|
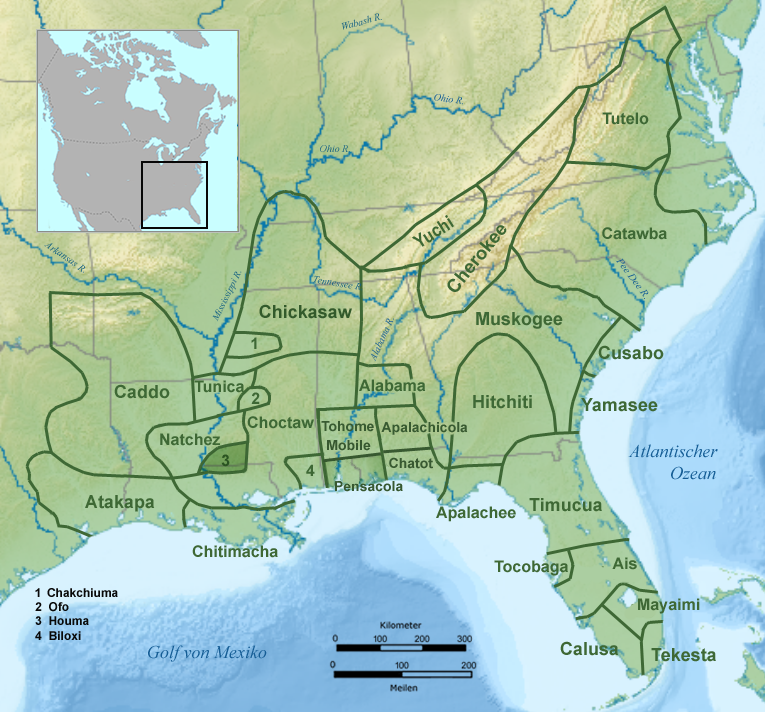
Apalachee-Alabama-Koasati Languages
Muskogean (also Muskhogean, Muskogee) is a Native American language family spoken in different areas of the Southeastern United States. Though the debate concerning their interrelationships is ongoing, the Muskogean languages are generally divided into two branches, Eastern Muskogean and Western Muskogean. Typologically, Muskogean languages are agglutinative. One documented language, Apalachee, is extinct and the remaining languages are critically endangered. Genetic relationships Family division The Muskogean family consists of six languages that are still spoken: Alabama, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek-Seminole, Koasati, and Mikasuki, as well as the now-extinct Apalachee, Houma, and Hitchiti (the last is generally considered a dialect of Mikasuki). "Seminole" is listed as one of the Muskogean languages in Hardy's list, but it is generally considered a dialect of Creek rather than a separate language, as she comments. The major subdivisions of the family have long been controve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamasee
The Yamasees (also spelled Yamassees or Yemassees) were a multiethnic confederation of Native Americans who lived in the coastal region of present-day northern coastal Georgia near the Savannah River and later in northeastern Florida. The Yamasees engaged in revolts and wars with other native groups and Europeans living in North America, specifically from Florida to North Carolina. The Yamasees, along with the Guale, are considered from linguistic evidence by many scholars to have been a Muskogean language people. For instance, the Yamasee term "Mico", meaning chief, is also common in Muskogee. After the Yamasees migrated to the Carolinas, they began participating in the Indian slave trade in the American Southeast. They raided other tribes to take captives for sale to European colonists. Captives from other Native American tribes were sold into slavery, with some being transported to West Indian plantations. Their enemies fought back, and slave trading was a large cause of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitimacha Language
Chitimacha ( or , Sitimaxa) is a language isolate historically spoken by the Chitimacha people of Louisiana, United States. It became extinct in 1940 with the death of the last fluent speaker, Delphine Ducloux. Although no longer spoken, it is fairly extensively documented in the early 20th-century work (mostly unpublished) of linguists Morris Swadesh and John R. Swanton. Swadesh in particular wrote a full grammar and dictionary, and collected numerous texts from the last two speakers, although none of this is published. Language revitalization efforts are underway to teach the language to a new generation of speakers. Tribal members have received Rosetta Stone (software), Rosetta Stone software for learning the language. As of 2015, a new Chitimacha dictionary is in preparation, and classes are being taught on the Chitimacha reservation. Classification Chitimacha has recently been proposed to be related to, or a member of, the hypothetical Totozoquean languages, Totozoquean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atakapa Language
Atakapa (,Sturtevant, 659 natively ''Yukhiti'') is an extinct language isolate native to southwestern Louisiana and nearby coastal eastern Texas. It was spoken by the Atakapa people (also known as ''Ishak'', after their word for "the people"). The language became extinct in the early 20th century. Classification While considered an isolate, there have been attempts to connect Atakapa with other languages of the Southeast. In 1919 John R. Swanton proposed a Tunican language family that would include Atakapa, Tunica, and Chitimacha; Morris Swadesh would later provide work focusing on connections between Atakapa and Chitimacha. Mary Haas later expanded the proposal by adding Natchez and the Muskogean languages, a hypothesis known as Gulf. These proposed families have not been proven. The similarities between Atakapa and Chitimacha, at least, may be attributable to periods of "intense contact etween speakers of the two languagesowing to their geographic proximity." Geographica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The number of language isolates is unknown. A language isolate is unrelated to any other, which makes it the only language in its own language family. It is a natural language with no demonstrable genealogical (or "genetic") relationships—one that has not been demonstrated to descend from an ancestor common with any other language. One explanation for the existence of language isolates is that they might be the last remaining branch of a larger language family. The language possibly had relatives in the past which have since disappeared without being documented. Another explanation for language isolates is that they developed in isolation from other languages. This explanation mostly applies to sign languages that have arisen independently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Languages
The Gulf languages are a proposed family of native North American languages composed of the Muskogean languages, along with four language isolates: Natchez, Tunica, Atakapa, and (possibly) Chitimacha. History of proposal Gulf was proposed as a language family by Mary Haas (Haas 1951, 1952), but the family has not been rigorously established by the comparative method. Historical linguists such as Lyle Campbell (Campbell and Mithun 1979, Campbell 1997) list the relationship as unproven, though a number of Muskogean scholars believe that Muskogean is at least related to Natchez (Campbell 1997:305). However, the Gulf hypothesis is considered by a number of specialists on Muskogean languages, including Mary Haas and Pamela Munro. Munro (1995) has regarded the hypothesis of a Gulf family of languages as promising; Haas thought the closest language to Muskogean would be Natchez, followed by Tunica, Atakapa, and, rather dubiously, Chitimacha.Munro, Pamela. 1995. Gulf and Yuki-Gulf. ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobilian Jargon
Mobilian Jargon (also Mobilian trade language, Mobilian Trade Jargon, Chickasaw–Choctaw trade language, Yamá) was a pidgin used as a lingua franca among Native American groups living along the Gulf of Mexico around the time of European settlement of the region. It was the main language among Indian tribes in this area, mainly Louisiana. There is evidence indicating its existence as early as the late 17th to early 18th century. The Indian groups that are said to have used it were the Alabama, Apalachee, Biloxi, Chacato, Pakana, Pascagoula, Taensa, Tunica, Caddo, Chickasaw, Houma, Choctaw, Chitimacha, Natchez, and Ofo. The name is thought to refer to the Mobile Indians of the central Gulf Coast, but did not originate from this group; Mobilian Jargon is linguistically and grammatically different from the language traditionally spoken by the Mobile Indians. Mobilian Jargon facilitated trade between tribes speaking different languages and European settlers. There is continuin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houma Tribe
The Houma () are a historic Native American people of Louisiana on the east side of the Red River of the South. Their descendants, the Houma people or organization "The United Houma Nation", have been recognized by the state as a tribe since 1972, but are not recognized by the federal government. According to the tribe, they have about 17,000 enrolled tribal citizens residing within a six-parish area that encompasses 4,750 square miles. The parishes are St. Mary, Terrebonne, Lafourche, Jefferson, Plaquemines, and St. Bernard. The city of Houma (meaning "red"), and the Red River were both named after this people. Oklahoma shares a similar etymology, as the root ''humma'' means "red" in Choctaw and related Western Muskogean languages, including Houma. Ethnobotany The Houma people take a decoction of dried '' Gamochaeta purpurea'' for colds and influenza.Speck, Frank G., 1941, "A List of Plant Curatives Obtained From the Houma Indians of Louisiana", ''Primitive Man'' 14:4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking. As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoian languages are severely or critically endangered, with only a few elderly speakers remaining. The two languages with the most speakers, Mohawk in New York and Cherokee, are spoken by less than 10% of the populations of their tribes. Family division :Northern Iroquoian ::Lake Iroquoian :::Iroquois Proper ::::Seneca (severely endangered) :::: Cayuga (severely endangered) ::::Onondaga (severely endangered) :::: Susquehannock/Conestoga (*) ::::Mohawk–Oneida ::::: Oneida (severely endangered) :::::Mohawk :::Huronian (†) :::: Huron-Wyandot (*) :::: Petun (Tobacco) (*) :::Tuscarora–Nottoway (*) ::::Tuscarora *) :::: Nottoway (*) :::Unclear :::: Wenrohronon/Wenro (*) ::::Neutral (*) ::::Erie (*) :::: Laurentian (*) :Southern Iroquoian: ::::Che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siouan
Siouan or Siouan–Catawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east. Name Authors who call the entire family ''Siouan'' distinguish the two branches as '' Western Siouan'' and '' Eastern Siouan'' or as ''Siouan-proper'' and ''Catawban''. Others restrict the name "Siouan" to the western branch and use the name ''Siouan–Catawban'' for the entire family. Generally, however, the name "Siouan" is used without distinction. Family division Siouan languages can be grouped into the Western Siouan languages and Catawban languages. The Western Siouan languages can be divided into Missouri River languages (such as Crow and Hidatsa), Mandan, Mississippi River languages (such as Dakotan, Chiwere- Winnebago, and Dhegihan languages), and Ohio Valley Siouan branches. The Catawban languages consist only of Catawban and Woccon. Proto-Siouan Previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no) , anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind" , Former = Province of South Carolina , seat = Columbia , LargestCity = Charleston , LargestMetro = Greenville (combined and metro) Columbia (urban) , BorderingStates = Georgia, North Carolina , OfficialLang = English , population_demonym = South Carolinian , Governor = , Lieutenant Governor = , Legislature = General Assembly , Upperhouse = Senate , Lowerhouse = House of Representatives , Judiciary = South Carolina Supreme Court , Senators = , Representative = 6 Republicans1 Democrat , postal_code = SC , TradAbbreviation = S.C. , area_rank = 40th , area_total_sq_mi = 32,020 , area_total_km2 = 82,932 , area_land_sq_mi = 30,109 , area_land_km2 = 77,982 , area_water_sq_mi = 1,911 , area_water_km2 = 4,949 , area_water_percent = 6 , population_rank = 23rd , population_as_of = 2022 , 2010Pop = 5282634 , population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
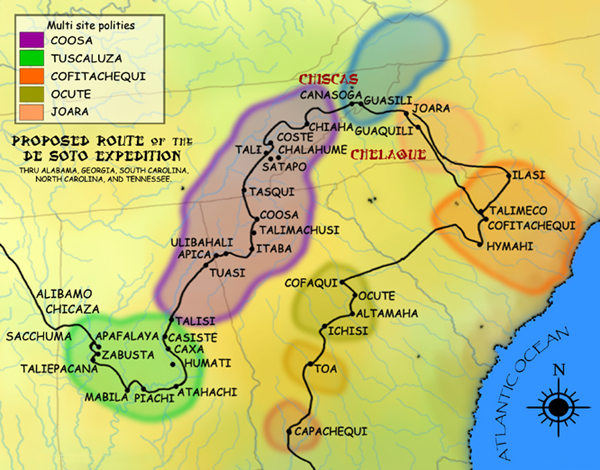
Cofitachequi
Cofitachequi was a paramount chiefdom founded about 1300 AD and encountered by the Hernando de Soto expedition in South Carolina in April 1540. Cofitachequi was later visited by Juan Pardo during his two expeditions (1566–1568) and by Henry Woodward in 1670. Cofitachequi ceased to exist as a political entity prior to 1701. The town and ceremonial center of Cofitachequi was located near the present-day city of Camden, South Carolina. Cofitachequi ruled a large number of towns in an area of several thousand square miles in the northeastern part of South Carolina. It was the easternmost manifestation of the Mississippian culture that extended over much of the southern part of the future United States. Location The hunt for the location of Cofitachequi has been stimulated by the century-old search for the route of Hernando de Soto in his 4-year traverse of much of the southeastern United States. The Spaniards described Cofitachequi as about 10 days travel eastward from Ocute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)