|
All Saints' Church, Shuart
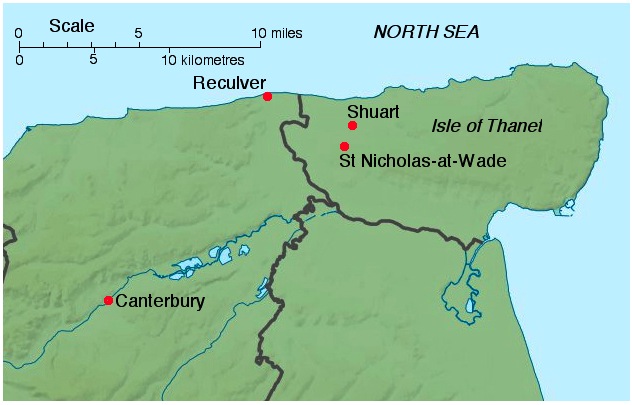
All Saints' Church, Shuart (), in the north-west of the Isle of Thanet, Kent, in the south-east of England, was established in the Anglo-Saxon period as a chapel of ease for the parish of St Mary's Church, Reculver, which was centred on the north-eastern corner of mainland Kent, adjacent to the island. The Isle of Thanet was then separated from the mainland by the sea, which formed a strait known as the Wantsum Channel. The last church on the site was demolished by the early 17th century, and there is nothing remaining above ground to show that a church once stood there. The area of the Isle of Thanet where All Saints' Church stood had been settled since the Bronze Age, and land in the west of the Isle of Thanet was given to the church at Reculver in the 7th century. All Saints' Church remained a chapel of ease for the parish of Reculver until the early 14th century, when the parish was broken up to form separate parishes for Herne and St Nicholas-at-Wade. The area served by Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map NE Kent With Shuart
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deserted Medieval Village
In the United Kingdom, a deserted medieval village (DMV) is a former settlement which was abandoned during the Middle Ages, typically leaving no trace apart from earthworks or cropmarks. If there are fewer than three inhabited houses the convention is to regard the site as deserted; if there are more than three houses, it is regarded as a shrunken medieval village. There are estimated to be more than 3,000 DMVs in England alone. Other deserted settlements Not all sites are medieval: villages reduced in size or disappeared over a long period, from as early as Anglo-Saxon times to as late as the 1960s, due to numerous different causes. Reasons for desertion Over the centuries, settlements have been deserted as a result of natural events, such as rivers changing course or silting up, flooding (especially during the wet 13th and 14th centuries) as well as coastal and estuarine erosion or being overwhelmed by windblown sand. Many were thought to have been abandoned due to the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monkton, Kent
Monkton is a village and civil parish in the Thanet District of Kent, England. The village is located at the south-west edge of the Isle of Thanet and is situated mainly along the B2047 road, leading off the A253 road between Canterbury and Ramsgate. The civil parish stretches south to the River Stour and northwards towards Acol. The hamlet of Gore Street is included in the parish. Community Monkton was subject to an explosion during 2007, and was largely evacuated as a result. Kent Fire and Rescue Service said that crews were faced with "a well developed fire in a large single-storey building", which was among the largest in the village. Monkton Nature Reserve, run by the environmental charity, Thanet Countryside Trust, is situated on chalk hills to the north of the village. The reserve is set in a abandoned chalk quarry which has been reclaimed by nature. It is notable for its geology and many important habitats, a pond and rare orchids. It also houses the Thanet Astronom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westgate-on-Sea
Westgate-on-Sea is a seaside town and civil parish on the north-east coast of Kent, England. It is within the Thanet local government district and borders the larger seaside resort of Margate. Its two sandy beaches have remained a popular tourist attraction since the town's development in the 1860s from a small farming community. The town had a population of 6,996 at the 2011 Census. The town is notable for once being the location of a Royal Naval Air Service seaplane base at St Mildred's Bay, which defended the Thames Estuary coastal towns during World War I. The town is the subject of Sir John Betjeman's poem, "Westgate-on-Sea". Residents have included the 19th-century surgeon Sir Erasmus Wilson and former archbishop of Canterbury William Temple. The artist Sir William Quiller Orchardson painted several of his best-known pictures whilst living in Westgate-on-Sea. The British composer Arnold Cooke attended the town's Streete Preparatory School in the early 20th century, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minster-in-Thanet
Minster, also known as Minster-in-Thanet, is a village and civil parish in the Thanet District of Kent, England. It is the site of Minster in Thanet Priory. The village is west of Ramsgate (which is the post town) and to the north east of Canterbury; it lies just south west of Kent International Airport and just north of the River Stour. Minster is also the "ancient capital of Thanet".Minster-In-Thanet ; retrieved on 22 May 2008 At the 2011 Census the hamlet of Ebbsfleet was included. Toponymy The name ultimately comes from the ''monasterium'', denoting the hi ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Monastery
A double monastery (also dual monastery or double house) is a monastery combining separate communities of monks and of nuns, joined in one institution to share one church and other facilities. The practice is believed to have started in the East at the dawn of monasticism. It is considered more common in the monasticism of Eastern Christianity, where it is traceable to the 4th century. In the West the establishment of double monasteries became popular after Columbanus and sprang up in Gaul and in Anglo-Saxon England. Double monasteries were forbidden by the Second Council of Nicaea in 787, though it took many years for the decree to be enforced.Hefele 385. Double monasteries were revived again after the 12th century in a significantly different wayParisse 1258. when a number of religious houses were established on this pattern among Benedictines and possibly the Dominicans. The 14th-century Bridgittines were purposely founded using this form of community. In the Roman church, monk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbess
An abbess (Latin: ''abbatissa''), also known as a mother superior, is the female superior of a community of Catholic nuns in an abbey. Description In the Catholic Church (both the Latin Church and Eastern Catholic), Eastern Orthodox, Coptic and Anglican abbeys, the mode of election, position, rights, and authority of an abbess correspond generally with those of an abbot. She must be at least 40 years old and have been a nun for 10 years. The age requirement in the Catholic Church has evolved over time, ranging from 30 to 60. The requirement of 10 years as a nun is only eight in Catholicism. In the rare case of there not being a nun with the qualifications, the requirements may be lowered to 30 years of age and five of those in an "upright manner", as determined by the superior. A woman who is of illegitimate birth, is not a virgin, has undergone non-salutory public penance, is a widow, or is blind or deaf, is typically disqualified for the position, saving by permission of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domne Eafe
Domne Eafe (; floruit late 7th century), also ''Domneva'', ''Domne Éue'', ''Æbbe'', ''Ebba'', was, according to the Kentish royal legend, a granddaughter of King Eadbald of Kent and the foundress of the double monastery of Minster in Thanet Priory at Minster-in-Thanet during the reign of her cousin King Ecgberht of Kent. A 1000-year-old confusion with her sister Eormenburg means she is often now known by that name. Married to Merewalh of Mercia, she had at least four children. When her two brothers, Æthelred and Æthelberht, were murdered (and subsequently venerated as saintly martyrs) she obtained the land in Thanet to build an abbey, from a repentant King Ecgberht. Her three daughters all went on to become abbesses and saints, the most famous of which, Mildrith, ended up with a shrine in St Augustine's Abbey, Canterbury. Origins According to the Kentish royal legend, Domne Eafe's father was Eormenred, son of King Eadbald of Kent and Emma of Austrasia, and grandson of Æthel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was raised to the status of a Roman province. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by other Celtic tribes during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells ('' musculi'') according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over the sea. Three years later, Claudius directed four legi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Iron Age
The British Iron Age is a conventional name used in the archaeology of Great Britain, referring to the prehistoric and protohistoric phases of the Iron Age culture of the main island and the smaller islands, typically excluding prehistoric Ireland, which had an independent Iron Age culture of its own. The parallel phase of Irish archaeology is termed the Irish Iron Age. The Iron Age is not an archaeological horizon of common artefacts but is rather a locally-diverse cultural phase. The British Iron Age followed the British Bronze Age and lasted in theory from the first significant use of iron for tools and weapons in Britain to the Romanisation of the southern half of the island. The Romanised culture is termed Roman Britain and is considered to supplant the British Iron Age. The tribes living in Britain during this time are often popularly considered to be part of a broadly-Celtic culture, but in recent years, that has been disputed. At a minimum, "Celtic" is a linguistic ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elmham Map Thanet All Saints St Nicholas St Giles
North Elmham is a village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. It covers an area of and had a population of 1,428 in 624 households at the 2001 census, including Gateley and increasing slightly to 1,433 at the 2011 Census. For the purposes of local government, it falls within the Elmham and Mattishall division of Norfolk County Council and the Upper Wensum ward of Breckland District Council. The village is located along the B1145 a route which runs between King's Lynn and Mundesley. The village is about north of East Dereham on the west bank of the River Wensum. North Elmham was the site of a pre-Norman cathedral, seat of the Bishop of Elmham until 1075. History The name North Elmham comes from the Old English, meaning "village where elms grow" and is first mentioned in 1035. Only ruins now survive of a Norman Chapel which is now looked after by English Heritage. The chapel is on the site of an earlier Anglo Saxon timber cathedral which housed the episc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |