|
Archa (document Store)
An archa or arca (plural archae) was a mediaeval document repository, such as a chest, associated with the financial records of Jews in England at the time. According to Jewish Communities and Records, UK, the archa was "an official chest, provided with three locks and seals, in which a counterpart of all deeds and contracts involving Jews was to be deposited in order to preserve the records." Similarly the Jewish Encyclopedia of 1906 describes an archa as a "repository in which chirographs and other deeds were preserved." quoting C. Gross in ''Papers of the Anglo-Jewish Historical Exhibition'', pp. 182-190. Worcester, England, Worcester and Winchester were two of the 26 Jewish centres of the time to have archae. The introduction of archae in Worcester was part of the reorganization of English Jewry ordered by King Richard I in light of the History of the Jews in England (1066–1290), massacres of Jews that took place in 1189-1190 at, and shortly following, his coronation. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jews In England
The history of the Jews in England goes back to the reign of William the Conqueror. Although it is likely that there had been some Jewish presence in the Roman period, there is no definitive evidence, and no reason to suppose that there was any community during Anglo-Saxon times. The first written record of Jewish settlement in England dates from 1070. The Jewish settlement continued until King Edward I's Edict of Expulsion in 1290. After the expulsion, there was no overt Jewish community (as opposed to individuals practising Judaism secretly) until the rule of Oliver Cromwell. While Cromwell never officially readmitted Jews to the Commonwealth of England, a small colony of Sephardic Jews living in London was identified in 1656 and allowed to remain. The Jewish Naturalisation Act of 1753, an attempt to legalise the Jewish presence in England, remained in force for only a few months. Historians commonly date Jewish Emancipation to either 1829 or 1858, while Benjamin Disraeli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirograph
A chirograph is a medieval document, which has been written in duplicate, triplicate or very occasionally quadruplicate (four copies) on a single piece of parchment, with the Latin word ''chirographum'' (occasionally replaced by some other term) written across the middle, and then cut through to separate the parts. The term also refers to a papal decree whose circulation is limited to the Roman curia. Etymology The Latin word ''chirographum'', often spelled ''cirographum'' or ''cyrographum'' in the medieval period, is derived from the Greek χειρόγραφον, and simply means "handwritten". Description The intention of the chirograph was to produce two (or more) identical written copies of a legal agreement, that could be retained by each party to the transaction, and if necessary verified at a later date through comparison with one another. Whereas Charters were typically used for titles of property and did not give each party a copy, chirographs could be used for almost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worcester, England
Worcester ( ) is a cathedral city in Worcestershire, England, of which it is the county town. It is south-west of Birmingham, north-west of London, north of Gloucester and north-east of Hereford. The population was 103,872 in the 2021 Census. The River Severn flanks the western side of the city centre. It is overlooked by Worcester Cathedral. Worcester is the home of Royal Worcester, Royal Worcester Porcelain, composer Edward Elgar, Lea & Perrins, makers of traditional Worcestershire sauce, the University of Worcester, and ''Berrow's Worcester Journal'', claimed as the world's oldest newspaper. The Battle of Worcester in 1651 was the final battle of the English Civil War, during which Oliver Cromwell's New Model Army defeated Charles II of England, King Charles II's Cavalier, Royalists. History Early history The trade route past Worcester, later part of the Roman roads in Britain, Roman Ryknild Street, dates from Neolithic times. It commanded a ford crossing over the Rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs National Park, on the River Itchen, Hampshire, River Itchen. It is south-west of London and from Southampton, its nearest city. At the 2011 census, Winchester had a population of 45,184. The wider City of Winchester district, which includes towns such as New Alresford, Alresford and Bishop's Waltham, has a population of 116,595. Winchester is the county town of Hampshire and contains the head offices of Hampshire County Council. Winchester developed from the Roman Britain, Roman town of Venta Belgarum, which in turn developed from an Iron Age oppidum. Winchester was one of the most important cities in England until the Norman conquest of England, Norman conquest in the eleventh century. It has since become one of the most expensive and afflue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Richard I
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199) was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Aquitaine and Gascony, Lord of Cyprus, and Count of Poitiers, Anjou, Maine, and Nantes, and was overlord of Brittany at various times during the same period. He was the third of five sons of King Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine and seemed unlikely to become king, but all his brothers except the youngest, John, predeceased their father. Richard is known as Richard Cœur de Lion (Norman French: ''Le quor de lion'') or Richard the Lionheart because of his reputation as a great military leader and warrior. The troubadour Bertran de Born also called him Richard Oc-e-Non (Occitan for ''Yes and No''), possibly from a reputation for terseness. By the age of 16, Richard had taken command of his own army, putting down rebellions in Poitou against his father. Richard was an important Christian commander during the Third Crusade, leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Jews In England (1066–1290)
It is believed that the first Jews in England arrived during the Norman Conquest of the country by William the Conqueror (the future William I) in 1066. The first written record of Jewish settlement in England dates from 1070. They suffered massacres in 1189–90. In 1290, all Jews were expelled from England by the Edict of Expulsion. William I to Henry I: 1066–1135 There is no record of Jews in England before the Norman Conquest in 1066. The few references to Jews in the Anglo-Saxon laws of the Roman Catholic Church relate to Jewish practices about Easter. Believing that their commercial skills and incoming capital would make England more prosperous, William I (William the Conqueror) invited a group of Jewish merchants from Rouen, in Normandy, to England in 1070. However, Jews were not permitted to own land or to participate in trades (except for medicine). They were limited primarily to money lending. As Catholic doctrine held that money lending for interest was the sin of u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exchequer Of The Jews
The Exchequer of the Jews (Latin: ''Scaccarium Judaeorum'') was a division of the Exchequer of Pleas, Court of Exchequer at Westminster, which recorded and regulated the taxes and the law-cases of the History of the Jews in England, Jews in England and History of the Jews in Wales, Wales. It operated from the late 1190s until the eventual Edict of expulsion, expulsion of the Jews in 1290. Background Jews began to settle in England soon after the Norman conquest of England, Norman Conquest in 1066. For the most part they escaped the massacres during the First Crusade, First (1096–1099) and Second Crusade, Second (1145–1149) Crusades, and despite occasional imposition of fines and special levies, their numbers and prosperity increased under the protection of the king. There was a reason Jews were protected by the Crown. Surviving records of the Exchequer Pipe rolls, Pipe Roll of the reign of Henry I of England, Henry I show that the Jews of England constituted a major source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
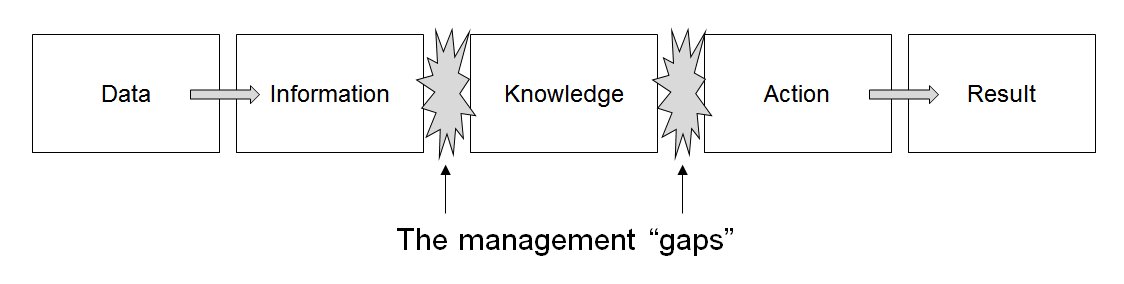
Information Management
Information management (IM) concerns a cycle of organizational activity: the acquisition of information from one or more sources, the custodianship and the distribution of that information to those who need it, and its ultimate disposal through archiving or deletion. This cycle of information organisation involves a variety of stakeholders, including those who are responsible for assuring the quality, accessibility and utility of acquired information; those who are responsible for its safe storage and disposal; and those who need it for decision making. Stakeholders might have rights to originate, change, distribute or delete information according to organisational information management policies. Information management embraces all the generic concepts of management, including the planning, organizing, structuring, processing, controlling, evaluation and reporting of information activities, all of which is needed in order to meet the needs of those with organisational r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accounting Source Documents
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the measurement, processing, and communication of financial and non financial information about economic entities such as businesses and corporations. Accounting, which has been called the "language of business", measures the results of an organization's economic activities and conveys this information to a variety of stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and regulators. Practitioners of accounting are known as accountants. The terms "accounting" and "financial reporting" are often used as synonyms. Accounting can be divided into several fields including financial accounting, management accounting, tax accounting and cost accounting. Financial accounting focuses on the reporting of an organization's financial information, including the preparation of financial statements, to the external users of the information, such as investors, regulators and suppliers; and management accounting focuses on the measurement, ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archives In England
An archive is an accumulation of historical records or materials – in any medium – or the physical facility in which they are located. Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organization's lifetime, and are kept to show the function of that person or organization. Professional archivists and historians generally understand archives to be records that have been naturally and necessarily generated as a product of regular legal, commercial, administrative, or social activities. They have been metaphorically defined as "the secretions of an organism", and are distinguished from documents that have been consciously written or created to communicate a particular message to posterity. In general, archives consist of records that have been selected for permanent or long-term preservation on grounds of their enduring cultural, historical, or evidentiary value. Archival records are normally unpublished and almost alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |