|
Argument From Fallacy
Argument from fallacy is the formal fallacy of analyzing an argument and inferring that, since it contains a fallacy, its ''conclusion'' must be false. It is also called argument to logic (''argumentum ad logicam''), the fallacy fallacy, the fallacist's fallacy, and the bad reasons fallacy. Form An argument from fallacy has the following general argument form: Thus, it is a special case of denying the antecedent where the antecedent, rather than being a proposition that is false, is an entire argument that is fallacious. A fallacious argument, just as with a false antecedent, can still have a consequent that happens to be true. The fallacy is in concluding the consequent of a fallacious argument has to be false. That the argument is fallacious only means that the argument cannot succeed in proving its consequent.John Woods''The death of argument: fallacies in agent based reasoning'' Springer 2004, pp. XXIII–XXV But showing how one argument in a complex thesis is fallaciously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Fallacy
In logic and philosophical logic, philosophy, a formal fallacy is a pattern of reasoning rendered validity (logic), invalid by a flaw in its logical structure. propositional calculus, Propositional logic, for example, is concerned with the meanings of sentences and the relationships between them. It focuses on the role of logical operators, called propositional connectives, in determining whether a sentence is true. An error in the sequence will result in a deductive argument that is invalid. The argument itself could have true premises, but still have a false logical consequence, conclusion. Thus, a formal fallacy is a fallacy in which deduction goes wrong, and is no longer a logical process. This may not affect the truth of the conclusion, since validity and truth are separate in formal logic. While a logical argument is a ''non sequitur'' if, and only if, it is invalid, the term "non sequitur" typically refers to those types of invalid arguments which do not constitute formal fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Lapidem
Appeal to the stone, also known as argumentum ad lapidem, is a logical fallacy A fallacy is the use of invalid or otherwise faulty reasoning in the construction of an argument that may appear to be well-reasoned if unnoticed. The term was introduced in the Western intellectual tradition by the Aristotelian '' De Sophisti ... that dismisses an argument as untrue or absurd. The dismissal is made by stating or reiterating that the argument is absurd, without providing further argumentation. This theory is closely tied to proof by assertion due to the lack of evidence behind the statement and its attempt to persuade without providing any evidence. Appeal to the stone is a Fallacy, logical fallacy. Specifically, it is an Fallacy#Informal fallacy, informal fallacy, which means that it relies on inductive reasoning in an argument to justify an Proof by assertion, assertion. Informal fallacies contain erroneous reasoning in content of the argument and not the form or structure of it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Existential Comics
Existential Comics is a webcomic about philosophy created by Corey Mohler, a software engineer in Portland, Oregon. Mohler created the comic in December 2013 in an attempt to help popularize philosophy through comedy. The comic tends to depict philosophers of different backgrounds and often has them interacting and arguing with each other. It also gives textual descriptions of the jokes and associated philosophy to help educate readers. In May 2018 Mohler once called Elon Musk "the villain from ''Atlas Shrugged''". Musk responded during SpaceX's launch of a Falcon 9 rocket. Mohler later published a comic about the incident. Philosophers As of April 2023, the comic has covered over 200 philosophers, examining a wide variety of thought from Pre-Socratic philosophy to contemporary philosophy. Mohler has described both Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir as his favorite philosophers. Alongside existentialism, Mohler has also written extensively about Stoicism and communism Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absence Of Evidence Is Not Evidence Of Absence
Argument from ignorance (), or appeal to ignorance, is an informal fallacy where something is claimed to be true or false because of a lack of evidence to the contrary. The fallacy is committed when one asserts that a proposition is true because it has not yet been proven false or a proposition is false because it has not yet been proven true. If a proposition has not yet been proven true, one is not entitled to conclude, solely on that basis, that it is false, and if a proposition has not yet been proven false, one is not entitled to conclude, solely on that basis, that it is true. Another way of expressing this is that a proposition is true only if proven true, and a proposition is false only if proven false. If no proof is offered (in either direction), then the proposition can be called unproven, undecided, inconclusive, an open problem or a conjecture. Use The term was likely coined by philosopher John Locke in the late 17th century. In debates, appealing to ignorance is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuous Truth
In mathematics and logic, a vacuous truth is a conditional or universal statement (a universal statement that can be converted to a conditional statement) that is true because the antecedent cannot be satisfied. It is sometimes said that a statement is vacuously true because it does not really say anything. For example, the statement "all cell phones in the room are turned off" will be true when no cell phones are present in the room. In this case, the statement "all cell phones in the room are turned ''on''" would also be vacuously true, as would the conjunction of the two: "all cell phones in the room are turned on ''and'' turned off", which would otherwise be incoherent and false. More formally, a relatively well-defined usage refers to a conditional statement (or a universal conditional statement) with a false antecedent. One example of such a statement is "if Tokyo is in Spain, then the Eiffel Tower is in Bolivia". Such statements are considered vacuous truths becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straw Man
A straw man fallacy (sometimes written as strawman) is the informal fallacy of refuting an argument different from the one actually under discussion, while not recognizing or acknowledging the distinction. One who engages in this fallacy is said to be "attacking a straw man". The typical straw man argument creates the illusion of having refuted or defeated an opponent's proposition through the covert replacement of it with a different proposition (i.e., "stand up a straw man") and the subsequent refutation of that false argument ("knock down a straw man"), instead of the opponent's proposition. Straw man arguments have been used throughout history in polemical debate, particularly regarding highly charged emotional subjects. Straw man tactics in the United Kingdom may also be known as an Aunt Sally, after a pub game of the same name, where patrons throw sticks or battens at a post to knock off a skittle balanced on top. Overview The straw man fallacy occurs in the following p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductio Ad Absurdum
In logic, (Latin for "reduction to absurdity"), also known as (Latin for "argument to absurdity") or ''apagogical argument'', is the form of argument that attempts to establish a claim by showing that the opposite scenario would lead to absurdity or contradiction. This argument form traces back to Ancient Greek philosophy and has been used throughout history in both formal mathematical and philosophical reasoning, as well as in debate. In mathematics, the technique is called ''proof by contradiction''. In formal logic, this technique is captured by an axiom for "Reductio ad Absurdum", normally given the abbreviation RAA, which is expressible in propositional logic. This axiom is the introduction rule for negation (see ''negation introduction''). Examples The "absurd" conclusion of a ''reductio ad absurdum'' argument can take a range of forms, as these examples show: * The Earth cannot be flat; otherwise, since the Earth is assumed to be finite in extent, we would find peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Fallacies
In logic and philosophy, a formal fallacy is a pattern of reasoning rendered invalid by a flaw in its logical structure. Propositional logic, for example, is concerned with the meanings of sentences and the relationships between them. It focuses on the role of logical operators, called propositional connectives, in determining whether a sentence is true. An error in the sequence will result in a deductive argument that is invalid. The argument itself could have true premises, but still have a false conclusion. Thus, a formal fallacy is a fallacy in which deduction goes wrong, and is no longer a logical process. This may not affect the truth of the conclusion, since validity and truth are separate in formal logic. While a logical argument is a ''non sequitur'' if, and only if, it is invalid, the term "non sequitur" typically refers to those types of invalid arguments which do not constitute formal fallacies covered by particular terms (e.g., affirming the consequent). In other wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Extreme
A logical extreme is a useful, though sometimes fallacious, rhetorical device for the disputation of propositions. Quite simply, a logical extreme is the relevant statement of an extreme or preposterous position that is consistent with the proposition in question. Therefore, as the logically extreme position is both relevant and untenable, it has succeeded in calling the proposition into question, at least in its stated form. An example is in Basil Liddell Hart's essay ''Armed Forces and the Art of War: Armies in The New Cambridge Modern History'': See also * ''Reductio ad absurdum In logic, (Latin for "reduction to absurdity"), also known as (Latin for "argument to absurdity") or ''apagogical argument'', is the form of argument that attempts to establish a claim by showing that the opposite scenario would lead to absur ...'' References {{DEFAULTSORT:Logical Extreme Logic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Fallacy
The genetic fallacy (also known as the fallacy of origins or fallacy of virtue) is a fallacy of irrelevance in which arguments or information are dismissed or validated based solely on their source of origin rather than their content. In other words, a claim is ignored or given credibility based on its source rather than the claim itself. The fallacy therefore fails to assess the claim on its merit. The first criterion of a good argument is that the premises must have bearing on the truth or falsity of the claim in question. Genetic accounts of an issue may be true and may help illuminate the reasons why the issue has assumed its present form, but they are not conclusive in determining its merits. In ''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy ''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'' (1995; second edition 2005) is a reference work in philosophy edited by the philosopher Ted Honderich and published by Oxford University Press Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
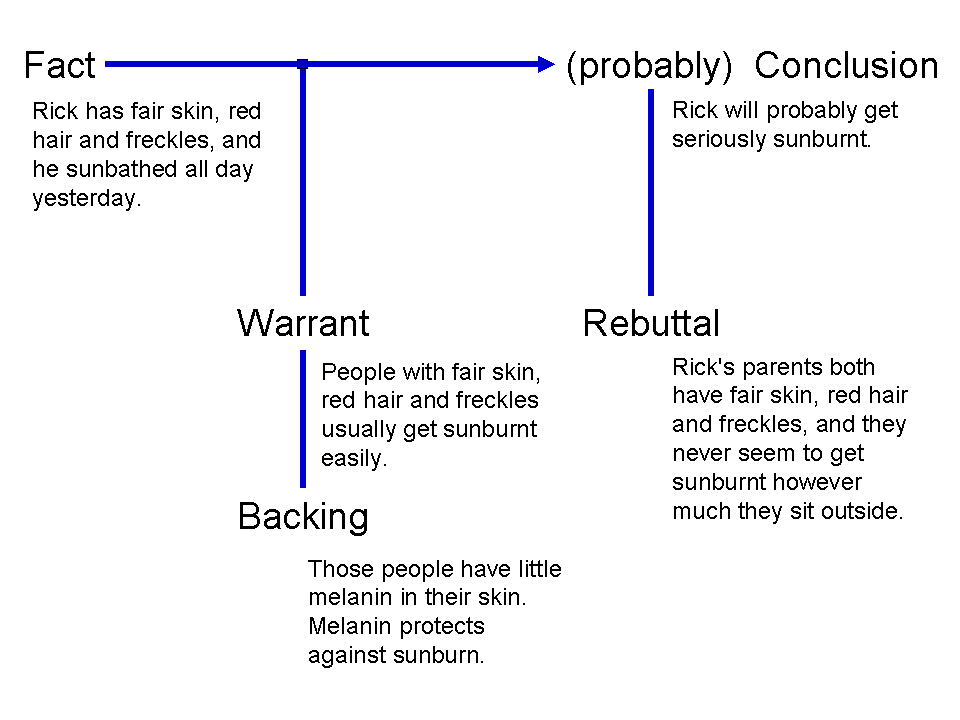
Argumentation Theory
Argumentation theory is the interdisciplinary study of how conclusions can be supported or undermined by premises through logical reasoning. With historical origins in logic, dialectic, and rhetoric, argumentation theory includes the arts and sciences of civil debate, dialogue, conversation, and persuasion. It studies rules of inference, logic, and procedural rules in both artificial and real-world settings. Argumentation includes various forms of dialogue such as deliberation and negotiation which are concerned with collaborative decision-making procedures. It also encompasses eristic dialogue, the branch of social debate in which victory over an opponent is the primary goal, and didactic dialogue used for teaching. This discipline also studies the means by which people can express and rationally resolve or at least manage their disagreements. Argumentation is a daily occurrence, such as in public debate, science, and law. For example in law, in courts by the judge, the partie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argument From Ignorance
Argument from ignorance (), or appeal to ignorance, is an informal fallacy where something is claimed to be true or false because of a lack of evidence to the contrary. The fallacy is committed when one asserts that a proposition is true because it has not yet been proven false or a proposition is false because it has not yet been proven true. If a proposition has not yet been proven true, one is not entitled to conclude, solely on that basis, that it is false, and if a proposition has not yet been proven false, one is not entitled to conclude, solely on that basis, that it is true. Another way of expressing this is that a proposition is true only if proven true, and a proposition is false only if proven false. If no proof is offered (in either direction), then the proposition can be called unproven, undecided, inconclusive, an open problem or a conjecture. Use The term was likely coined by philosopher John Locke in the late 17th century. In debates, appealing to ignorance is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |