|
Amplitude-shift Keying
Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave. In an ASK system, a Symbol rate, symbol, representing one or more bits, is sent by transmitting a fixed-amplitude carrier wave at a fixed frequency for a specific time duration. For example, if each symbol represents a single bit, then the carrier signal could be transmitted at nominal amplitude when the input value is 1, but transmitted at reduced amplitude or not at all when the input value is 0. Method Any digital modulation scheme uses a wikt:finite, finite number of distinct signals to represent digital data. ASK uses a finite number of amplitudes, each assigned a unique pattern of bit, binary digits. Usually, each amplitude encodes an equal number of bits. Each pattern of bits forms the Symbol (data), symbol that is represented by the particular amplitude. The demodulator, which is designed specifically for the symbol-set used by the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its Phase (waves), phase, as in phase modulation. AM was the earliest modulation method used for transmitting audio in radio broadcasting. It was developed during the first quarter of the 20th century beginning with Roberto Landell de Moura and Reginald Fessenden's radiotelephone experiments in 1900. This original form of AM is sometimes called double-sideband amplitude modulation (DSBAM), because the standard method produces sidebands on either side of the carrier frequency. Single-sideband modulation uses bandpass filters to eliminate one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSTN
The public switched telephone network (PSTN) is the aggregate of the world's telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators. It provides infrastructure and services for public telephony. The PSTN consists of telephone lines, fiber-optic cables, microwave transmission links, cellular networks, communications satellites, and undersea telephone cables interconnected by switching centers, such as central offices, network tandems, and international gateways, which allow telephone users to communicate with each other. Originally a network of fixed-line analog telephone systems, the PSTN is now predominantly digital in its core network and includes terrestrial cellular, satellite, and landline systems. These interconnected networks enable global communication, allowing calls to be made to and from nearly any telephone worldwide. Many of these networks are progressively transitioning to Internet Protocol to carry their telephony tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
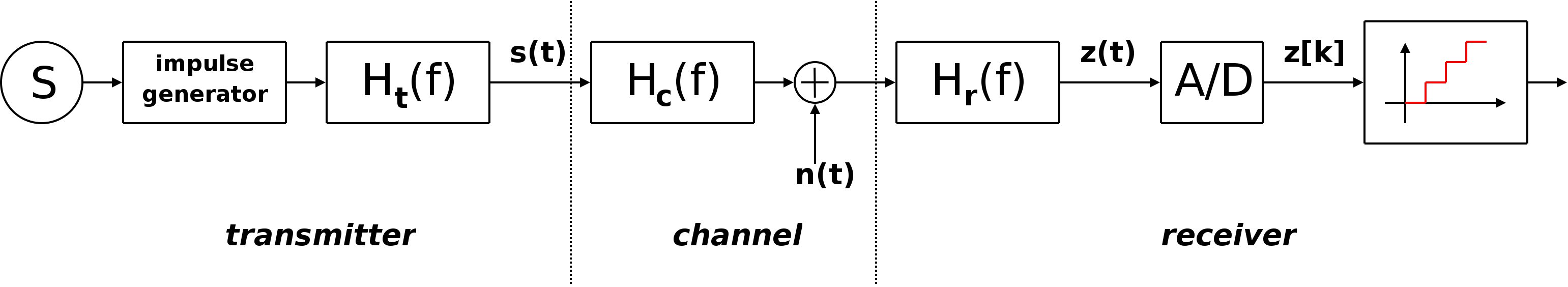
Quantized Radio Modulation Modes
Quantization is the process of constraining an input from a continuous or otherwise large set of values (such as the real numbers) to a discrete set (such as the integers). The term ''quantization'' may refer to: Signal processing * Quantization (signal processing), in mathematics and digital signal processing ** Quantization (image processing) *** Color quantization ** Vector quantization ** Quantization (music) Physics * Quantization (physics) ** Canonical quantization ** Geometric quantization * Discrete spectrum, or otherwise discrete quantity ** Spatial quantization ** Charge quantization Linguistics * Quantization (linguistics) Similar terms * Quantification (science) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency-shift Keying
Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is encoded on a carrier signal by periodically shifting the frequency of the carrier between several discrete frequencies. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands. The simplest FSK is binary FSK (BFSK, which is also commonly referred to as 2FSK or 2-FSK), in which the carrier is shifted between two discrete frequencies to transmit binary (0s and 1s) information. Modulating and demodulating Reference implementations of FSK modems exist and are documented in detail. The demodulation of a binary FSK signal can be done using the Goertzel algorithm very efficiently, even on low-power microcontrollers. Variations Multiple frequency-shift keying Continuous-phase frequency-shift keying In principle FSK can be implemented by usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyquist ISI Criterion
In communications, the Nyquist ISI criterion describes the conditions which, when satisfied by a communication channel (including responses of transmit and receive filters), result in no intersymbol interference or ISI. It provides a method for constructing band-limited functions to overcome the effects of intersymbol interference. When consecutive symbols are transmitted over a channel by a linear modulation (such as ASK, QAM, etc.), the impulse response (or equivalently the frequency response) of the channel causes a transmitted symbol to be spread in the time domain. This causes intersymbol interference because the previously transmitted symbols affect the currently received symbol, thus reducing tolerance for noise. The Nyquist theorem relates this time-domain condition to an equivalent frequency-domain condition. The Nyquist criterion is closely related to the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, with only a differing point of view. Nyquist criterion If we denote t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ask Dia Calc Prob 2
Ask is the active verb for a direct question. Ask may also refer to: Places * Ask, Akershus, a village in Gjerdrum municipality, Akershus county, Norway * Ask, Buskerud, a village in Ringerike municipality, Buskerud county, Norway * Ask, Vestland, a village in Askøy municipality, Vestland county, Norway * Ask, Iran, a village in Mazandaran Province People * Ask la Cour, Danish ballet dancer * Beatrice Ask (born 1956), Swedish politician * Morten Ask (born 1980), Norwegian ice hockey player Other * Ask (horse), a British Thoroughbred race horse * "Ask" (song), a 1986 song by The Smiths * Ask and Embla, in Norse mythology * Ask price, in economics * Ask.com, a web search engine, formerly Ask Jeeves * Ask.fm, a social Q&A web site * "Ask", a song by Avail from '' Over the James'' See also *ASK (other) Ask is the active verb for a direct question. Ask may also refer to: Places * Ask, Akershus, a village in Gjerdrum municipality, Akershus county, Norway * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On-off Keying
On-off or Onoff may refer to: * On-off control, a type of feedback controller * On-off keying, a type of line modulation * On-off relationship, a form of personal relationship * On-Off Singles, a type of tennis game * On-off switch, a type of electric switch * Onoff (retailer), an electronics retailer in Estonia, formerly also active in Sweden and Finland Music * Onoff (Irish band), an Irish punk-rock band * On/Off (Japanese band), a Japanese j-pop band * ''On/Off'' (ONF EP), 2017 * ''On/Off'' (Run On EP), 1995 * ''On-Off'' (album), a 2006 album by Marcin Rozynek See also * On and Off (other) * " Off & On", a song by Sophie Ellis-Bextor * "Off/On", a 2022 song by Collar * '' OffOn'', a film by Scott Bartlett {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its Phase (waves), phase, as in phase modulation. AM was the earliest modulation method used for transmitting audio in radio broadcasting. It was developed during the first quarter of the 20th century beginning with Roberto Landell de Moura and Reginald Fessenden's radiotelephone experiments in 1900. This original form of AM is sometimes called double-sideband amplitude modulation (DSBAM), because the standard method produces sidebands on either side of the carrier frequency. Single-sideband modulation uses bandpass filters to eliminate one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Data
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is information represented as a string of Discrete mathematics, discrete symbols, each of which can take on one of only a finite number of values from some alphabet (formal languages), alphabet, such as letters or digits. An example is a text document, which consists of a string of alphanumeric characters. The most common form of digital data in modern information systems is ''binary data'', which is represented by a string of binary digits (bits) each of which can have one of two values, either 0 or 1. Digital data can be contrasted with ''analog data'', which is represented by a value from a continuous variable, continuous range of real numbers. Analog data is transmitted by an analog signal, which not only takes on continuous values but can vary continuously with time, a continuous real-valued function of time. An example is the air pressure variation in a sound wave. The word ''digital'' comes from the same sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase (waves)
In physics and mathematics, the phase (symbol φ or ϕ) of a wave or other periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is expressed in such a scale that it varies by one full turn as the variable t goes through each period (and F(t) goes through each complete cycle). It may be measured in any angular unit such as degrees or radians, thus increasing by 360° or 2\pi as the variable t completes a full period. This convention is especially appropriate for a sinusoidal function, since its value at any argument t then can be expressed as \varphi(t), the sine of the phase, multiplied by some factor (the amplitude of the sinusoid). (The cosine may be used instead of sine, depending on where one considers each period to start.) Usually, whole turns are ignored when expressing the phase; so that \varphi(t) is also a periodic function, with the same period as F, that repeatedly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |