|
Amsterdam Criteria
The Amsterdam criteria are a set of diagnostic criteria used by doctors to help identify families which are likely to have Lynch syndrome, also known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). The Amsterdam criteria arose as a result of a meeting of the International Collaborative Group on Hereditary Non-Polyposis Colon Cancer in Amsterdam, in 1990. Following this, some of the genetic mechanisms underlying Lynch syndrome were elucidated during the 1990s and the significance of tumours outside the colon, such as those of the endometrium, small intestine and ureter, became clearer. These changes in the knowledge of the syndrome lead to a revision of the Amsterdam criteria and were published in Gastroenterology journal in 1999. Criteria The initial Amsterdam criteria were a series of clinical criteria that were colloquially known as the ''3-2-1'' rule. They were formulated to serve as a common starting point for future research into the genetics underlying the disease. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynch Syndrome
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) or Lynch syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic condition that is associated with a high risk of colon cancer as well as other cancers including endometrial cancer (second most common), ovary, stomach, small intestine, hepatobiliary tract, upper urinary tract, brain, and skin. The increased risk for these cancers is due to inherited mutations that impair DNA mismatch repair. It is a type of cancer syndrome. Because patients with Lynch syndrome can have polyps, the term HNPCC has fallen out of favor. Signs and symptoms Risk of cancer ''Lifetime risk and mean age at diagnosis for Lynch syndrome associated cancers'' In addition to the types of cancer found in the chart above, it is understood that Lynch syndrome also contributes to an increased risk of small bowel cancer, pancreatic cancer, ureter/renal pelvis cancer, biliary tract cancer, brain cancer, and sebaceous neoplasms. Increased risk of prostate cancer and breast cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colon (anatomy)
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being removed by defecation. The colon is the longest portion of the large intestine, and the terms are often used interchangeably but most sources define the large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. Some other sources exclude the anal canal. In humans, the large intestine begins in the right iliac region of the pelvis, just at or below the waist, where it is joined to the end of the small intestine at the cecum, via the ileocecal valve. It then continues as the colon ascending the abdomen, across the width of the abdominal cavity as the transverse colon, and then descending to the rectum and its endpoint at the anal canal. Overall, in humans, the large intestine is about long, which is about one-fifth o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum, the shortest, is where preparation for absorption through small finger-like protrusions called villi begins. The jejunum is specialized for the absorption through its lining by enterocytes: small nutrient particles which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ureter
The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In a human adult, the ureters are usually long and around in diameter. The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional epithelium, and has an additional smooth muscle layer that assists with peristalsis in its lowest third. The ureters can be affected by a number of diseases, including urinary tract infections and kidney stone. is when a ureter is narrowed, due to for example chronic inflammation. Congenital abnormalities that affect the ureters can include the development of two ureters on the same side or abnormally placed ureters. Additionally, reflux of urine from the bladder back up the ureters is a condition commonly seen in children. The ureters have been identified for at least two thousand years, with the word "ureter" stemming from the stem relating to urinating and seen in written records since at least the time of Hippocrates. It is, however, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenterology (journal)
''Gastroenterology'' is the official medical journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. Its first issue was published in 1943. It is currently published by Elsevier. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 22.682, ranking it 4th among 92 journals in the category "Gasteroenterology & Hepatology". References External links * Elsevier academic journals Publications established in 1943 Gastroenterology and hepatology journals English-language journals Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies Journals published between 13 and 25 times per year {{med-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant inherited condition in which numerous Adenomatous polyps, adenomatous Colorectal polyp, polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the colon (anatomy), large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colorectal cancer, colon cancer occurs when they are left untreated. Three variants are known to exist, FAP and attenuated FAP (originally called hereditary flat adenoma syndrome) are caused by APC gene defects on chromosome 5 while autosomal recessive FAP (or MUTYH-associated polyposis) is caused by defects in the ''MUTYH'' gene on chromosome 1. Of the three, FAP itself is the most severe and most common; although for all three, the resulting colonic polyps and cancers are initially confined to the colon wall. Detection and removal before metastasis outside the colon can greatly reduce and in many cases eliminate the spread of cancer. The root cause of FAP is understood to be a genetic mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, and fatigue. Most colorectal cancers are due to old age and lifestyle factors, with only a small number of cases due to underlying genetic disorders. Risk factors include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity. Dietary factors that increase the risk include red meat, processed meat, and alcohol. Another risk factor is inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Some of the inherited genetic disorders that can cause colorectal cancer include familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer; however, these represent less than 5% of cases. It typically starts as a benign tumor, often in the form of a polyp, which over time becomes cancerous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant inherited condition in which numerous Adenomatous polyps, adenomatous Colorectal polyp, polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the colon (anatomy), large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colorectal cancer, colon cancer occurs when they are left untreated. Three variants are known to exist, FAP and attenuated FAP (originally called hereditary flat adenoma syndrome) are caused by APC gene defects on chromosome 5 while autosomal recessive FAP (or MUTYH-associated polyposis) is caused by defects in the ''MUTYH'' gene on chromosome 1. Of the three, FAP itself is the most severe and most common; although for all three, the resulting colonic polyps and cancers are initially confined to the colon wall. Detection and removal before metastasis outside the colon can greatly reduce and in many cases eliminate the spread of cancer. The root cause of FAP is understood to be a genetic mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Cancer Institute
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) coordinates the United States National Cancer Program and is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which is one of eleven agencies that are part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. The NCI conducts and supports research, training, health information dissemination, and other activities related to the causes, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer; the supportive care of cancer patients and their families; and cancer survivorship. NCI is the oldest and has the largest budget and research program of the 27 institutes and centers of the NIH ($6.9 billion in 2020). It fulfills the majority of its mission via an extramural program that provides grants for cancer research. Additionally, the National Cancer Institute has intramural research programs in Bethesda, Maryland, and at the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research at Fort Detrick in Frederick, Maryland. The NCI receives more than in funding each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsatellite Instability
Microsatellite instability (MSI) is the condition of genetic hypermutability (predisposition to mutation) that results from impaired DNA mismatch repair (MMR). The presence of MSI represents phenotypic evidence that MMR is not functioning normally. MMR corrects errors that spontaneously occur during DNA replication, such as single base mismatches or short insertions and deletions. The proteins involved in MMR correct polymerase errors by forming a complex that binds to the mismatched section of DNA, excises the error, and inserts the correct sequence in its place. Cells with abnormally functioning MMR are unable to correct errors that occur during DNA replication and consequently accumulate errors. This causes the creation of novel microsatellite fragments. Polymerase chain reaction-based assays can reveal these novel microsatellites and provide evidence for the presence of MSI. Microsatellites are repeated sequences of DNA. These sequences can be made of units of 1 to 6 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
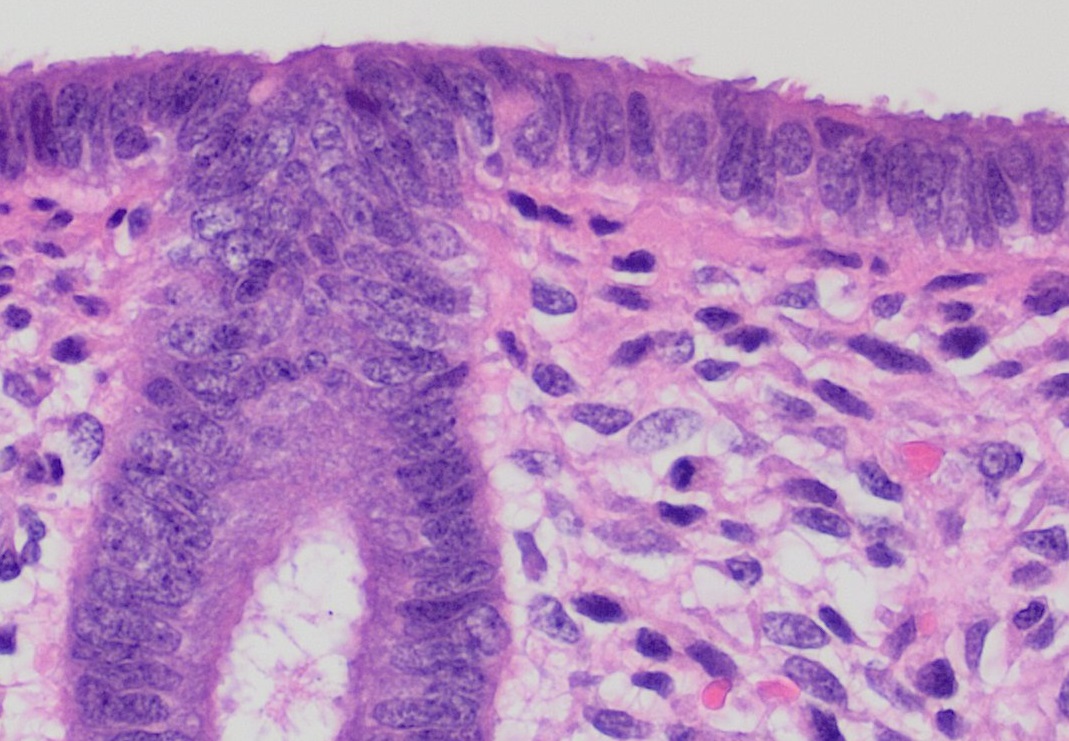
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |