|
Arbia's Law Of Geography
Arbia's law of geography states, "Everything is related to everything else, but things observed at a coarse spatial resolution are more related than things observed at a finer resolution." Originally proposed as the 2nd law of geography, this is one of several laws competing for that title. Because of this, Arbia's law is sometimes referred to as the second law of geography, or Arbia's second law of geography. Background Since Tobler first invoked the first law of geography in his 1970s paper, there have been many attempts at a second law, including Tobler's second law of geography, and Arbia's law is one such contender. Arbia's law builds on Tobler's first law of geography which states, "Everything is related to everything else, but near things tend to be more related than distant." While Tobler's first law relates to spatial autocorrelation and distance decay, Arbia's law relates to the modifiable areal unit problem, or MAUP and scale dependence of correlation. Arbia's la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Resolution
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail. Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how close lines can be to each other and still be visibly ''resolved''. Resolution units can be tied to physical sizes (e.g. lines per mm, lines per inch), to the overall size of a picture (lines per picture height, also known simply as lines, TV lines, or TVL), or to angular subtense. Instead of single lines, line pairs are often used, composed of a dark line and an adjacent light line; for example, a resolution of 10 lines per millimeter means 5 dark lines alternating with 5 light lines, or 5 line pairs per millimeter (5 LP/mm). Photographic lens are most often quoted in line pairs per millimeter. Types The resolution of digital cameras can be described in many different ways. Pixel count The term ''resolution'' is often considered eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modifiable Temporal Unit Problem
The Modified Temporal Unit Problem (MTUP) is a source of statistical bias that occurs in time series and spatial analysis when using temporal data that has been aggregated into temporal units. In such cases, choosing a temporal unit (e.g., days, months, years) can affect the analysis results and lead to inconsistencies or errors in statistical hypothesis testing. Background The MTUP is closely related to the modifiable areal unit problem or MAUP, in that they both relate to the scale of analysis and the issue of choosing an appropriate analysis. While the MAUP refers to the choice of spatial enumeration units, the MTUP arises because different temporal units have different properties and characteristics, such as the number of periods they contain or the amount of detail they provide. For example, daily sales data for a product can be aggregated into weekly, monthly, or yearly sales data. In this case, using monthly data instead of daily data can result in losing important inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Of Analysis
Level of analysis is used in the social sciences to point to the location, size, or scale of a research target. It is distinct from unit of observation in that the former refers to a more or less integrated set of relationships while the latter refers to the distinct unit from which data have been or will be gathered. Together, the unit of observation and the level of analysis help define the population of a research enterprise. Level of analysis vs unit of analysis Level of analysis is closely related to the term unit of analysis, and some scholars have used them interchangingly, while others argue for a need for distinction. Ahmet Nuri Yurdusev wrote that "the level of analysis is more of an issue related to the framework/context of analysis and the level at which one conducts one's analysis, whereas the question of the unit of analysis is a matter of the 'actor' or the 'entity' to be studied". Manasseh Wepundi noted the difference between "the unit of analysis, that is the ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indicators Of Spatial Association
Indicators of spatial association are statistics that evaluate the existence of clusters in the spatial arrangement of a given variable. For instance, if we are studying cancer rates among census tracts in a given city local clusters in the rates mean that there are areas that have higher or lower rates than is to be expected by chance alone; that is, the values occurring are above or below those of a random distribution in space. Global indicators Notable global indicators of spatial association include: * Global Moran's ''I'': The most commonly used measure of global spatial autocorrelation or the overall clustering of the spatial data developed by Patrick Alfred Pierce Moran. * Geary's ''C'' (Geary's Contiguity Ratio): A measure of global spatial autocorrelation developed by Roy C. Geary in 1954. It is inversely related to Moran's ''I'', but more sensitive to local autocorrelation than Moran's ''I''. * Getis–Ord ''G'' (Getis–Ord global G, Geleral G-Statistic): Introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Geography
Human geography or anthropogeography is the branch of geography which studies spatial relationships between human communities, cultures, economies, and their interactions with the environment, examples of which include urban sprawl and urban redevelopment. It analyzes spatial interdependencies between social interactions and the environment through Qualitative geography, qualitative and Quantitative geography, quantitative methods. This multidisciplinary approach draws from sociology, anthropology, economics, and environmental science, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the intricate connections that shape lived spaces. History The Royal Geographical Society was founded in England in 1830. The first professor of geography in the United Kingdom was appointed in 1883, and the first major geographical intellect to emerge in the UK was Halford John Mackinder, appointed professor of geography at the London School of Economics in 1922. The National Geographic Societ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information Science
Geographic information science (GIScience, GISc) or geoinformation science is a scientific discipline at the crossroads of computational science, social science, and natural science that studies geographic information, including how it represents phenomena in the real world, how it represents the way humans understand the world, and how it can be captured, organized, and analyzed. It is a sub-field of geography, specifically part of technical geography. It has applications to both physical geography and human geography, although its techniques can be applied to many other fields of study as well as many different industries. As a field of study or profession, it can be contrasted with geographic information systems (GIS), which are the actual repositories of geospatial data, the software tools for carrying out relevant tasks, and the profession of GIS users. That said, one of the major goals of GIScience is to find practical ways to improve GIS data, software, and profess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively. The fundamental objectives of traditional cartography are to: * Set the map's agenda and select traits of the object to be mapped. This is the concern of map editing. Traits may be physical, such as roads or land masses, or may be abstract, such as toponyms or political boundaries. * Represent the terrain of the mapped object on flat media. This is the concern of map projections. * Eliminate the mapped object's characteristics that are irrelevant to the map's purpose. This is the concern of Cartographic generalization, generalization. * Reduce the complexity of the characteristics that will be mapped. This is also the concern of generalization. * Orchestrate the elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
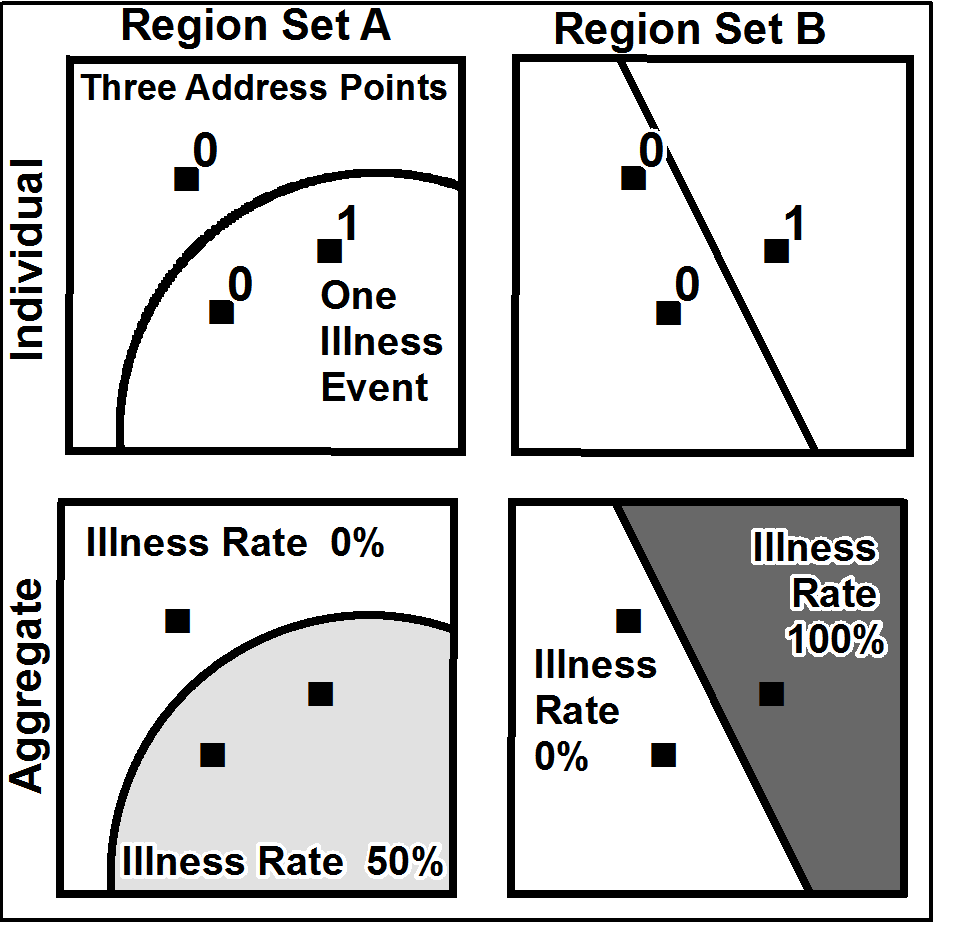
Boundary Problem
A boundary problem in analysis is a phenomenon in which geographical patterns are differentiated by the shape and arrangement of boundaries that are drawn for administrative or measurement purposes. The boundary problem occurs because of the loss of neighbors in analyses that depend on the values of the neighbors. While geographic phenomena are measured and analyzed within a specific unit, identical spatial data can appear either dispersed or clustered depending on the boundary placed around the data. In analysis with point data, dispersion is evaluated as dependent of the boundary. In analysis with areal data, statistics should be interpreted based upon the boundary. Definition In spatial analysis, four major problems interfere with an accurate estimation of the statistical parameter: the boundary problem, scale problem, pattern problem (or spatial autocorrelation), and modifiable areal unit problem. The boundary problem occurs because of the loss of neighbours in analyses that d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concepts And Techniques In Modern Geography
''Concepts and Techniques in Modern Geography'' (CATMOG), is a series of 59 short publications, each focused on an individual method or theory in geography. Background and impact ''Concepts and Techniques in Modern Geography'' were produced by the Study Group in Quantitative Methods of the Institute of British Geographers. Each CATMOG publication was written on an individual topic in geography rather than a series of broad topics like traditional textbooks and ranged between 40 and 70 pages.c This à la carte approach allowed only purchasing publications on topics of interest, keeping each CATMOG relatively cheap and accessible, lowering student costs with early copies sold for around $2.00. This also offered instructors more flexibility in designing courses. The first of these publications was published in 1975, and the last in 1996. Each was written by someone working professionally with its topic, which created some issues in consistency between publications in terms of expec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Laws
Scientific laws or laws of science are statements, based on repeated experiments or observations, that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena. The term ''law'' has diverse usage in many cases (approximate, accurate, broad, or narrow) across all fields of natural science (physics, chemistry, astronomy, geoscience, biology). Laws are developed from data and can be further developed through mathematics; in all cases they are directly or indirectly based on empirical evidence. It is generally understood that they implicitly reflect, though they do not explicitly assert, causal relationships fundamental to reality, and are discovered rather than invented. Scientific laws summarize the results of experiments or observations, usually within a certain range of application. In general, the accuracy of a law does not change when a new theory of the relevant phenomenon is worked out, but rather the scope of the law's application, since the mathematics or statement representing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerrymandering
Gerrymandering, ( , originally ) defined in the contexts of Representative democracy, representative electoral systems, is the political manipulation of Boundary delimitation, electoral district boundaries to advantage a Political party, party, group, or socioeconomic class within the constituency. The manipulation may involve "cracking" (diluting the voting power of the opposing party's supporters across many districts) or "packing" (concentrating the opposing party's voting power in one district to reduce their voting power in other districts). Gerrymandering can also be used to protect incumbents. Wayne Dawkins, a professor at Morgan State University, describes it as politicians picking their voters instead of voters picking their politicians. The term ''gerrymandering'' is a portmanteau of a salamander and Elbridge Gerry, Vice President of the United States at the time of his death, who, as governor of Massachusetts in 1812, signed a bill that created a partisan distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |