|
Andaquí People
The Andaquí are an Indigenous people of Colombia, who live in the Upper Caquetá River Basin, the Fragua Valley of Cauca Department, and the Suaza Valley of southwest Huila Department. Name The Andaquí, sometimes written ''Andakí'', are also known as the Aguanunga or Churuba. History The Andakí are first mentioned in the texts of the Spanish conquistadors in the late 16th century, several decades after the uprisings against the Spanish initiated under the leadership of La Cacica Gaitana in 1536, that united the Yalcon, Nasa, Timaná and other Indigenous nations from the Upper Magdalena Valley. In 1637, conquistador Francisco Dias was attacked by the Andakí and Pijao, which was reported in an act of the cabildo of Timaná on January 28 of that year. The Andakí resistance to colonization lasted until the 18th century and a 1721 uprising included all of the Indigenous nations, such as the Andakí, Tama and Mocoa, of Putumayo and Caquetá. Language The Andakí lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andoque People
Andoque (or Andoke) are an Indigenous people in Colombia. They live along the Aduche tributary of the Japurá River. The people refer to themselves as ''Pʌʌsiʌʌ́ hʌ'', meaning ‘People of the Axe’. Language and culture The Andoque language is a language isolate and is extinct in Peru. The culture values "sacred plants" and a ritual called "Yuruparí." The "Yuruparí" ritual concerns their transcendent vision of cosmology. The Yuruparí ritual makes men initiates "die" then be "reborn" as members of the tribe. Religion and oral history The various bee species originated from the nasal bone of Heron-of-the-Center when he was consumed by fire while wearing a jaguar-skin. Tapirs of various colors originated from "the star people, who are bees and wasps", when they ate the body of a honey-drinking old man, who "fell into a trap" which had been dug by his own son.Jara 1995, p. 157 Notes References Fabio Jara : "Bees and Wasps : Ethno-Entomological Notions and Myths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel María Abis
Manuel may refer to: People * Manuel (name), a given name and surname * Manuel (''Fawlty Towers''), a fictional character from the sitcom ''Fawlty Towers'' * Manuel I Komnenos, emperor of the Byzantine Empire * Manuel I of Portugal, king of Portugal * Manuel I of Trebizond, Emperor of Trebizond Places *Manuel, Valencia, a municipality in the province of Valencia, Spain *Manuel Junction, railway station near Falkirk, Scotland Other * Manuel (American horse), a thoroughbred racehorse * Manuel (Australian horse), a thoroughbred racehorse * Manuel and The Music of The Mountains, a musical ensemble * ''Manuel'' (album), music album by Dalida, 1974 See also *Manny (other), a common nickname for those named Manuel *Manoel (other) *Immanuel (other) *Emmanuel (other) *Emanuel (other) *Emmanuelle (other) *Manuela (other) Manuela may refer to: People * Manuela (given name), a Spanish and Portuguese feminine given na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Friede
Juan Friede Alter (Wlava, Russian Empire, 17 February 1901 - Bogotá, Colombia, 28 June 1990) was a Ukrainian-Colombian historian of Jewish descent who is recognised as one of the most important writers about Colombian history, the Spanish conquest of the Muisca, Spanish conquests and a proponent of indigenism; the defense of the rights and descriptions of the oppression of indigenous peoples of Colombia, indigenous people. Juan Friede went to Colombia in 1926 for business and his fascination for the country, its climate and culture made him emigrate. He became a Colombian citizen in 1930. During the 1940s, Friede made extensive studies about various indigenous peoples in the country. He was a professor at the newly founded Department of Social Sciences of the National University of Colombia and is considered one of the pioneers of the "New History" movement in Colombia, together with Jaime Jaramillo Uribe, Luis Eduardo Nieto Arteta and Luis Ospina Vásquez. His former house in S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofán Language
Cofán or Kofán, known in the language itself as ''Aingae'', is the primary language of the Cofán people, an indigenous group whose ancestral territory lies at the interface between the Andean foothills and Amazonia in the northeast of Ecuador ( Sucumbíos province) and southern Colombia ( Putumayo & Nariño provinces), who call themselves the ''Ai''. Although still robustly learned by children in Ecuadorian communities, Cofán is considered an 'endangered' language with estimates of around 1,500 native speakers. Classification While past classifications have identified Cofán as belonging to linguistic families such as Chibchan or Andean B, it is now widely agreed to be a language isolate, with no known genetic relatives. History and current status Aingae is a language isolate of Amazonia spoken by the Cofán people in Sucumbios Province in northeastern Ecuador and the departments of Putumayo and Nariño in southern Colombia. The language has approximately 1500 spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
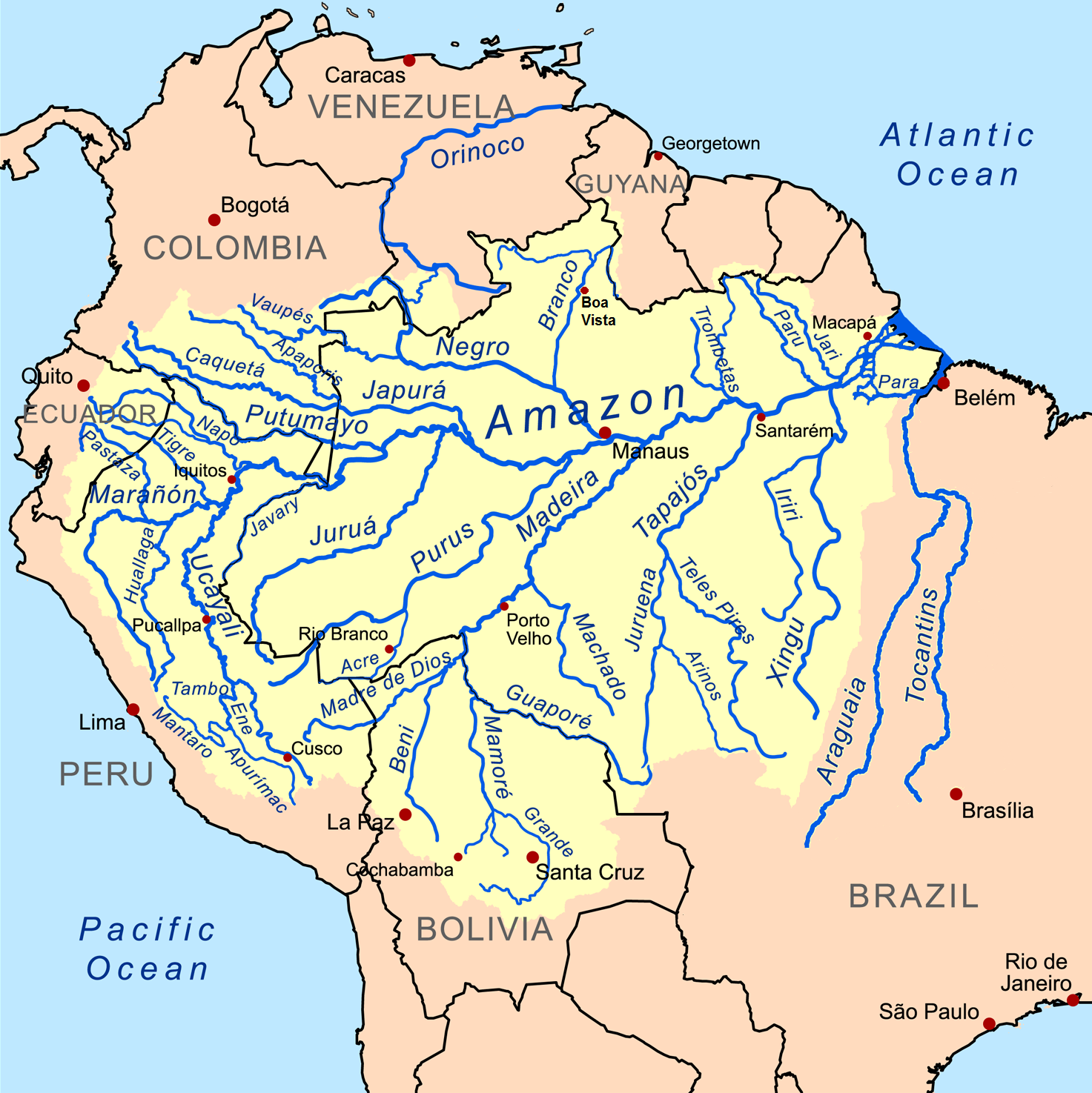
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributary, tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazon rainforest, Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, it is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes, Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurímac River, Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the Drainage divide, watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . The Amazon River Basin occupies the entire central and eastern area of South America, lying to the east of the Andes mountain range and extending from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Páez Language
Páez (also Paez, Paes; or the autonym Nasa Yuwe 'Nasa language') is a language of Colombia, spoken by the Páez people. Crevels (2011) estimates 60,000 speakers out of an ethnic population of 140,000. The language is spoken by the second largest Colombian indigenous community, the Páez, in the north of the Cauca Department, in southwestern Colombia. However, the people had to move to other departments of Colombia like Huila, Tolima and Valle del Cauca. Classification Páez is generally considered to be a language isolate, or at least the only surviving member of its family (Adelaar & Muysken 2004). Language contact Jolkesky (2016) notes that there are lexical similarities with the Chibcha, Barbakoa, Choko, Tukano, Andaki, and Kofan language families due to contact. Varieties Below is a full list of Paezan language varieties listed by Loukotka (1968), including names of unattested varieties. *Paez / Paisa – the language spoken in the villages of the Paez River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Isolate
A language isolate is a language that has no demonstrable genetic relationship with any other languages. Basque in Europe, Ainu and Burushaski in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, Haida and Zuni in North America, Kanoê in South America, and Tiwi in Oceania are all examples of such languages. The exact number of language isolates is yet unknown due to insufficient data on several languages. One explanation for the existence of language isolates is that they might be the last remaining member of a larger language family. Such languages might have had relatives in the past that have since disappeared without being documented, leaving them an orphaned language. One example is the Ket language spoken in central Siberia, which belongs to the wider Yeniseian language family; had it been discovered in recent times independently from its now extinct relatives, such as Yugh and Kott, it would have been classified as an isolate. Another explanation for language isolates is that they aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chibcha Language
Chibcha, Mosca, Muisca, Muysca (*/ˈmɨska/ * �mʷɨska, or Muysca de Bogotá is a language spoken by the Muisca people, one of the many indigenous cultures of the Americas. The Muisca inhabit the Altiplano Cundiboyacense of what today is the country of Colombia. The name of the language ''Muysc cubun'' in its own language means "language of the people", from ''muysca'' ("people") and ''cubun'' ("language" or "word"). Despite the disappearance of the language in the 17th century (approximately), several language revitalization processes are underway within the current Muisca communities. The Muisca people remain ethnically distinct and their communities are recognized by the Colombian state. Important scholars who have contributed to the knowledge of the Muisca language include Juan de Castellanos, Bernardo de Lugo, José Domingo Duquesne and Ezequiel Uricoechea. Classification The Muysca language is part of the Chibcha linguistic family, which in turn belongs to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andakí Language
Andaqui (or Andaki) is an extinct language from the southern highlands of Colombia. It has been linked to the Paezan or Barbacoan languages, but no connections have been demonstrated. It was spoken by the Andaqui people of Colombia. Language contact Jolkesky (2016) notes that there are lexical similarities with Paez, Chibcha (also proposed by Rivet 1924Rivet, Paul. 1924. La langue Andakí. ''Journal de la Société des Américanistes'', 16:99-110.), and Tinigua-Pamigua due to contact. Varieties Other unattested varieties possibly related to Andaqui that are listed by Loukotka (1968): *Timaná – once spoken on the Magdalena River and Guarapas River around the city of Timaná. * Yalcon / Cambi – once spoken between the Magdalena River and La Plata River. Vocabulary Loukotka (1968) lists the following basic vocabulary items. : See also *Macro-Paesan languages Macro-Paesan (also spelled Macro-Paezan) is a proposal linking several small families and language isolate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |