|
Amphipyra Berbera
Svensson's copper underwing (''Amphipyra berbera'') is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Charles E. Rungs in 1949. It is distributed throughout Europe including Russia east to the Urals. This species has a wingspan of 47–56 mm, the female usually larger than the male. The forewings are brown, marked with pale fascia and a dark-centred pale stigma. The hindwings are bright copper-coloured. This species is very similar to the copper underwing (''Amphipyra pyramidea'') but can usually be distinguished by the pattern on the underside of the hindwings: ''A. pyramidea'' has a pale central area, contrasting strongly with darker margins; ''A berbera'' is much more uniformly coloured. See Townsend et al. ''A. berbera'' flies at night from July to September and is attracted to light and strongly to sugar. The larva feeds on a range of trees and shrubs (see list below). The species overwinters as an egg. # ''The flight season refers to the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles E
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Some Germanic languages, for example Dutch and German, have retained the word in two separate senses. In the particular case of Dutch, ''Karel'' refers to the given name, whereas the noun ''kerel'' means "a bloke, fellow, man". Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (< Old English ''ċeorl''), which developed its depr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
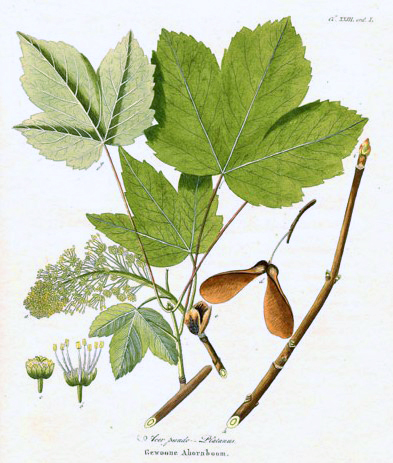
Sycamore Maple
''Acer pseudoplatanus'', known as the sycamore in the British Isles and as the sycamore maple in the United States, is a species of flowering plant in the soapberry and lychee family Sapindaceae. It is a large deciduous, broad-leaved tree, tolerant of wind and coastal exposure. It is native to Central Europe and Western Asia, from France eastward to Ukraine, northern Turkey and the Caucasus and southward in the mountains of Italy and northern Iberia. The sycamore establishes itself easily from seed and was introduced to the British Isles by 1500. It is now naturalised there and in other parts of Europe, North America, Australia and New Zealand, where it may become an invasive species. The sycamore can grow to a height of about and the branches form a broad, rounded crown. The bark is grey, smooth when young and later flaking in irregular patches. The leaves grow on long leafstalks and are large and palmate, with five large radiating lobes. The flowers are greenish-yellow a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Described In 1949
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphipyrinae
Amphipyrinae is a subfamily of owlet moths in the family Noctuidae. There are more than 50 genera and 210 described species in Amphipyrinae, although the classifications are likely to change over time. This subfamily has been used as a catchall for members of Noctuidae that don't fit well into other subfamilies. As such, many of its members lack morphological traits that would allow assignment into one of the other subfamilies. Genetic analysis conducted on Amphipyrinae is improving the classification of these genera. In 2021, phylogenetic research resulted in 11 genera being transferred from Amphipyrinae to six different subfamilies, and it is expected that more members of Amphipyrinae will be reassigned as further research is done. Psaphidini is included here as a tribe, but is sometimes treated as the subfamily Psaphidinae. The Australian genera in Acronictinae are sometimes considered part of Amphipyrinae. Genera These 52 genera belong to the subfamily Amphipyrinae: ; Trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Colour Identification Guide To Moths Of The British Isles
''The Colour Identification Guide to Moths of the British Isles (Macrolepidoptera)'' by Bernard Skinner is a single volume identification guide to the macromoths of Britain and Ireland published by Viking Books, often referred by moth recorders simply as "Skinner". The first edition (black dust jacket) was published in 1984, and a second, revised edition (pale green dust jacket) in 1998. The book became the standard guide to macromoth identification used by moth recorders in the field in Britain, and the increased popularity of moth recording in Britain in the 1990s is often attributed in large part to this book. The first edition of the guide was illustrated by 42 colour photographic plates of pinned moth specimens, photographed by David Wilson. An extra plate by Wilson, showing additional species or aberrations was included in the second edition. For some species, additional line drawings showing specific identification features are included within the text. A companion guid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisteria Sinensis
''Wisteria sinensis'', commonly known as the Chinese wisteria, is a species of flowering plant in the pea family, native to China, in the provinces of Guangxi, Guizhou, Hebei, Henan, Hubei, Shaanxi, and Yunnan. Growing tall, it is a deciduous vine. It is widely cultivated in temperate regions for its twisting stems and masses of scented flowers in hanging racemes, in spring. Description ''Wisteria sinensis'' clings to supporting plants or man-made structures by counterclockwise-twining stems. The leaves are shiny, green, pinnately compound, 10–30 cm in length, with 9-13 oblong leaflets that are each 2–6 cm long. The flowers are white, violet, or blue, produced on 15–20 cm racemes before the leaves emerge in spring. The flowers on each raceme open simultaneously before the foliage has expanded, and have a distinctive fragrance similar to that of grapes. Though it has shorter racemes than ''Wisteria floribunda'' (Japanese wisteria), it often has a higher qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Museum, London
The Natural History Museum in London is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, the others being the Science Museum and the Victoria and Albert Museum. The Natural History Museum's main frontage, however, is on Cromwell Road. The museum is home to life and earth science specimens comprising some 80 million items within five main collections: botany, entomology, mineralogy, palaeontology and zoology. The museum is a centre of research specialising in taxonomy, identification and conservation. Given the age of the institution, many of the collections have great historical as well as scientific value, such as specimens collected by Charles Darwin. The museum is particularly famous for its exhibition of dinosaur skeletons and ornate architecture—sometimes dubbed a ''cathedral of nature''—both exemplified by the large ''Diplodocus'' cast that domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilia
''Tilia'' is a genus of about 30 species of trees or bushes, native throughout most of the temperateness, temperate Northern Hemisphere. The tree is known as linden for the European species, and basswood for North American species. In Britain and Ireland they are commonly called lime trees, although they are not related to the citrus Lime (fruit), lime. The genus occurs in Europe and eastern North America, but the greatest species diversity is found in Asia. Under the Cronquist system, Cronquist classification system, this genus was placed in the family Tiliaceae, but genetic research summarised by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group has resulted in the incorporation of this genus, and of most of the previous family, into the Malvaceae. ''Tilia'' species are mostly large, deciduous trees, reaching typically tall, with oblique-cordate (heart-shaped) leaves across. As with elms, the exact number of species is uncertain, as many of the species can Hybrid (biology), hybridise readily, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lilac
''Syringa'' is a genus of 12 currently recognized species of flowering plant, flowering woody plants in the olive family or Oleaceae called lilacs. These lilacs are native to woodland and scrub from southeastern Europe to eastern Asia, and widely and commonly cultivated in temperate zone, temperate areas elsewhere.Flora Europaea''Syringa''/ref>Flora of China丁香属 ding xiang shu ''Syringa''/ref>Flora of Pakistan''Syringa''/ref>Germplasm Resources Information Network''Syringa'' The genus is most closely related to ''Ligustrum'' (privet), classified with it in Oleaceae tribus Oleeae subtribus Ligustrinae.University of Oxford, Oleaceae information siteNew classification of the Oleaceae/ref> Lilacs are used as food plants by the larvae of some moth species, including copper underwing, scalloped oak and Svensson's copper underwing. Description They are small trees, ranging in size from tall, with stems up to diameter. The leaf, leaves are opposite (occasionally in whorls o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rowan
The rowans ( or ) or mountain-ashes are shrubs or trees in the genus ''Sorbus ''Sorbus'' is a genus of over 100 species of trees and shrubs in the rose family, Rosaceae. Species of ''Sorbus'' (''s.l.'') are commonly known as whitebeam, rowan ( mountain-ash) and service tree. The exact number of species is disputed depe ...'' of the rose family, Rosaceae. They are native throughout the cool temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, with the highest species diversity in the Himalaya, southern Tibet and parts of western China, where numerous apomictic microspecies occur.Rushforth, K. (1999). ''Trees of Britain and Europe''. Collins . The name ''rowan'' was originally applied to the species ''Sorbus aucuparia'' and is also used for other species in ''Sorbus'' subgenus ''Sorbus''. Formerly, when a wider variety of fruits were commonly eaten in Europe and North America, ''Sorbus'' was a domestically used fruit throughout these regions. It is still used in some countries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions. Most species are known as willow, but some narrow-leaved shrub species are called osier, and some broader-leaved species are referred to as sallow (from Old English ''sealh'', related to the Latin word ''salix'', willow). Some willows (particularly arctic and alpine species) are low-growing or creeping shrubs; for example, the dwarf willow (''Salix herbacea'') rarely exceeds in height, though it spreads widely across the ground. Description Willows all have abundant watery bark sap, which is heavily charged with salicylic acid, soft, usually pliant, tough wood, slender branches, and large, fibrous, often stoloniferous roots. The roots are remarkable for their toughness, size, and tenacity to live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhododendron
''Rhododendron'' (; from Ancient Greek ''rhódon'' "rose" and ''déndron'' "tree") is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants in the heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are native to eastern Asia and the Himalayan region, but smaller numbers occur elsewhere in Asia, and in North America, Europe and Australia. It is the national flower of Nepal, the state flower of Washington and West Virginia in the United States, the state flower of Nagaland in India, the provincial flower of Jiangxi in China and the state tree of Sikkim and Uttarakhand in India. Most species have brightly colored flowers which bloom from late winter through to early summer. Azaleas make up two subgenera of ''Rhododendron''. They are distinguished from "true" rhododendrons by having only five anthers per flower. Species Description ''Rhododendron'' is a genus of shrubs and small to (rarely) large trees, the smallest species growing to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)