|
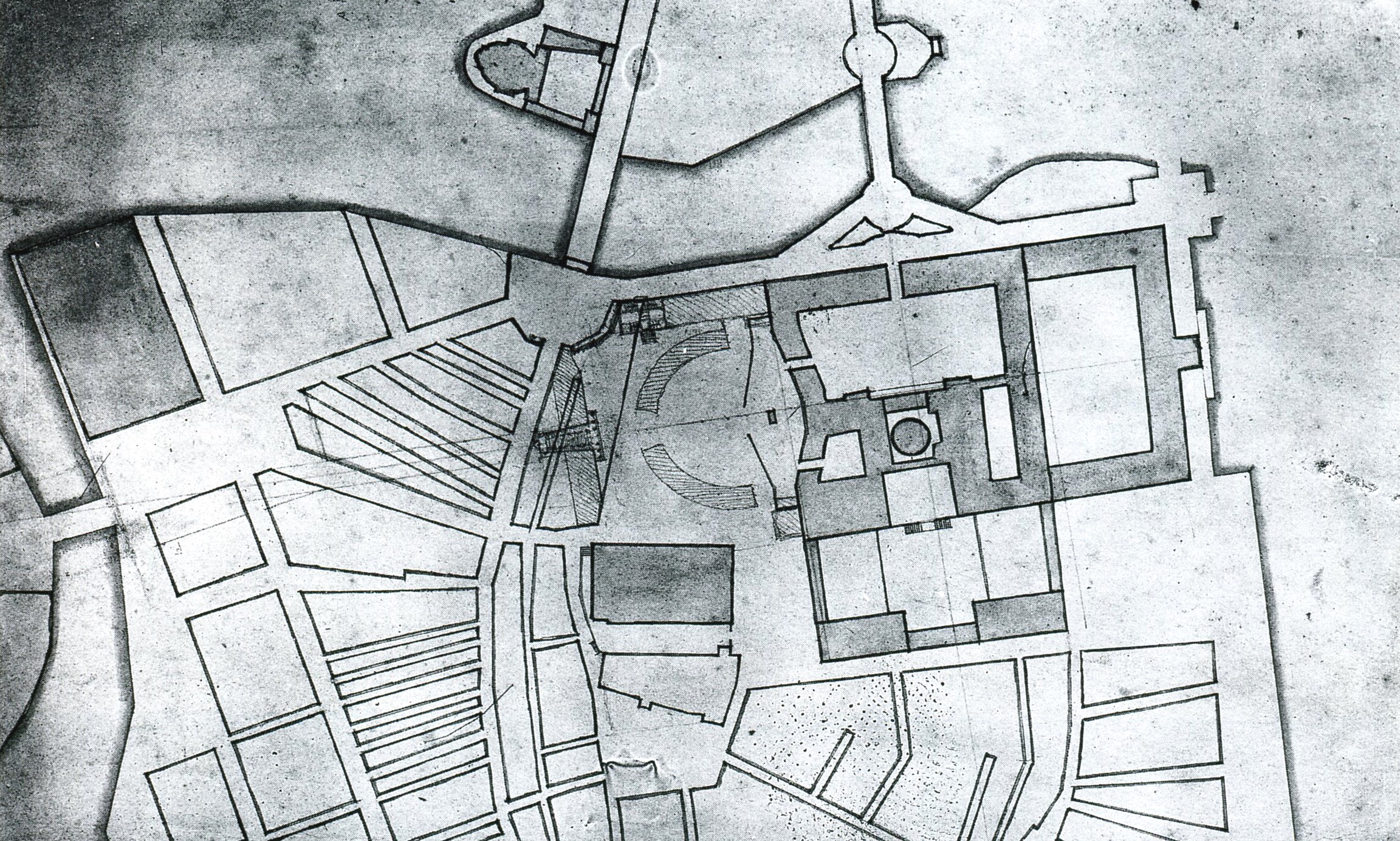
AlmarestûÊket's Castle
AlmarestûÊket's castle (or Sankt Erik's castle) is a medieval castle ruin in Upplands-Bro Municipality, Upplands-Bro municipality in Stockholm County. The complex is named after Eric IX of Sweden and was once one of Sweden's strongest and most famous castles,Informationstavla pûË platsen uppsatt av Stockholms lûÊns museum och Upplands bro kommun located at the important choke point of AlmarestûÊket, a strait at the inlet to MûÊlaren, Lake MûÊlaren. AlmarestûÊket's castle is listed as an ancient monument by the Swedish National Heritage Board. History A castle was built during the 12th century on StûÊketsholmen (which was then an island), and served as a defense facility for the cities of Sigtuna and Uppsala. An important waterway ran here between Stockholm and Uppsala, and whoever had control over the waterways also had control over the kingdom. Throughout the Middle Ages, there was a constant tug-of-war between the king and the church over the rule of the castle. The castle was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suecia 1-093 ; AlmarestûÊket
In Modern English, the name of Sweden ( ) is derived from 17th century Middle Dutch and Middle Low German. In Old English, the country was named ''Swáoland'' (literally "Swede land") and ''Swáorá¨áe'' (literally "Swede kingdom"); the latter is cognate with Old Norse ''SvûÙarûÙki''. Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman of the 12th and 13th centuries used ''Suane'' and ''Swane'' (with the adjective as ''Suaneis''). In Scots language, Scots, ''Swane'' and ''Swaine'' appear in the 16th century. Early Modern English used ''Swedeland''. The Old English name for Sweden was ''Swáoland'' or ''Swáorá¨áe'', land or kingdom of the ''Swáon'', whereas the Germanic tribe of the ''Swedes (tribe), Swedes'' was called ''SvûÙûƒjû°û¯'' in Old Norse. The latter is a compositum consisting of ''SvûÙ'' which means Swedish and ''ûƒjû°û¯'' which means people. The word ''ûƒjû°û¯'' has its origin in the elder Indo-European word ''teuteh''. The name of the ''Sviar'' is derived from a self-designation con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockholm Bloodbath
The Stockholm Bloodbath () was a trial that led to a series of executions in Stockholm between 7 and 9 November 1520. The event is also known as the Stockholm massacre. The events occurred after the coronation of Christian II as the new king of Sweden, when guests in the crowning party were invited to a meeting at Tre Kronor castle. Archbishop Gustav Trolle, demanding economic compensation for things such as the demolition of AlmarestûÊket's fortress, questioned whether the former Swedish regent Sten Sture the Younger and his supporters had been guilty of heresy. Supported by canon law, nearly 100 people were executed in the days following the meeting despite promises of amnesty. Among those killed were many people from the aristocracy who had been supporting the ''Sture Party'' in the previous years. Thereafter King Christian II became known in Sweden as ("Christian heTyrant"). Background Political factions in Sweden The Stockholm Bloodbath was a consequence of conflict b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riksdag
The Riksdag ( , ; also or , ) is the parliament and the parliamentary sovereignty, supreme decision-making body of the Kingdom of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral parliament with 349 members (), elected proportional representation, proportionally and serving, since 1994, fixed four-year terms. The 2022 Swedish general election is the most recent general election. The constitutional mandates of the Riksdag are enumerated in the ''Basic Laws of Sweden#Instrument of Government, Instrument of Government'' (), and its internal workings are specified in greater detail in the Riksdag Act ().Instrument of Government as of 2012. Retrieved on 16 November 2012. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excommunication
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular those of being in Koinonia, communion with other members of the congregation, and of receiving the sacraments. It is practiced by all of the ancient churches (such as the Catholic Church, Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodox churches and the Eastern Orthodoxy, Eastern Orthodox churches) as well as by other Christian denominations; however, it is also used more generally to refer to similar types of institutional religious exclusionary practices and shunning among other religious groups. The Amish have also been known to excommunicate members that were either seen or known for breaking rules, or questioning the church, a practice known as shunning. Jehovah's Witnesses use the term disfellowship to refer to their form of excommunication. The word ''excommunication'' means putting a specific indiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sten Sture The Younger
Sten Sture the Younger () (1493 ã 3 February 1520), was a Swedish nobleman who served as the regent of Sweden, during the era of the Kalmar Union. Biography Sture was born in 1493, as the son of Svante Nilsson (regent of Sweden) and Iliana Gisladotter GûÊdda, heiress of UlvûËsa. At the death of his father, regent Svante, Sture was only 18 years old. High Councillor Erik Trolle, Eric Trolle was chosen as regent by the High Council. He supported the union with Denmark. However, Sture utilized the castles and troops fiefed to him by his late father and executed a coup. After Sture promised to continue union negotiations with Denmark, the High Council accepted him as regent replacing Eric Trolle. In reality, Sture's purpose was to keep Sweden independent from Denmark. He adopted the Sture surname, heritage from his great-grandmother, because it symbolized independence from Denmark and as a reminder of Sten Sture the Elder, his father's third cousin. Conflict soon arose between S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav Trolle
Gustav Eriksson Trolle (September 1488 ã 1535) was the archbishop of Uppsala in Sweden, in two sessions, during the turbulent Reformation events. He was the son of Eric Arvidsson Trolle, a former regent of Sweden during the era of the Kalmar Union. After returning from studies abroad, in Cologne and Rome, he was in 1513 elected vicar in LinkûÑping. One year later he became Archbishop of Uppsala. In 1515, he got into an argument with the Swedish regent Sten Sture the Younger, who spread the rumour that he was allied with the King Christian II of Denmark. True or not, it resulted in Trolle being removed from his office and put under siege in the archbishop's mansion AlmarestûÊket at lake MûÊlaren. In the winter of 1517, AlmarestûÊket was demolished by orders from the Swedish government. The Danish threat grew stronger, and Trolle was among those who spoke in favour of the Danish King. In 1520, Christian II of Denmark entered Sweden, and Trolle was rewarded by being reappointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolaus Ragvaldi
Nicolaus Ragvaldi (; early 1380s ã 17 February 1448) was the bishop of VûÊxjûÑ and the archbishop of Uppsala in Sweden from 1438 to 1448. He is known as an early representative of the Gothicist tradition. On 12 November 1434 he held a speech at the council of Basel, where he argued that the Swedish monarch, Eric of Pomerania, was a successor to the Gothic kings, and that the Swedish delegation deserved senior rank. The Spanish delegation responded with a claim of seniority because of the Visigoths. Notes of these speeches were written down and preserved, and included by Johannes Magnus when he wrote the influential ''History of the Nordic People'' about 150 years later. His research results resulted in Gustav Vasa's son styling himself as Eric XIV, although his father disapproved. See also * List of archbishops of Uppsala ReferencesArticle ''Nils Ragvaldsson''from the Nordisk Familjebok (Swedish) * 1380s births Roman Catholic archbishops of Uppsala 15th-cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engelbrekt Engelbrektsson
Engelbrekt Engelbrektsson (1390s ã 4 May 1436) was a Swedish nobleman, rebel leader and military leader of German ancestry. He was the leader of the Engelbrekt rebellion in 1434 against Eric of Pomerania, king of the Kalmar Union. Biography Engelbrekt Engelbrektsson was the owner of a mine and ironworks in the historic mining region of Bergslagen. He was from the parish of Norberg (''Norbergs socken'') in VûÊstmanland. His family originally came from Germany, having migrated to Sweden in the 1360s.NE (2023)''Engelbrekt Engelbrektsson''(''Nationalencyklopedin''). (Link checked 13 May 2013.) The family coat of arms shows three half-lilies formed into a triangle. Engelbrekt was dissatisfied by the numerous offences of the Danish local bailiffs and heavy taxation. In 1434 he started a rebellion Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockholm Castle
Stockholm Palace, or the Royal Palace, ( or ) is the official residence and major Crown palaces in Sweden, royal palace of the Monarchy of Sweden, Swedish monarch (King Carl XVI Gustaf of Sweden, Carl XVI Gustaf and Queen Silvia of Sweden, Queen Silvia use Drottningholm Palace as their usual residence). Stockholm Palace is in Stadsholmen, in Gamla stan in the capital city, capital, Stockholm. It neighbours the Parliament House, Stockholm, Riksdag building. The offices of the King, the other members of the Swedish royal family, and the Royal Court of Sweden are here. The palace is used for representative purposes by the King whilst performing his duties as the head of state. This royal residence has been in the same location by NorrstrûÑm in the northern part of Gamla stan in Stockholm since the middle of the 13th century when Tre Kronor (castle), Tre Kronor Castle was built. In modern times the name relates to the building called ''Kungliga Slottet''. The palace was designed by N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Of Pomerania
Erik of Pomerania ( 1381/1382 ã 24 September 1459) ruled over the Kalmar Union from 1396 until 1439. He was initially co-ruler with his great-aunt Margaret I of Denmark, Margaret I until her death in 1412. Erik is known as Erik III as King of Norway (1389ã1442), Erik VII as King of Denmark (1396ã1439) and has been called Erik XIII as King of Sweden (1396ã1434, 1436ã39). Erik was ultimately deposed from all three kingdoms of the union, but in 1449 he inherited one of the partitions of the Duchy of Pomerania and ruled it as duke until his death in 1459. His epithet ''of Pomerania'' was a pejorative intended to insinuate that he did not belong in Scandinavia. Succession background Erik was born in either 1381 or 1382 in Daréowo (formerly Rû¥genwalde), Pomerania, Poland. Named Boguséaw (Bogislaw) at birth, he was the son of Wartislaw VII, Duke of Pomerania, and Maria of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. Bogislaw's great-aunt Margaret I of Denmark, Margaret I, who ruled the kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle Eastãonce part of the Byzantine Empireã ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |