|
Alloterocucus
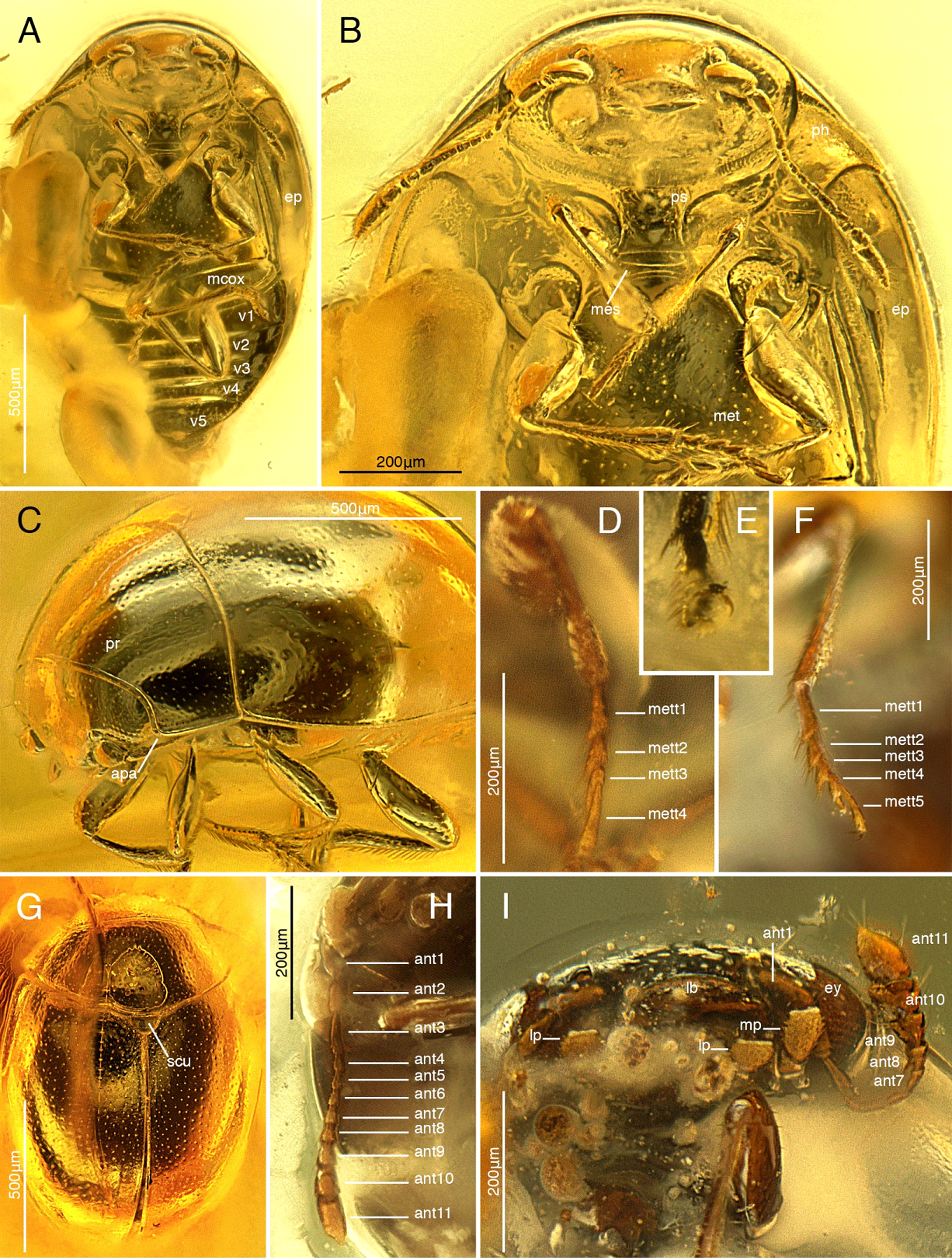
''Alloterocucus'' is an extinct genus of beetle. It is known from a single species, ''Alloterocucus atratus'', known from the mid Cretaceous (latest Albian-earliest Cenomanian) Burmese amber of Myanmar. It belongs to the clade Cucujiformia, probably Cucujoidea, and is not assigned to any family. Cladistic analysis suggests that it is closely related to Cyclaxyridae (sooty mold beetles), Tasmosalpingidae, and Lamingtoniidae ''Lamingtonium'' is the only genus in the family Lamingtoniidae, of the beetle superfamily Cucujoidea. It contains three species endemic to Australia.Lawrence, J. F., and Leschen, R. A. B. (2003). Review of Lamingtoniidae (Coleoptera: Cucujoidea ..., and is possibly most closely related to Lamingtoniidae. References Fossils of Myanmar Fossil taxa described in 2022 Cucujoidea Cucujoidea genera Cretaceous Asia Fossil beetle genera {{Cucujoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cucujoidea Genera
Cucujoidea is a superfamily of beetles. This group formerly included all of the families now included in the superfamily Coccinelloidea. They include some fungus beetles and a diversity of lineages of "bark beetles" unrelated to the "true" bark beetles ( Scolytinae), which are weevils (superfamily Curculionoidea). Morphology The morphology of Cucujoidea is varied and there are no features uniting all members of the superfamily. Adults can be recognised by the procoxal cavities being internally open in most taxa, females having tarsal formula 5-5-5 and males 5-5-5 or 5-5-4 (rarely 4-4-4), females with tergite VIII concealed dorsally by tergite VII, and males with tergite X completely membraneous. Larvae have frontal arms usually lyriform, the mandible mesal surface usually with well-developed mola, a maxillary articulating area usually present, a hypopharyngeal sclerome usually present, and two pretarsal setae. Taxonomy According to a 2015 revision, the following 25 families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cucujoidea
Cucujoidea is a superfamily of beetles. This group formerly included all of the families now included in the superfamily Coccinelloidea. They include some fungus beetles and a diversity of lineages of "bark beetles" unrelated to the "true" bark beetles ( Scolytinae), which are weevils (superfamily Curculionoidea). Morphology The morphology of Cucujoidea is varied and there are no features uniting all members of the superfamily. Adults can be recognised by the procoxal cavities being internally open in most taxa, females having tarsal formula 5-5-5 and males 5-5-5 or 5-5-4 (rarely 4-4-4), females with tergite VIII concealed dorsally by tergite VII, and males with tergite X completely membraneous. Larvae have frontal arms usually lyriform, the mandible mesal surface usually with well-developed mola, a maxillary articulating area usually present, a hypopharyngeal sclerome usually present, and two pretarsal setae. Taxonomy According to a 2015 revision, the following 25 families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albian
The Albian is both an age of the geologic timescale and a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest or uppermost subdivision of the Early/Lower Cretaceous Epoch/Series. Its approximate time range is 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma to 100.5 ± 0.9 Ma (million years ago). The Albian is preceded by the Aptian and followed by the Cenomanian. Stratigraphic definitions The Albian Stage was first proposed in 1842 by Alcide d'Orbigny. It was named after Alba, the Latin name for River Aube in France. A Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP), ratified by the IUGS in 2016, defines the base of the Albian as the first occurrence of the planktonic foraminiferan '' Microhedbergella renilaevis'' at the Col de Pré-Guittard section, Arnayon, Drôme, France. The top of the Albian Stage (the base of the Cenomanian Stage and Upper Cretaceous Series) is defined as the place where the foram species '' Rotalipora globotruncanoides'' first appears in the stratigraphic column. The Albia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenomanian
The Cenomanian is, in the ICS' geological timescale, the oldest or earliest age of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or the lowest stage of the Upper Cretaceous Series. An age is a unit of geochronology; it is a unit of time; the stage is a unit in the stratigraphic column deposited during the corresponding age. Both age and stage bear the same name. As a unit of geologic time measure, the Cenomanian Age spans the time between 100.5 and 93.9 million years ago (Mya). In the geologic timescale, it is preceded by the Albian and is followed by the Turonian. The Upper Cenomanian starts around at 95 Mya. The Cenomanian is coeval with the Woodbinian of the regional timescale of the Gulf of Mexico and the early part of the Eaglefordian of the regional timescale of the East Coast of the United States. At the end of the Cenomanian, an anoxic event took place, called the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event or the "Bonarelli event", that is associated with a minor extinction event for marine spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burmese Amber
Burmese amber, also known as Burmite or Kachin amber, is amber from the Hukawng Valley in northern Myanmar. The amber is dated to around 100 million years ago, during the latest Albian to earliest Cenomanian ages of the mid-Cretaceous period. The amber is of significant palaeontological interest due to the diversity of flora and fauna contained as inclusions, particularly arthropods including insects and arachnids but also birds, lizards, snakes, frogs and fragmentary dinosaur remains. The amber has been known and commercially exploited since the first century AD, and has been known to science since the mid-nineteenth century. Research on the deposit has attracted controversy due to its alleged role in funding internal conflict in Myanmar and hazardous working conditions in the mines where it is collected. Geological context, depositional environment and age The amber is found within the Hukawng Basin, a large Cretaceous-Cenozoic sedimentary basin within northern Myanmar. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cucujiformia
Cucujiformia is an infraorder of polyphagan beetles, representing most plant-eating beetles. The infraorder contains the seven superfamilies: * Chrysomeloidea (~7 families including longhorn beetles and leaf beetles) * Cleroidea (checkered beetles, bark-gnawing beetles and soft-winged flower beetles) * Coccinelloidea (15 families, includes ladybirds and fungus beetles) * Cucujoidea (~27 families) * Curculionoidea (~8 families primarily consisting of weevils and also including snout beetles and bark beetles) * Lymexyloidea (ship-timber beetles) * Tenebrionoidea (formerly "Heteromera") (30 families including blister beetle Blister beetles are beetles of the family Meloidae, so called for their defensive secretion of a blistering agent, cantharidin. About 7,500 species are known worldwide. Many are conspicuous and some are aposematically colored, announcing their ...s and ant-like beetles) References External links * Insect infraorders Taxa named by Auguste L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladistic Analysis
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived characteristics (synapomorphies'')'' that are not present in more distant groups and ancestors. However, from an empirical perspective, common ancestors are inferences based on a cladistic hypothesis of relationships of taxa whose character states can be observed. Theoretically, a last common ancestor and all its descendants constitute a (minimal) clade. Importantly, all descendants stay in their overarching ancestral clade. For example, if the terms ''worms'' or ''fishes'' were used within a ''strict'' cladistic framework, these terms would include humans. Many of these terms are normally used paraphyletically, outside of cladistics, e.g. as a 'grade', which are fruitless to precisely delineate, especially when including extinct species. Radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclaxyridae
Cyclaxyridae are a family of beetles in the superfamily Cucujoidea. The only living genus is ''Cyclaxyra'', with two species endemic to New Zealand. Other species have been named from fossils. They are also known as sooty mould beetles due to the association of ''Cyclaxyra'' with sooty mould. The extant species are mycophagous, feeding on spores, conidia, and hyphae. Genera * ''Cyclaxyra'' Broun, 1893, New Zealand, recent ** ''Cyclaxyra jelineki'' Gimmel, 2009 ** ''Cyclaxyra politula'' (Broun, 1881) * †'' Electroxyra'' Gimmel, Szawaryn, Cai and Leschen, 2019 ** ''Electroxyra cretacea'' (Wu in Wu, Li and Ding, 2018) Burmese amber, Myanmar, Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) * †'' Pacyclaxyra'' Tihelka, Huang and Cai, 2021 ** ''Pacyclaxyra azari'' Tihelka, Huang and Cai, 2021 Burmese amber, Myanmar, Cenomanian * †'' Neolitochropus'' Lyubarsky and Perkovsky, 2016 ** ''Neolitochropus hoffeinsorum'' Lyubarsky & Perkovsky, 2016 Bitterfeld amber, Rovno amber, Baltic amber, Europe, Eoce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasmosalpingidae
''Tasmosalpingus'' is the only genus in the beetle family Tasmosalpingidae (superfamily Cucujoidea). There are two species in ''Tasmosalpingus'', found in Australia in Tasmania, Victoria and New South Wales. Adults have been collected using malaise traps, while a possible larval specimen was found under the bark of the podocarp '' Phyllocladus aspleniifolius.'' Gut contents indicate that they are mycophagous, feeding on fungal hypha A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or ...e. Species These species belong to the genus ''Tasmosalpingus'': * ''Tasmosalpingus quadrispilotus'' Lea, 1919 (syn ''Tasmosalpingus promiscuus'' Lea, 1919) * ''Tasmosalpingus magnus'' Liu, Porch & Ślipiński, 2023 References Cucujoidea genera Beetles of Australia Endemic fauna of Australia [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamingtoniidae
''Lamingtonium'' is the only genus in the family Lamingtoniidae, of the beetle superfamily Cucujoidea. It contains three species endemic to Australia.Lawrence, J. F., and Leschen, R. A. B. (2003). Review of Lamingtoniidae (Coleoptera: Cucujoidea) with descriptions of two new species. In ‘Systematics of Coleoptera: Papers Celebrating the Retirement of Ivan Löbl’. (Eds G. Cuccodoro and R. A. B. Leschen.) pp 905–919. (International Associated Publishers, Memoirs on Entomology, International, Volume 17.) (Associated Publishers: Gainesville, FL, USA.) The holotype of the type species was collected on at Lamington National Park, Binna Burra, Queensland under the bark of a dead tree. The adults and larvae of two species have been found associated with basidiocarps of fungi belonging to the family Polyporaceae The Polyporaceae are a family of poroid fungi belonging to the Basidiomycota. The flesh of their fruit bodies varies from soft (as in the case of the dryad's saddle i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Myanmar
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)