|
Anti-Jewish Violence In Central And Eastern Europe, 1944–1946
The anti-Jewish violence in Central and Eastern Europe following the retreat of Nazi German occupational forces and the arrival of the Soviet Red Army – during the latter stages of World War II – was linked in part to postwar anarchy and economic chaos exacerbated by the Stalinist policies imposed across the territories of expanded Soviet republics and new satellite countries. The anti-Semitic attacks had become frequent in Soviet towns ravaged by war; at the marketplaces, in depleted stores, in schools, and even at state enterprises. Protest letters were sent to Moscow from numerous Russian, Ukrainian and Belarusian towns by the Jewish Anti-Fascist Committee involved in documenting the Holocaust. History The Soviet authorities failed to address the years of Hitler's anti-Jewish propaganda, wrote Colonel David Dragunsky; anti-Semitic elements from among the former Nazi collaborators in the Soviet Union were often put in charge of state enterprises. Solomon Mikhailovich Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi German
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole '' Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, and his word became the highest law. The government was not a coordinated, coopera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rootless Cosmopolitan
"Rootless cosmopolitan" ( ) was a pejorative epithet that was mostly applied to intellectuals and Jews with ties to the West during the Stalinist era of the Soviet Union. It became especially prevalent during the country's anti-cosmopolitan campaign, which began in 1948 and continued until Stalin's death in 1953, as part of a post-1946 assault on " bourgeois Western influences" that widely targeted writers and other intellectuals, culminating in the doctors' plot against the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. In the Communist Party's discourse, rootless cosmopolitans were defined as unpatriotic Soviet citizens, chiefly Jewish intellectuals with ties to the West, who disseminated foreign influence favouring the socio-political atmosphere or aesthetics of Western Europe or the United States. The term is considered to be an antisemitic trope. Origin The expression was coined in the 19th century by Russian literary critic Vissarion Belinsky to describe writers who lacked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a mainly continental climate, and an area of with a population of 19 million people. Romania is the List of European countries by area, twelfth-largest country in Europe and the List of European Union member states by population, sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Europe's second-longest river, the Danube, empties into the Danube Delta in the southeast of the country. The Carpathian Mountains cross Romania from the north to the southwest and include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Bucharest is the country's Bucharest metropolitan area, largest urban area and Economy of Romania, financial centre. Other major urban centers, urban areas include Cluj-Napoca, Timiș ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yad Vashem
Yad Vashem (; ) is Israel's official memorial institution to the victims of Holocaust, the Holocaust known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (). It is dedicated to preserving the memory of the Jews who were murdered; echoing the stories of the survivors; honoring Jews who fought against their Nazi oppressors and gentiles who selflessly aided Jews in need; and researching the phenomenon of the Holocaust in particular and genocide in general, with the aim of avoiding such events in the future. Yad Vashem's vision, as stated on its website, is: "To lead the documentation, research, education and commemoration of the Holocaust, and to convey the chronicles of this singular Jewish and human event to every person in Israel, to the Jewish people, and to every significant and relevant audience worldwide." Established in 1953, Yad Vashem is located on the Mount of Remembrance, on the western slope of Mount Herzl, a height in western Jerusalem, Above mean sea level, above sea level and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Jewish Violence In Poland, 1944–46
Antisemitism or Jew-hatred is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who harbours it is called an antisemite. Whether antisemitism is considered a form of racism depends on the school of thought. Antisemitic tendencies may be motivated primarily by negative sentiment towards Jews as a people or negative sentiment towards Jews with regard to Judaism. In the former case, usually known as racial antisemitism, a person's hostility is driven by the belief that Jews constitute a distinct race with inherent traits or characteristics that are repulsive or inferior to the preferred traits or characteristics within that person's society. In the latter case, known as religious antisemitism, a person's hostility is driven by their religion's perception of Jews and Judaism, typically encompassing doctrines of supersession that expect or demand Jews to turn away from Judaism and submit to the religion presenting itself as Judaism's successor faith—thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Żydowski Instytut Historyczny
The Jewish Historical Institute ( or ''ŻIH''; ), also known as the Emanuel Ringelblum Jewish Historical Institute, is a public cultural and research institution in Warsaw, Poland, chiefly dealing with the history of Jews in Poland and Jewish culture. History The Jewish Historical Institute was created in 1947 as a continuation of the , founded in 1944. The Jewish Historical Institute Association is the corporate body responsible for the building and the institute's holdings. The Institute falls under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Culture and National Heritage. In 2009 it was named after Emanuel Ringelblum and became a public cultural institution. The institute is a repository of documentary materials relating to the Jewish historical presence in Poland. It is also a centre for academic research, study and the dissemination of knowledge about the history and culture of Polish Jewry. The most valuable part of the collection is the Warsaw Ghetto Archive, known as the Ringe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-communist Resistance In Poland (1944–1946)
Anti-communist resistance in Poland may refer to: * Anti-communist resistance in Poland (1944–1953), armed partisan struggle * Anti-communist resistance in Poland (1944–1989), armed partisan struggle and the non-violent, civil resistance struggle {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan T
Jan, JaN or JAN may refer to: Acronyms * Jackson, Mississippi (Amtrak station), US, Amtrak station code JAN * Jackson-Evers International Airport, Mississippi, US, IATA code * Jabhat al-Nusra (JaN), a Syrian militant group * Japanese Article Number, a barcode standard compatible with EAN * Japanese Accepted Name, a Japanese nonproprietary drug name * Job Accommodation Network, US, for people with disabilities * '' Joint Army-Navy'', US standards for electronic color codes, etc. * ''Journal of Advanced Nursing'' Personal name * Jan (name), male variant of ''John'', female shortened form of ''Janet'' and ''Janice'' * Jan (Persian name), Persian word meaning 'life', 'soul', 'dear'; also used as a name * Ran (surname), romanized from Mandarin as Jan in Wade–Giles * Ján, Slovak name Other uses * January, as an abbreviation for the first month of the year in the Gregorian calendar * Jan (cards), a term in some card games when a player loses without taking any tricks or scoring a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
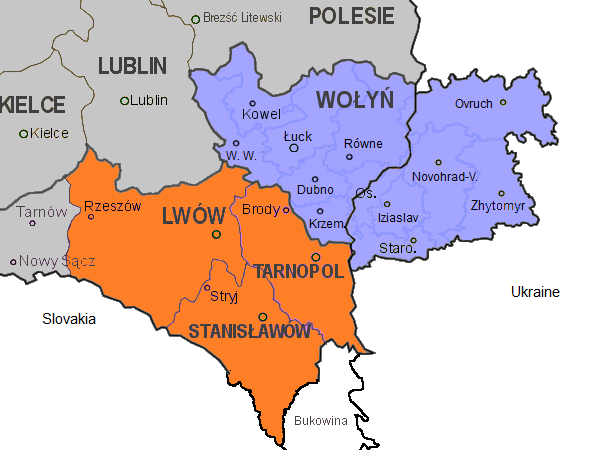
Volhynia
Volhynia or Volynia ( ; see #Names and etymology, below) is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between southeastern Poland, southwestern Belarus, and northwestern Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but in Ukraine it is roughly equivalent to Volyn Oblast, Volyn and Rivne Oblasts; the territory that still carries the name is Volyn Oblast. Volhynia has changed hands numerous times throughout history and been divided among competing powers. For centuries it was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the Russian annexation during the Partitions of Poland, all of Volhynia was made part of the Pale of Settlement on the southwestern border of the Russian Empire. Important cities include Rivne, Lutsk, Zviahel, and Volodymyr (city), Volodymyr. Names and etymology *, ; * ; *, ; * or ; *; * ; *; *; * or (both ); Volhynian German: , , or (all ); *, or . The alternative name for the region is Lodomeria after the city of Volodymyr (city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainische Hilfspolizei
The Ukrainian Auxiliary Police (; ) was the official title of the local police formation (a type of hilfspolizei) set up by Nazi Germany during World War II in Eastern Galicia and ''Reichskommissariat Ukraine'', shortly after the German occupation of the Western Ukrainian SSR in Operation Barbarossa. The Ukrainian Auxiliary Police was created by Heinrich Himmler in mid-August 1941 and put under the control of German ''Ordnungspolizei'' within General Government. The actual ''Reichskommissariat Ukraine'' was formed officially on 20 August 1941.Jürgen Matthäus, Jewish Responses to Persecution: 1941–1942.' AltaMira Press, p. 524. The uniformed force was composed in large part of the former members of the Ukrainian People's Militia created by the Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists (OUN) in June. There were two categories of German-controlled Ukrainian armed organisations. The first comprised mobile police units most often called '' Schutzmannschaft'', or ''Schuma'', organize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byelorussian Home Defence
The Belarusian Home Defence, or Belarusian Home Guard (, BKA; ) were collaborationist volunteer battalions formed by the Belarusian Central Council (1943–1944), a pro-Nazi Belarusian self-government within ''Reichskommissariat Ostland'' during World War II. The BKA operated from February 23, 1944, to April 28, 1945. The 20,000 strong Belarusian Home Defence Force was formed under the leadership of Commissioner-General Curt von Gottberg, with logistical help from the German SS-Sonderbataillon Dirlewanger, " commanded by Oskar Dirlewanger. Creation After the Wehrmacht suffered two major strategic defeats at Stalingrad (in February 1943) and at Kursk (in August 1943) the Germans made some concessions to the Belarusian collaborators by proposing a Belarusian quasi-state. Assistance was offered by the local administrative governments from the Soviet era, and former members of public organizations including the Soviet Belarusian Youth. On March 6, 1944 the general mobilization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schutzmannschaft
The ''Schutzmannschaft'', or Auxiliary Police ( "protection team"; plural: ''Schutzmannschaften'', abbreviated as ''Schuma'') was the collaborationist auxiliary police of native policemen serving in those areas of the Soviet Union and the Baltic states occupied by Nazi Germany during World War II. Heinrich Himmler, head of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS), established the ''Schutzmannschaft'' on 25 July 1941, and subordinated it to the Order Police (''Ordnungspolizei''; Orpo). By the end of 1941, some 45,000 men served in ''Schutzmannschaft'' units, about half of them in the battalions. During 1942, ''Schutzmannschaften'' expanded to an estimated 300,000 men, with battalions accounting for about a third, or less than one half of the local force. Everywhere, local police far outnumbered the equivalent German personnel several times; in most places, the ratio of Germans to natives was about 1-to-10. The auxiliary police battalions (''Schutzmannschaft-Bataillone'') were created to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |