|
Amchitka
Amchitka (; ale, Amchixtax̂; russian: Амчитка) is a volcanic, tectonically unstable and uninhabited island in the Rat Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in southwest Alaska. It is part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. The island, with a land area of roughly , is about long and wide. The area has a maritime climate, with many storms, and mostly overcast skies. Amchitka was populated for more than 2,500 years by the Aleut people, but has had no permanent population since 1832. The island has been part of the United States since the Alaska Purchase of 1867. During World War II, it was used as an airfield by US forces in the Aleutian Islands Campaign. Amchitka was selected by the United States Atomic Energy Commission to be the site for underground detonations of nuclear weapons. Three such tests were carried out: ''Long Shot'', an blast in 1965; ''Milrow'', a blast in 1969; and '' Cannikin'' in 1971 – at , the largest underground test eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
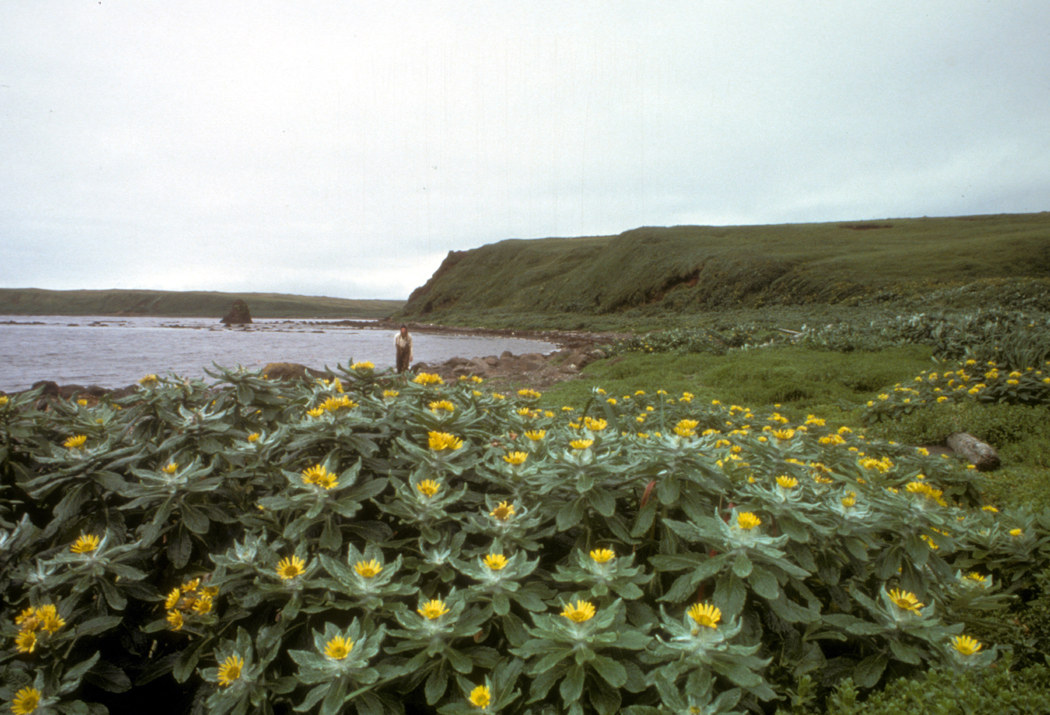
Amchitka Island, Beach Fleabane In Full Bloom - Senecio Pseudo-arnica
Amchitka (; ale, Amchixtax̂; russian: Амчитка) is a volcanic, tectonically unstable and uninhabited island in the Rat Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in southwest Alaska. It is part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. The island, with a land area of roughly , is about long and wide. The area has a maritime climate, with many storms, and mostly overcast skies. Amchitka was populated for more than 2,500 years by the Aleut people, but has had no permanent population since 1832. The island has been part of the United States since the Alaska Purchase of 1867. During World War II, it was used as an airfield by US forces in the Aleutian Islands Campaign. Amchitka was selected by the United States Atomic Energy Commission to be the site for underground detonations of nuclear weapons. Three such tests were carried out: ''Long Shot'', an blast in 1965; ''Milrow'', a blast in 1969; and '' Cannikin'' in 1971 – at , the largest underground test ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amchitka Island, Harlequin Beach
Amchitka (; ale, Amchixtax̂; russian: Амчитка) is a volcanic, tectonically unstable and uninhabited island in the Rat Islands group of the Aleutian Islands in southwest Alaska. It is part of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. The island, with a land area of roughly , is about long and wide. The area has a maritime climate, with many storms, and mostly overcast skies. Amchitka was populated for more than 2,500 years by the Aleut people, but has had no permanent population since 1832. The island has been part of the United States since the Alaska Purchase of 1867. During World War II, it was used as an airfield by US forces in the Aleutian Islands Campaign. Amchitka was selected by the United States Atomic Energy Commission to be the site for underground detonations of nuclear weapons. Three such tests were carried out: ''Long Shot'', an blast in 1965; ''Milrow'', a blast in 1969; and '' Cannikin'' in 1971 – at , the largest underground test ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
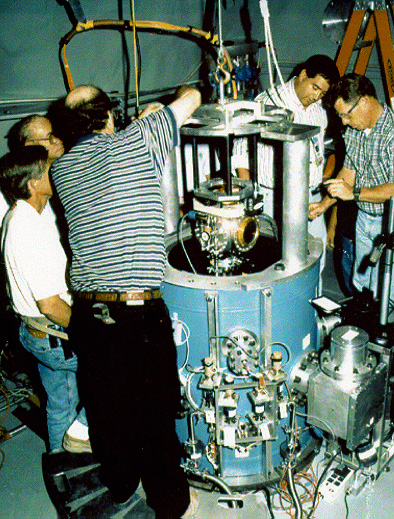
Cannikin
Cannikin was an underground nuclear weapons test performed on November 6, 1971, on Amchitka island, Alaska, by the United States Atomic Energy Commission. The experiment, part of the Operation Grommet nuclear test series, tested the unique W71 warhead design for the LIM-49 Spartan anti-ballistic missile. With an explosive yield of almost , the test was the largest underground explosion ever detonated by the United States. Prior to the main five-megaton test in 1971, a test took place on the island on October 2, 1969, for calibration purposes, and to ensure the subsequent Cannikin test could be contained. This test, Milrow, was included in the Operation Mandrel nuclear test series. The Cannikin test faced considerable opposition on environmental grounds. The campaigning environmental organization Greenpeace grew out of efforts to oppose the test. Siting The Cannikin test was too large to be conducted safely in Nevada. Amchitka had been considered in the 1950s as a potentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing 180th meridian, longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude (Amatignak Island) and the easternmost by longitude ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleut People
The Aleuts ( ; russian: Алеуты, Aleuty) are the indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleut people and the islands are politically divided between the US state of Alaska and the Russian administrative division of Kamchatka Krai. Etymology In the Aleut language they are known by the endonyms Unangan (eastern dialect) and Unangas (western dialect), both of which mean "people". The Russian term "Aleut" was a general term used for both the native population of the Aleutian Islands and their neighbors to the east in the Kodiak Archipelago, who were also referred to as "Pacific Eskimos". Language Aleut people speak Unangam Tunuu, the Aleut language, as well as English and Russian in the United States and Russia respectively. An estimated 150 people in the United States and five people in Russia speak Aleut. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underground Nuclear Testing
Underground nuclear testing is the test detonation of nuclear weapons that is performed underground. When the device being tested is buried at sufficient depth, the nuclear explosion may be contained, with no release of radioactive materials to the atmosphere. The extreme heat and pressure of an underground nuclear explosion causes changes in the surrounding rock. The rock closest to the location of the test is vaporised, forming a cavity. Farther away, there are zones of crushed, cracked, and irreversibly strained rock. Following the explosion, the rock above the cavity may collapse, forming a rubble chimney. If this chimney reaches the surface, a bowl-shaped subsidence crater may form. The first underground test took place in 1951; further tests provided information that eventually led to the signing of the Limited Test Ban Treaty in 1963, which banned all nuclear tests except for those performed underground. From then until the signing of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rat Islands
The Rat Islands ( ale, Qax̂um tanangis, russian: Крысьи острова) are a group of American High islands, volcanic islands in the Aleutian Islands in southwestern Alaska, between Buldir Island and the Near Islands group to its west, and Amchitka Pass and the Andreanof Islands group to its east. The largest islands in the group are, from west to east, Kiska, Little Kiska Island, Little Kiska, Segula Island, Segula, Hawadax Island, Hawadax or Kryssei, Khvostof Island, Khvostof, Davidof Island, Davidof, Little Sitkin Island, Little Sitkin, Amchitka, and Semisopochnoi Island, Semisopochnoi. The total land area of the Rat Islands is 360.849 sq mi (934.594 km2). None of the islands are inhabited. The name ''Rat Islands'' is the English translation of the name given to the islands by Captain Fyodor Petrovich Litke in 1827 when he visited the Aleutian Islands on a voyage around the world. The islands are named so because rats were accidentally introduced to Hawadax Isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by U.S. Congress to foster and control the peacetime development of atomic science and technology. President Harry S. Truman signed the McMahon/Atomic Energy Act on August 1, 1946, transferring the control of atomic energy from military to civilian hands, effective on January 1, 1947. This shift gave the members of the AEC complete control of the plants, laboratories, equipment, and personnel assembled during the war to produce the atomic bomb. An increasing number of critics during the 1960s charged that the AEC's regulations were insufficiently rigorous in several important areas, including radiation protection standards, nuclear reactor safety, plant siting, and environmental protection. By 1974, the AEC's regulatory programs had come under such strong attack that the U.S. Congress decided to abolish the AEC. The AEC was abolished by the Ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Testing
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by different conditions, and how personnel, structures, and equipment are affected when subjected to nuclear explosions. However, nuclear testing has often been used as an indicator of scientific and military strength. Many tests have been overtly political in their intention; most nuclear weapons states publicly declared their nuclear status through a nuclear test. The first nuclear device was detonated as a test by the United States at the Trinity site in New Mexico on July 16, 1945, with a yield approximately equivalent to 20 kilotons of TNT. The first thermonuclear weapon technology test of an engineered device, codenamed "Ivy Mike", was tested at the Enewetak Atoll in the Marshall Islands on November 1, 1952 (local date), also by the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Test
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by different conditions, and how personnel, structures, and equipment are affected when subjected to nuclear explosions. However, nuclear testing has often been used as an indicator of scientific and military strength. Many tests have been overtly political in their intention; most nuclear weapons states publicly declared their nuclear status through a nuclear test. The first nuclear device was detonated as a test by the United States at the Trinity site in New Mexico on July 16, 1945, with a yield approximately equivalent to 20 kilotons of TNT. The first thermonuclear weapon technology test of an engineered device, codenamed "Ivy Mike", was tested at the Enewetak Atoll in the Marshall Islands on November 1, 1952 (local date), also by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Arc
The Aleutian Arc is a large volcanic arc in the U.S. state of Alaska. It consists of a number of active and dormant volcanoes that have formed as a result of subduction along the Aleutian Trench. Although taking its name from the Aleutian Islands, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one, and the Aleutian Arc extends through the Alaska Peninsula following the Aleutian Range to the Aleutian Islands. The Aleutian Arc reflects subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate. It extends from the Kamchatka Peninsula in the west to the Gulf of Alaska in the east. Unimak Pass at the southwestern end of the Alaska Peninsula marks the eastward transition from an intra-oceanic in the west to a continental arc in the east. Due to the arcuate geometry of the trench, the relative velocity vector changes from almost trench-normal in the Gulf of Alaska to almost trench-parallel in the west. Along the oceanic part of the subduction zone, convergence varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |