth largest city by population and ninth largest urban agglomeration in India. It is the administrative capital of the Surat district. The city is located south of the state capital, Gandhinagar; south of Ahmedabad; and north of Mumbai. The city centre is located on the Tapti River, close to Arabian Sea. Surat will be the world's fastest growing city from 2019 to 2035, acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second-most populous city in India after Delhi and the eighth-most populous city in the world with a population of roughly 20 million (2 crore). As per the Indian government population census of 2011, Mumbai was the most populous city in India with an estimated city proper population of 12.5 million (1.25 crore) living under the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation. Mumbai is the centre of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, the sixth most populous metropolitan area in the world with a population of over 23 million (2.3 crore). Mumbai lies on the Konkan coast on the west coast of India and has a deep natural harbour. In 2008, Mumbai was named an alpha world city. It has the highest number of millionaires and billionaires among all cities i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radula
The radula (, ; plural radulae or radulas) is an anatomical structure used by molluscs for feeding, sometimes compared to a tongue. It is a minutely toothed, chitinous ribbon, which is typically used for scraping or cutting food before the food enters the esophagus. The radula is unique to the molluscs, and is found in every class of mollusc except the bivalves, which instead use cilia, waving filaments that bring minute organisms to the mouth. Within the gastropods, the radula is used in feeding by both herbivorous and carnivorous snails and slugs. The arrangement of teeth ( denticles) on the radular ribbon varies considerably from one group to another. In most of the more ancient lineages of gastropods, the radula is used to graze, by scraping diatoms and other microscopic algae off rock surfaces and other substrates. Predatory marine snails such as the Naticidae use the radula plus an acidic secretion to bore through the shell of other molluscs. Other predatory marine snails ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Love Dart
A love dart (also known as a gypsobelum, shooting darts, or just as darts) is a sharp, calcareous or chitinous dart which some hermaphroditic land snails and slugs create. Love darts are both formed and stored internally in a dart sac. These darts are made in sexually mature animals only, and are used as part of the sequence of events during courtship, before actual mating takes place. Darts are quite large compared to the size of the animal: in the case of the semi-slug genus ''Parmarion'', the length of a dart can be up to one fifth that of the semi-slug's foot. The process of using love darts in snails is a form of sexual selection. Prior to copulation, each of the two snails (or slugs) attempts to "shoot" one (or more) darts into the other snail (or slug). There is no organ to receive the dart; this action is more analogous to stabbing, or to being shot with an arrow or flechette. The dart does not fly through the air to reach its target, but is "fired" as a contact shot. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariophanta Laevipes Dart
''Ariophanta'' is a genus of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the subfamily Ariophantinae of the family Ariophantidae. MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Ariophanta Des Moulins, 1829. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=995732 on 2021-06-13 The shell is sinistral or left-handed in its coiling. Species ''Ariophanta laevipes'' is the type species of the genus ''Ariophanta''. Blanford W. T. & Godwin-Austen H. H. 1908. ''The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma''Mollusca. Testacellidae and Zonitidae'. Taylor & Francis, London, 311 pp.page 25€“30. Species in the genus ''Ariophanta'' include: * '' Ariophanta albata'' (W. T. Blanford, 1880) * '' Ariophanta ammonia'' (Deshayes, 1850) * '' Ariophanta basilessa'' (Benson, 1865) * '' Ariophanta basileus'' (Benson, 1861) * '' Ariophanta beddomei'' (W. T. Blanford, 1874) * '' Ariophanta belangeri'' (Desha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suture (gastropod)
In anatomy, a suture is a fairly rigid joint between two or more hard elements of an organism, with or without significant overlap of the elements. Sutures are found in the skeletons or exoskeletons of a wide range of animals, in both invertebrates and vertebrates. Sutures are found in animals with hard parts from the Cambrian period to the present day. Sutures were and are formed by several different methods, and they exist between hard parts that are made from several different materials. Vertebrate skeletons The skeletons of vertebrate animals (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals) are made of bone, in which the main rigid ingredient is calcium phosphate. Cranial sutures The skulls of most vertebrates consist of sets of bony plates held together by cranial sutures. These sutures are held together mainly by Sharpey's fibers which grow from each bone into the adjoining one. Sutures in the ankles of land vertebrates In the type of crurotarsal ankle which is found i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peristome
Peristome (from the Greek ''peri'', meaning 'around' or 'about', and ''stoma'', 'mouth') is an anatomical feature that surrounds an opening to an organ or structure. Some plants, fungi, and shelled gastropods have peristomes. In mosses In mosses, the peristome is a specialized structure in the sporangium that allows for gradual spore discharge, instead of releasing them all at once. Most mosses produce a capsule with a lid (the operculum) which falls off when the spores inside are mature and thus ready to be dispersed. The opening thus revealed is called the ''stoma'' (meaning "mouth") and is surrounded by one or two peristomes. Each peristome is a ring of triangular "teeth" formed from the remnants of dead cells with thickened cell walls. There are usually 16 such teeth in a single peristome, separate from each other and able to both fold in to cover the stoma as well as fold back to open the stoma. This articulation of the teeth is termed arthrodontous and is found in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Haversham Godwin-Austen
Lieutenant-Colonel Henry Haversham Godwin-Austen FRS FZS FRGS MBOU (6 July 1834 – 2 December 1923), known until 1854 as Henry Haversham Austen, was an English topographer, surveyor, naturalist and geologist. He explored the mountains in the Himalayas and surveyed the glaciers at the base of K2, also known as Mount Godwin-Austen. Geographer Kenneth Mason called Godwin-Austen "probably the greatest mountaineer of his day". He also remains the most important investigator of the terrestrial molluscs of the Indian subcontinent. Early life The eldest son of the geologist Robert Austen, who in 1854 added Godwin to his surname by royal licence, Henry Haversham Austen was probably born at Ogwell House, near Newton Abbot, Devon, where his father had recently taken up residence. His father's family, landowners in Cheshire and Surrey since the 12th century, was a family of merchant venturers, soldiers, scholars, and collectors. His grandfather, Sir Henry Edmund Austen (1785– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |