|
Anterior Ethmoidal Foramen
The anterior ethmoidal foramen is a small opening in the ethmoid bone in the skull. Lateral to either olfactory groove are the internal openings of the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramina (or canals). The anterior ethmoidal foramen, situated about the middle of the lateral margin of the olfactory groove, transmits the anterior ethmoidal artery, vein and nerve. The anterior ethmoidal nerve, a branch of the nasociliary nerve, runs in a groove along the lateral edge of the cribriform plate In mammalian anatomy, the cribriform plate (Latin for lit. ''sieve-shaped''), horizontal lamina or lamina cribrosa is part of the ethmoid bone. It is received into the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone and roofs in the nasal cavities. It supp ... to the above-mentioned slit-like opening . References External links * () (#5) Foramina of the skull {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
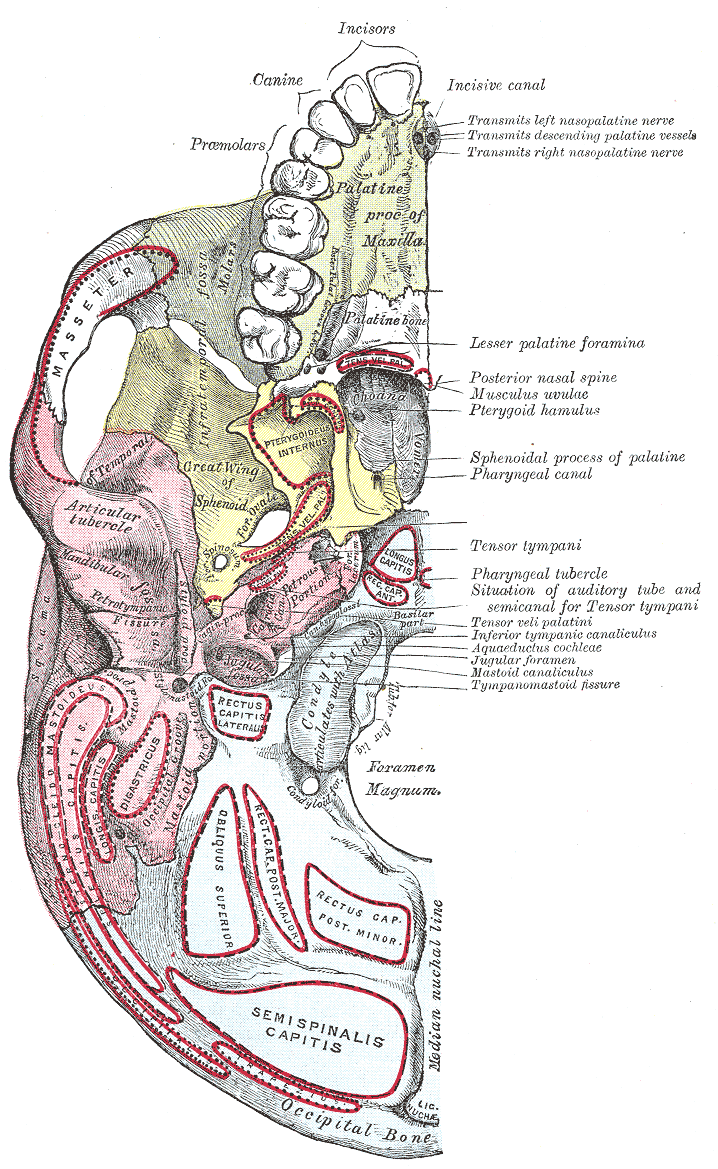
Base Of The Skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone * Sphenoid bone * Occipital bone *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses *Occipital sinus * Superior sagittal sinus *Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull * Foramen cecum *Optic foramen *Foramen lacerum *Foramen rotundum * Foramen magnum * Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen *Internal auditory meatus *Mastoid foramen *Sphenoidal emissary foramen *Foramen spinosum Sutures *Frontoethmoidal suture *Sphenofrontal suture *Sphenopetrosal suture *Sphenoethmoidal suture * Petrosquamous suture *Sphenosquamosal suture Other *Sphenoidal lingula *Subarcuate fossa *Dorsum sellae *Jugular process *Petro-occipital fissure *Condylar canal * Jugular tubercle * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Foramen
The ''optic foramen'' is the opening to the optic canal. The canal is located in the sphenoid bone; it is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid. The superior surface of the sphenoid bone is bounded behind by a ridge, which forms the anterior border of a narrow, transverse groove, the chiasmatic groove (optic groove), above and behind which lies the optic chiasma; the groove ends on either side in the optic foramen, which transmits the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery (with accompanying sympathetic nerve fibres) into the orbital cavity. Compared to the optic nerve, the ophthalmic artery is located inferolaterally within the canal. The left and right optic canals are 25mm apart posteriorly and 30mm apart anteriorly. The canals themselves are funnel-shaped (narrowest anteriorly). Additional images File:Orbital_bones.png, The seven bones which articulate to form the orbit. File:Gray145.png, Sphenoid bone. Upper surface. Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fissura Orbitalis Superior
The superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. It gives passage to multiple structures, including the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, ophthalmic nerve, abducens nerve, ophthalmic veins, and sympathetic fibres from the cavernous plexus. Structure The superior orbital fissure is usually 22 mm wide in adults, and is much larger medially. Its boundaries are formed by the (caudal surface of the) lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, and (medial border of the) greater wing of the sphenoid bone. Contents The superior orbital fissure is traversed by the following structures: * (superior and inferior divisions of the) oculomotor nerve (CN III) * trochlear nerve (CN IV) * lacrimal, frontal, and nasociliary branches of ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) * abducens nerve (CN VI) * superior ophthalmic vein and superior division of the inferior ophthalmic vein * sympathetic fibres from the cavernous nerve plexus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossa Sacci Lacrimalis
The lacrimal sac or lachrymal sac is the upper dilated end of the nasolacrimal duct, and is lodged in a deep groove formed by the lacrimal bone and frontal process of the maxilla. It connects the lacrimal canaliculi, which drain tears from the eye's surface, and the nasolacrimal duct, which conveys this fluid into the nasal cavity. Lacrimal sac occlusion leads to dacryocystitis. Structure It is oval in form and measures from 12 to 15 mm. in length; its upper end is closed and rounded; its lower is continued into the nasolacrimal duct. Its superficial surface is covered by a fibrous expansion derived from the medial palpebral ligament, and its deep surface is crossed by the lacrimal part of the orbicularis oculi, which is attached to the crest on the lacrimal bone. Histology Like the nasolacrimal duct, the sac is lined by stratified columnar epithelium with mucus-secreting goblet cells, with surrounding connective tissue. The Lacrimal Sac also drains the eye of debris and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraorbital Groove
The infraorbital groove (or sulcus) is located in the middle of the posterior part of the orbital surface of the maxilla. Its function is to act as the passage of the infraorbital artery, the infraorbital vein, and the infraorbital nerve. Structure The infraorbital groove begins at the middle of the posterior border of the maxilla (with which it is continuous). This is near the upper edge of the infratemporal surface of the maxilla. It passes forward, and ends in a canal which subdivides into two branches. The infraorbital groove has an average length of 16.7 mm, with a small amount of variation between people. It is similar in men and women. Function The infraorbital groove creates space that allows for passage of the infraorbital artery, the infraorbital vein, and the infraorbital nerve. Clinical significance The infraorbital groove is an important surgical landmark for local anaesthesia of the infraorbital nerve. See also * Infraorbital foramen In human anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Orbital Fissure
The inferior orbital fissure is formed by the sphenoid bone and the maxilla. It is located posteriorly along the boundary of the floor and lateral wall of the orbit. It transmits a number of structures, including: * the zygomatic branch of the maxillary nerve * the ascending branches from the pterygopalatine ganglion * the infraorbital vessels, which travel down the infraorbital groove into the infraorbital canal and exit through the infraorbital foramen * the inferior division of the ophthalmic vein Images File:Gray189.png, Left infratemporal fossa. File:Gray191.png, Horizontal section of nasal and orbital cavities. File:Gray787.png, Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure. File:Slide2rome.JPG, Inferior orbital fissure. See also *Foramina of skull *Superior orbital fissure The superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. It gives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraorbital Foramen
In human anatomy, the infraorbital foramen is one of two small holes in the skull's upper jawbone (maxillary bone), located below the eye socket and to the left and right of the nose. Both holes are used for blood vessels and nerves. In anatomical terms, it is located below the infraorbital margin of the orbit. It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve. It is typically from the infraorbital margin. Structure Forming the exterior end of the infraorbital canal, the infraorbital foramen communicates with the infraorbital groove, the canal's opening on the interior side. The ramifications of the three principal branches of the trigeminal nerve—at the supraorbital, infraorbital, and mental foramen—are distributed on a vertical line (in anterior view) passing through the middle of the pupil. The infraorbital foramen is used as a pressure point to test the sensitivity of the infraorbital nerve. Palpation of the inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoid Bone
The ethmoid bone (; from grc, ἡθμός, hēthmós, sieve) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that make up the orbit of the eye. Structure The ethmoid bone is an anterior cranial bone located between the eyes. It contributes to the medial wall of the orbit, the nasal cavity, and the nasal septum. The ethmoid has three parts: cribriform plate, ethmoidal labyrinth, and perpendicular plate. The cribriform plate forms the roof of the nasal cavity and also contributes to formation of the anterior cranial fossa, the ethmoidal labyrinth consists of a large mass on either side of the perpendicular plate, and the perpendicular plate forms the superior two-thirds of the nasal septum. Between the orbital plate and the nasal conchae are the ethmoidal sinuses or ethmoidal air cells, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory Groove
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste. In humans, it occurs when an odor binds to a receptor within the nasal cavity, transmitting a signal through the olfactory system. Glomeruli aggregate signals from these receptors and transmit them to the olfactory bulb, where the sensory input will start to interact with parts of the brain responsible for smell identification, memory, and emotion. There are many different causes for alteration, lack, or disturbance to a normal sense of smell, and can include damage to the nose or smell receptors, or central problems affecting the brain. Some causes include upper respiratory infections, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative disease. History of study Early scientific study of the sense of smell includes the extensive doctoral dissertation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Ethmoidal Foramina
Lateral to either olfactory groove are the internal openings of the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramina (or canals). The posterior ethmoidal foramen opens at the back part of this margin under cover of the projecting lamina of the sphenoid, and transmits the posterior ethmoidal vessels and nerve A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e .... External links * () (#4) Foramina of the skull {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Ethmoidal Artery
The anterior ethmoidal artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery in the orbit. It exits the orbit through the anterior ethmoidal foramen. The posterior ethmoidal artery is posterior to it. Structure The anterior ethmoidal artery branches from the ophthalmic artery distal to the posterior ethmoidal artery. It travels with the anterior ethmoidal nerve to exit the medial wall of the orbit at the anterior ethmoidal foramen. It then travels through the anterior ethmoidal canal and gives branches which supply the frontal sinus and anterior and middle ethmoid air cells. Following which, it enters the anterior cranial fossa where it bifurcates into a meningeal branch and nasal branch. The nasal branch travels through cribriform plate to enter the nasal cavity and runs in a groove on the deep surface of the nasal bone. Here it bifurcates into a medial and lateral branch. The lateral branch supplies blood to the lateral wall of the nasal cavity and the medial branch to the nasal septum. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |