|
Amarasi Language
Amarasi is a Central Malayo-Polynesian language of West Timor, and is spoken by the Amarasi. The Amarasi language has about 80,000 native speakers, with four main dialects called Ro'is, Kotos, Tais Nonof, and Ketun, though many differences exist between individual villages. It uses Subject-Object-Verb grammar structure. Speakers are interspersed with those of Helong. Classification Amarasi is a Malayo-Polynesian language with strong Melanesian roots, and additional Dutch and Portuguese influences. It belongs to a language group known as Timoric (sometimes Timor-Babar) that includes all the languages spoken on the island of Timor, as well as the nearby islands of Wetar and Babar. The most common languages in the Timor-Babar language group are Uab Meto (previously known as Dawan) on the western half of the island, and Tetum on the eastern half of the island. These languages have over a million speakers between them. Most Timoric languages are separated into east and west becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia is a presidential republic with an elected legislature. It has 38 provinces, of which nine have special status. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the world's second-most populous urban area. Indonesia shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the eastern part of Malaysia, as well as maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, and India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
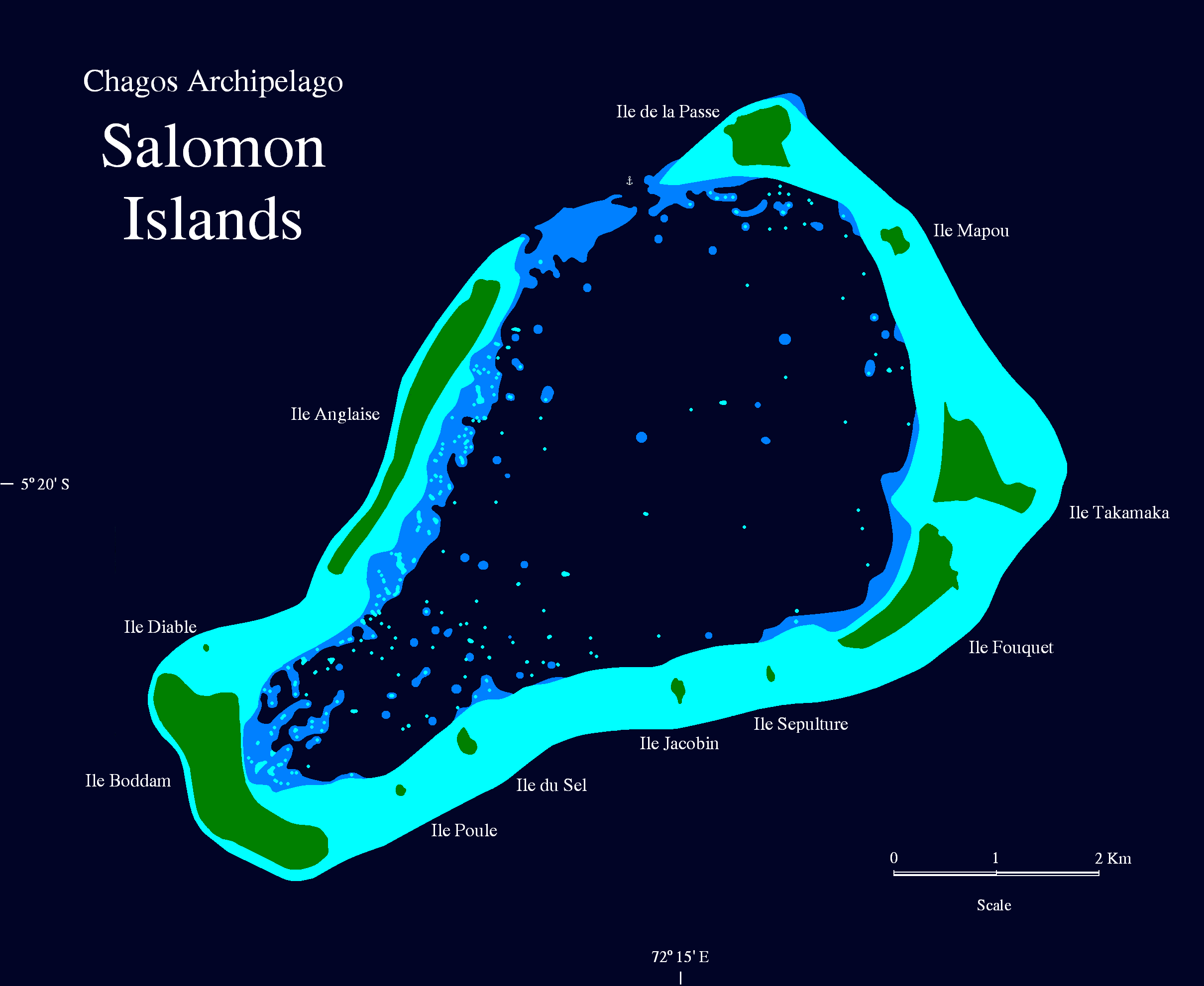
Salomon Islands
The Salomon Islands or Salomon Atoll is a small atoll of the Chagos Archipelago, British Indian Ocean Territory. Description The atoll is located in the northeast of the Chagos Archipelago, between Blenheim Reef and Peros Banhos. The main islands in the group are Île Boddam, with the former main settlement, and a land area of , and Île Anglaise (), both on the western rim of the reef. There were smaller settlements of Chagossians in Fouquet () and Takamaka () Islands. Île de la Passe is in area, and Île Mapou . The remaining islets are much smaller. The total land area is . There is a passage into the lagoon, named Baie de Salomon, on the Northern side, between Île Anglaise and Île de la Passe. The Salomon Islands are one of the favorite anchoring spots for itinerant yachtsmen passing through the Chagos, even though there are no proper moorings for yachts and a permit of the BIOT authorities is needed. Now uninhabited, the islands are overrun by low jungle between the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plosive
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or simply a stop, is a pulmonic consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be made with the tongue tip or blade (, ), tongue body (, ), lips (, ), or glottis (). Plosives contrast with nasals, where the vocal tract is blocked but airflow continues through the nose, as in and , and with fricatives, where partial occlusion impedes but does not block airflow in the vocal tract. Terminology The terms ''stop, occlusive,'' and ''plosive'' are often used interchangeably. Linguists who distinguish them may not agree on the distinction being made. The terms refer to different features of the consonant. "Stop" refers to the airflow that is stopped. "Occlusive" refers to the articulation, which occludes (blocks) the vocal tract. "Plosive" refers to the release burst (plosion) of the consonant. Some object to the use of "plosive" for inaudibly released stops, which may then instead be ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottal Consonant
Glottal consonants are consonants using the glottis as their primary articulation. Many phoneticians consider them, or at least the glottal fricative, to be transitional states of the glottis without a point of articulation as other consonants have, while some do not consider them to be consonants at all. However, glottal consonants behave as typical consonants in many languages. For example, in Literary Arabic, most words are formed from a root ''C-C-C'' consisting of three consonants, which are inserted into templates such as or . The glottal consonants and can occupy any of the three root consonant slots, just like "normal" consonants such as or . The glottal consonants in the International Phonetic Alphabet are as follows: Characteristics In many languages, the "fricatives" are not true fricatives. This is a historical usage of the word. They instead represent transitional states of the glottis ( phonation) without a specific place of articulation, and may behave as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velar Consonant
Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue (the dorsum) against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth (known also as the velum). Since the velar region of the roof of the mouth is relatively extensive and the movements of the dorsum are not very precise, velars easily undergo assimilation, shifting their articulation back or to the front depending on the quality of adjacent vowels. They often become automatically ''fronted'', that is partly or completely palatal before a following front vowel, and ''retracted'', that is partly or completely uvular before back vowels. Palatalised velars (like English in ''keen'' or ''cube'') are sometimes referred to as palatovelars. Many languages also have labialized velars, such as , in which the articulation is accompanied by rounding of the lips. There are also labial–velar consonants, which are doubly articulated at the velum and at the lips, such as . This distinction disappears with the approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatal Consonant
Palatals are consonants articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate (the middle part of the roof of the mouth). Consonants with the tip of the tongue curled back against the palate are called retroflex. Characteristics The most common type of palatal consonant is the extremely common approximant , which ranks as among the ten most common sounds in the world's languages. The nasal is also common, occurring in around 35 percent of the world's languages, in most of which its equivalent obstruent is not the stop , but the affricate . Only a few languages in northern Eurasia, the Americas and central Africa contrast palatal stops with postalveolar affricates—as in Hungarian, Czech, Latvian, Macedonian, Slovak, Turkish and Albanian. Consonants with other primary articulations may be palatalized, that is, accompanied by the raising of the tongue surface towards the hard palate. For example, English (spelled ''sh'') has such a palatal component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Consonant
An apical consonant is a phone (speech sound) produced by obstructing the air passage with the tip of the tongue (apex) in conjunction with upper articulators from lips to postalveolar, and possibly prepalatal. It contrasts with laminal consonants, which are produced by creating an obstruction with the blade of the tongue, just behind the tip. Sometimes ''apical'' is used exclusively for an articulation that involves only the tip of the tongue and ''apicolaminal'' for an articulation that involves both the tip and the blade of the tongue. However, the distinction is not always made and the latter one may be called simply ''apical'', especially when describing an apical dental articulation. As there is some laminal contact in the alveolar region, the apicolaminal dental consonants are also labelled as ''denti-alveolar''. It is not a very common distinction and is typically applied only to fricatives and affricates. Thus, many varieties of English have either apical or laminal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labial Consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. The two common labial articulations are bilabials, articulated using both lips, and labiodentals, articulated with the lower lip against the upper teeth, both of which are present in English. A third labial articulation is dentolabials, articulated with the upper lip against the lower teeth (the reverse of labiodental), normally only found in pathological speech. Generally precluded are linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue contacts the posterior side of the upper lip, making them coronals, though sometimes, they behave as labial consonants. The most common distribution between bilabials and labiodentals is the English one, in which the nasal and the stops, , , and , are bilabial and the fricatives, , and , are labiodental. The voiceless bilabial fricative, voiced bilabial fricative, and the bilabial approximant do not exist as the primary realizations of any sounds in English, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Occupation Of The Dutch East Indies
The Empire of Japan occupied the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia) during World War II from March 1942 until after the end of the war in September 1945. It was one of the most crucial and important periods in modern Indonesian history. In May 1940, Germany occupied the Netherlands, and martial law was declared in the Dutch East Indies. Following the failure of negotiations between the Dutch authorities and the Japanese, Japanese assets in the archipelago were frozen. The Dutch declared war on Japan following the 7 December 1941 Attack on Pearl Harbor. The Japanese invasion of the Dutch East Indies began on 10 January 1942, and the Imperial Japanese Army overran the entire colony in less than three months. The Dutch surrendered on 8 March. Initially, most Indonesians welcomed the Japanese as liberators from their Dutch colonial masters. The sentiment changed, however, as between 4 and 10 million Indonesians were recruited as forced labourers ('' romusha'') on economic deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kupang
Kupang ( id, Kota Kupang, ), formerly known as Koepang, is the capital of the Indonesian province of East Nusa Tenggara. At the 2020 C ensus, it had a population of 442,758; the official estimate as at mid 2021 was 455,850. It is the largest city and port on the island of Timor, and is a part of the Timor Leste-Indonesia-Australia Growth Triangle free trade zone. Geographically, Kupang is the southernmost city in Indonesia. History Early history and Portuguese domination Kupang was an important port and trading post during the Portuguese and Dutch colonial eras. There are still ruins and remnants of the colonial presence in the city. Representatives of the Dutch East India Company (VOC) first encountered Kupang in 1613 after having conquered the Portuguese fort on the island of Solor. At this time the area of the city was governed by a Raja of the Helong tribe, who claimed descent from the island of Ceram in the Maluku archipelago. Kupang occupied an ideal strategic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belu (province)
Belu (also Belos or Behale){{cite book, author=H.G. Schulte Nordholt, editor=M.J.L. Yperen, title=The Political System of the Atoni of Timor, year=2013, publisher=Springer Science & Business Media, isbn=94-015-1013-X was the Portuguese name for eastern part of Timor island, which included the kingdoms of Wehali, Lichisana and Suai-Cabanaza. In 1756 the western part of Belu and West Timor fell to the Dutch. See also * History of East Timor East Timor is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania known as Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste. The country comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor and the nearby islands of Atauro and Jaco. The first inhabitants are thought ... References Portuguese Timor Former Portuguese colonies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
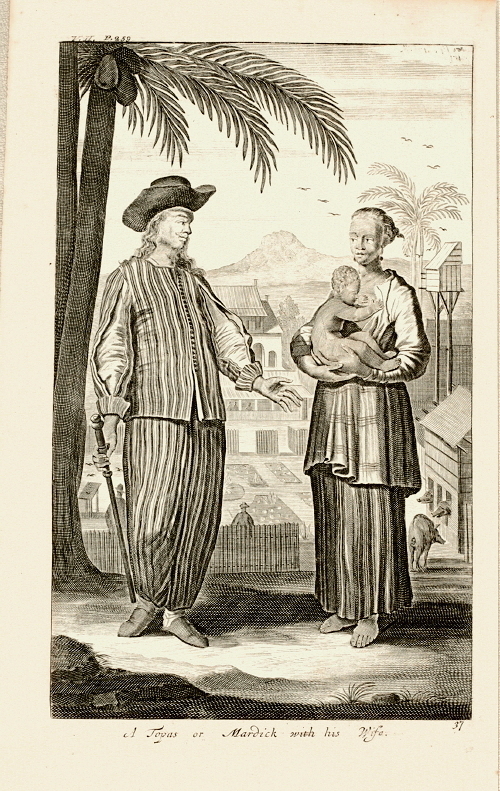
Topasses
Topasses (Tupasses, Topas, Topaz) were a group of people led by the two powerful families – Da Costa and Hornay – that resided in Oecussi and Flores. The Da Costa families were descendants of Portuguese Jewish merchants and Hornay were Dutch. The origins The etymology of the name is obscure. It might come from the Tamil term ''tuppasi'', "bilingual" or "interpreter". But it has also been associated with the Hindi word ''topi'' (hat) which refers to the characteristic hat worn by the men of this community as a marker of their cultural attachment to the European community. Hence, they are also referred to as ''gente de chapeo'' in Portuguese accounts or as ''gens à chapeau'' in French accounts. It partly overlapped with the Dutch concept mardijker, "free men", who also usually had a Portuguese cultural background, but had no European blood in their veins. While the mardijkers served under the Dutch colonial authorities, the topasses of Timor were staunchly opposed to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |