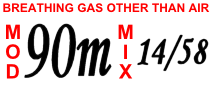|
Argox (breathing Gas)
Argox is the informal name for a scuba diving breathing gas consisting of argon and oxygen. Occasionally the term ''argonox'' has been used to mean the same mix. The blend may consist of varying fractions of argon and oxygen, depending on its intended use. The mixture is made with the same gas blending techniques used to make nitrox, except that for argox, the argon is added to the initial pure oxygen partial-fill, instead of air. Argox is essentially a theoretical diving gas, being rarely, if ever, used, and usually thought to have no practical applications where its benefits outweigh its drawbacks. Possible uses Human exploration of Mars Argox, or half-argox/half-nitrox is a possible oxygen mixture for human exploration of Mars due to the relative abundance of Argon in the Martian atmosphere. The Martian atmosphere is composed of approximately: 95% , 1.9% argon, 1.9% nitrogen. While it is possible for humans to breathe pure oxygen, a pure oxygen atmosphere was implicated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scuba Diving
Scuba diving is a mode of underwater diving whereby divers use breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface air supply. The name "scuba", an acronym for "Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus", was coined by Christian J. Lambertsen in a patent submitted in 1952. Scuba divers carry their own source of breathing gas, usually compressed air, affording them greater independence and movement than surface-supplied divers, and more time underwater than free divers. Although the use of compressed air is common, a gas blend with a higher oxygen content, known as enriched air or nitrox, has become popular due to the reduced nitrogen intake during long and/or repetitive dives. Also, breathing gas diluted with helium may be used to reduce the likelihood and effects of nitrogen narcosis during deeper dives. Open circuit scuba systems discharge the breathing gas into the environment as it is exhaled, and consist of one or more diving cylinders containing breat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Narcosis
Narcosis while diving (also known as nitrogen narcosis, inert gas narcosis, raptures of the deep, Martini effect) is a reversible alteration in consciousness that occurs while diving at depth. It is caused by the anesthetic effect of certain gases at high pressure. The Greek word (narkōsis), "the act of making numb", is derived from (narkē), "numbness, torpor", a term used by Homer and Hippocrates. Narcosis produces a state similar to drunkenness (alcohol intoxication), or nitrous oxide inhalation. It can occur during shallow dives, but does not usually become noticeable at depths less than . Except for helium and probably neon, all gases that can be breathed have a narcotic effect, although widely varying in degree. The effect is consistently greater for gases with a higher lipid solubility, and although the mechanism of this phenomenon is still not fully clear, there is good evidence that the two properties are mechanistically related. As depth increases, the mental im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrox (breathing Gas)
Hydrox, a gas mixture of hydrogen and oxygen, was used as a breathing gas in very deep diving. It allows divers to descend several hundred metres. Precautions are necessary when using hydrox, since mixtures containing more than a few percent of both oxygen and hydrogen are explosive if ignited. Hydrogen is the lightest gas (half the weight of helium) but still has a narcotic potential and may cause hydrogen narcosis. History Although the first reported use of hydrogen seems to be Antoine Lavoisier (1743–1794) experimenting on guinea pigs, the actual first uses of this gas in diving are usually attributed to trials by the Swedish engineer, Arne Zetterström in 1945. Zetterström showed that hydrogen was perfectly usable to great depths. Following a fault in using the surface equipment, he died during a demonstration dive. The study of hydrogen was not resumed until several years later by the United States Navy and by the Compagnie maritime d'expertises (Comex), initially duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydreliox
Hydreliox is an exotic breathing gas mixture of helium, oxygen and hydrogen. For the Hydra VIII (Hydra 8) mission at 50 atmospheres of ambient pressure, the mixture used was 49% hydrogen, 50.2% helium, and 0.8% oxygen. It is used primarily for research and scientific deep diving, usually below . Below this depth, extended breathing of heliox gas mixtures may cause high pressure nervous syndrome (HPNS). Two gas mixtures exist that attempt to combat this problem: trimix and hydreliox. Like trimix, hydreliox contains helium and oxygen and a third gas to counteract HPNS. The third gas in trimix is nitrogen and the third gas in hydreliox is hydrogen. Because hydrogen is the lightest gas, it is easier to breathe than nitrogen under high pressure. To avoid the risk of explosion, as a rule of thumb hydrogen is only considered for use in breathing mixtures if the proportion of oxygen in the mixture is less than 5%. However, the pressure during the dive must be such that the partial pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliox
Heliox is a breathing gas mixture of helium (He) and oxygen (O2). It is used as a medical treatment for patients with difficulty breathing because mixture generates less resistance than atmospheric air when passing through the airways of the lungs, and thus requires less effort by a patient to breathe in and out of the lungs. It is also used as a breathing gas diluent for deep ambient pressure diving as it is not narcotic at high pressure, and for its low work of breathing. Heliox has been used medically since the 1930s, and although the medical community adopted it initially to alleviate symptoms of upper airway obstruction, its range of medical uses has since expanded greatly, mostly because of the low density of the gas. Heliox is also used in saturation diving and sometimes during the deep phase of technical dives. Medical uses In medicine heliox may refer to a mixture of 21% O2 (the same as air) and 79% He, although other combinations are available (70/30 and 60/40). Hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decompression Stop
The practice of decompression by divers comprises the planning and monitoring of the profile indicated by the algorithms or tables of the chosen decompression model, to allow asymptomatic and harmless release of excess inert gases dissolved in the tissues as a result of breathing at ambient pressures greater than surface atmospheric pressure, the equipment available and appropriate to the circumstances of the dive, and the procedures authorized for the equipment and profile to be used. There is a large range of options in all of these aspects. Decompression may be continuous or staged, where the ascent is interrupted by stops at regular depth intervals, but the entire ascent is part of the decompression, and ascent rate can be critical to harmless elimination of inert gas. What is commonly known as no-decompression diving, or more accurately no-stop decompression, relies on limiting ascent rate for avoidance of excessive bubble formation. Staged decompression may include deep st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isobaric Counterdiffusion
In physiology, isobaric counterdiffusion (ICD) is the diffusion of different gases into and out of tissues while under a constant ambient pressure, after a change of gas composition, and the physiological effects of this phenomenon. The term inert gas counterdiffusion is sometimes used as a synonym, but can also be applied to situations where the ambient pressure changes. It has relevance in mixed gas diving and anesthesiology. Background Isobaric counterdiffusion was first described by Graves, Idicula, Lambertsen, and Quinn in 1973 in subjects who breathed one gas mixture (in which the inert component was nitrogen or neon) while being surrounded by another (helium based). Clinical relevance In medicine, ICD is the diffusion of gases in different directions that can increase the pressure inside open air spaces of the body and surrounding equipment. An example of this would be a patient breathing nitrous oxide in an operating room (surrounded by air). Cuffs on the endotrachea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Operating Depth
In underwater diving activities such as saturation diving, technical diving and nitrox diving, the maximum operating depth (MOD) of a breathing gas is the depth below which the partial pressure of oxygen (pO2) of the gas mix exceeds an acceptable limit. This limit is based on risk of central nervous system oxygen toxicity, and is somewhat arbitrary, and varies depending on the diver training agency or Code of Practice, the level of underwater exertion expected and the planned duration of the dive, but is normally in the range of 1.2 to 1.6 bar. The MOD is significant when planning dives using gases such as heliox, nitrox and trimix because the proportion of oxygen in the mix determines a maximum depth for breathing that gas at an acceptable risk. There is a risk of acute oxygen toxicity if the MOD is exceeded. The tables below show MODs for a selection of oxygen mixes. Atmospheric air contains approximately 21% oxygen, and has an MOD calculated by the same method. Safe limit of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Narcosis
Narcosis while diving (also known as nitrogen narcosis, inert gas narcosis, raptures of the deep, Martini effect) is a reversible alteration in consciousness that occurs while diving at depth. It is caused by the anesthetic effect of certain gases at high pressure. The Greek word (narkōsis), "the act of making numb", is derived from (narkē), "numbness, torpor", a term used by Homer and Hippocrates. Narcosis produces a state similar to drunkenness (alcohol intoxication), or nitrous oxide inhalation. It can occur during shallow dives, but does not usually become noticeable at depths less than . Except for helium and probably neon, all gases that can be breathed have a narcotic effect, although widely varying in degree. The effect is consistently greater for gases with a higher lipid solubility, and although the mechanism of this phenomenon is still not fully clear, there is good evidence that the two properties are mechanistically related. As depth increases, the mental im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pony Bottle
A pony bottle is a small diving cylinder which is fitted with an independent diving regulator, regulator, and carried by a scuba diver as an extension to the scuba set. In an emergency, such as depletion of the scuba diver, diver's main air supply, it can be used as an alternative air source or bailout bottle to allow a normal ascent in place of a controlled emergency swimming ascent. The key attribute of a pony bottle is that it provides a totally independent and Redundancy (engineering), redundant source of breathing gas for the diver. The name ''wikt:pony, pony'' is due to the smaller size, often of only a few litres capacity. Pony bottles are used by divers who understand that no matter their preparation and planning, accidents may happen, and cannot, or do not choose to depend on another diver for emergency breathing gas. They are carried by the diver in one of several alternative configurations, and the capacity and contents should be sufficient to allow a safe ascent from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diving Cylinder
A diving cylinder or diving gas cylinder is a gas cylinder used to store and transport high pressure gas used in diving operations. This may be breathing gas used with a scuba set, in which case the cylinder may also be referred to as a scuba cylinder, scuba tank or diving tank. When used for an emergency gas supply for surface supplied diving or scuba, it may be referred to as a bailout cylinder or bailout bottle. It may also be used for surface-supplied diving or as decompression gas . A diving cylinder may also be used to supply inflation gas for a dry suit or buoyancy compensator. Cylinders provide gas to the diver through the demand valve of a diving regulator or the breathing loop of a diving rebreather. Diving cylinders are usually manufactured from aluminium or steel alloys, and when used on a scuba set are normally fitted with one of two common types of cylinder valve for filling and connection to the regulator. Other accessories such as manifolds, cylinder band ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimix (breathing Gas)
Trimix is a breathing gas consisting of oxygen, helium and nitrogen and is used in deep commercial diving, during the deep phase of dives carried out using technical diving techniques, and in advanced recreational diving. The helium is included as a substitute for some of the nitrogen, to reduce the narcotic effect of the breathing gas at depth. With a mixture of three gases it is possible to create mixes suitable for different depths or purposes by adjusting the proportions of each gas. Oxygen content can be optimised for the depth to limit the risk of toxicity, and the inert component balanced between nitrogen (which is cheap but narcotic) and helium (which is not narcotic and reduces work of breathing, but is more expensive and increases heat loss). The mixture of helium and oxygen with a 0% nitrogen content is generally known as heliox. This is frequently used as a breathing gas in deep commercial diving operations, where it is often recycled to save the expensive helium c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |