|
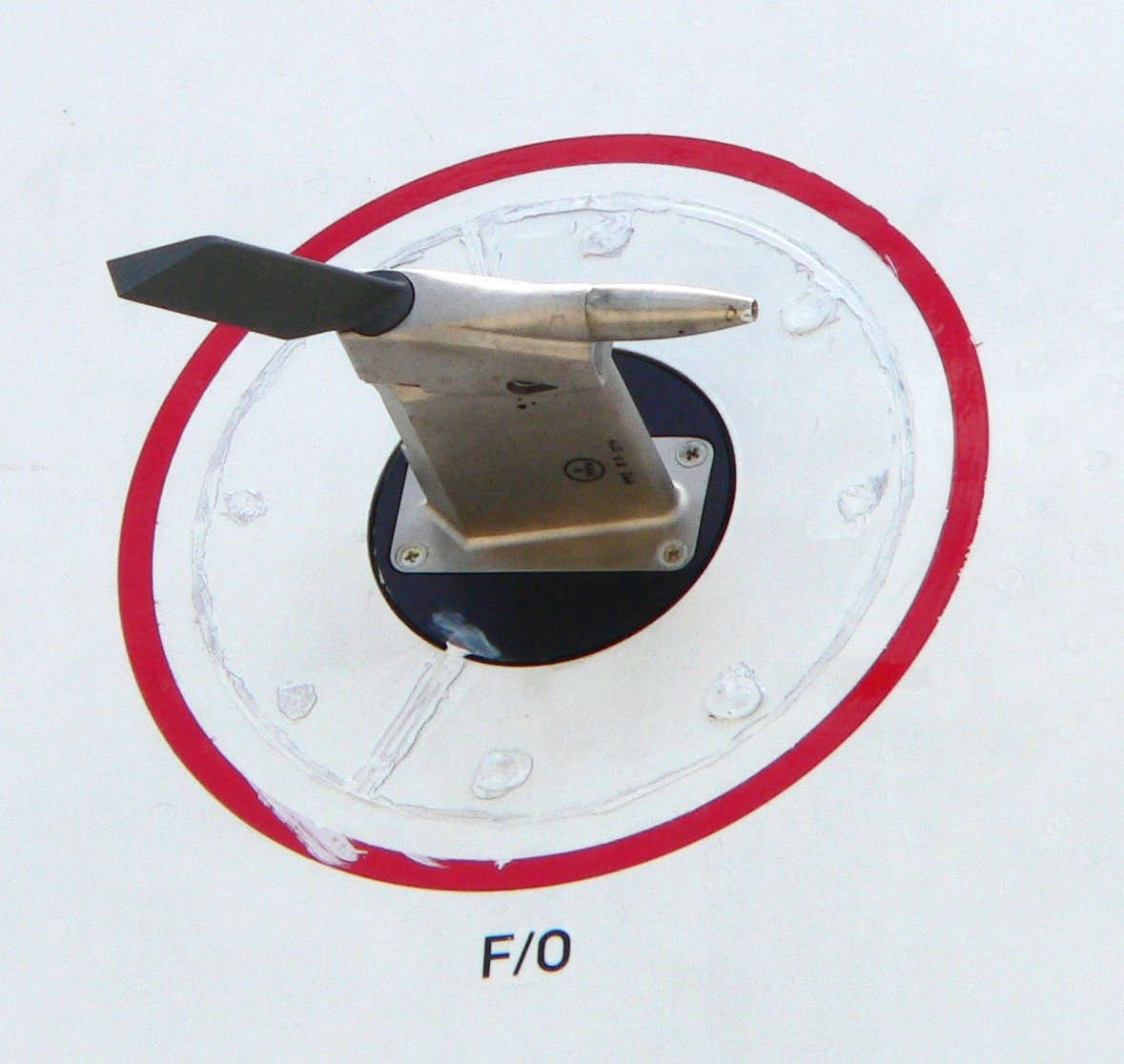
Air Data Boom
An air data boom provides air pressure, temperature, and airflow direction data to data acquisition systems for the computation of air, ground, and water vehicle orientation, speed, altitude/depth, and related information. Air data booms can be used as primary sensors or as a "measurement standard" of which primary sensors and instruments are compared to. Purpose and overview An air data boom is used to collect source data during the testing of air vehicles, ground vehicles, and water-borne vessels. The air data boom is mounted on the vehicle in a location that allows for relatively undisturbed air to be measured. To attain such undisturbed air, mounting is usually done on the nose, wing, or upper horizontal stabilizer of the vehicle. Typical components Air data booms may measure one, some, or all of these capabilities: * angle of attack (AoA, alpha) * angle of sideslip (AoS, beta) * static pressure (Ps) * total pressure (Pt, pitot pressure) * outside air temperature (OAT) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American X-15
The North American X-15 is a hypersonic rocket-powered aircraft. It was operated by the United States Air Force and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration as part of the X-plane series of experimental aircraft. The X-15 set speed and altitude records in the 1960s, reaching the edge of outer space and returning with valuable data used in aircraft and spacecraft design. The X-15's highest speed, , was achieved on 3October 1967, when William J. Knight flew at Mach6.7 at an altitude of , or 19.34miles. This set the official world record for the highest speed ever recorded by a crewed, powered aircraft, which remains unbroken. During the X-15 program, 12pilots flew a combined 199flights. Of these, 8pilots flew a combined 13flights which met the Air Force spaceflight criterion by exceeding the altitude of , thus qualifying these pilots as being astronauts; of those 13flights, two (flown by the same civilian pilot) met the FAI definition () of outer space. The 5Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodrich Corporation
The Goodrich Corporation, formerly the B.F. Goodrich Company, was an American manufacturing company based in Charlotte, North Carolina. Founded in Akron, Ohio in 1870 as Goodrich, Tew & Co. by Benjamin Goodrich, the company name was changed to the "B.F. Goodrich Company" in 1880, to BFGoodrich in the 1980s, and to "Goodrich Corporation" in 2001. Originally a rubber manufacturing company known for automobile tires, the company diversified its manufacturing businesses throughout the twentieth century and sold off its tire business in 1986 to focus on its other businesses, such as aerospace and chemical manufacturing. The BFGoodrich brand name continues to be used by Michelin, who acquired the tire manufacturing business in 1988. Following the acquisition by United Technologies in 2012, Goodrich became a part of UTC Aerospace Systems. In 1869, Benjamin Goodrich purchased the Hudson River Rubber Company, a small business in Hastings-on-Hudson, New York. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Air Temperature
In aviation, stagnation temperature is known as total air temperature and is measured by a temperature probe mounted on the surface of the aircraft. The probe is designed to bring the air to rest relative to the aircraft. As the air is brought to rest, kinetic energy is converted to internal energy. The air is compressed and experiences an adiabatic increase in temperature. Therefore, total air temperature is higher than the static (or ambient) air temperature. Total air temperature is an essential input to an air data computer in order to enable the computation of static air temperature and hence true airspeed. The relationship between static and total air temperatures is given by: \frac = where: *T_= static air temperature, SAT (kelvins or degrees Rankine) *T_\mathrm= total air temperature, TAT (kelvins or degrees Rankine) *M_= Mach number *\gamma\ =\, ratio of specific heats, approx 1.400 for dry air In practice, the total air temperature probe will not perfectly recover t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitot Tube
A pitot ( ) tube (pitot probe) measures fluid flow velocity. It was invented by a French engineer, Henri Pitot, in the early 18th century, and was modified to its modern form in the mid-19th century by a French scientist, Henry Darcy. It is widely used to determine the airspeed of aircraft; the water speed of boats; and the flow velocity of liquids, air, and gases in industry. Theory of operation The basic pitot tube consists of a tube pointing directly into the fluid flow. As this tube contains fluid, a pressure can be measured; the moving fluid is brought to rest (stagnates) as there is no outlet to allow flow to continue. This pressure is the stagnation pressure of the fluid, also known as the total pressure or (particularly in aviation) the pitot pressure. The measured stagnation pressure cannot itself be used to determine the fluid flow velocity (airspeed in aviation). However, Bernoulli's equation states: :Stagnation pressure = static pressure + dynamic pressure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitot-static System
A pitot-static system is a system of pressure-sensitive instruments that is most often used in aviation to determine an aircraft's airspeed, Mach number, altitude, and altitude trend. A pitot-static system generally consists of a pitot tube, a static port, and the pitot-static instruments. Other instruments that might be connected are air data computers, flight data recorders, altitude encoders, cabin pressurization controllers, and various airspeed switches. Errors in pitot-static system readings can be extremely dangerous as the information obtained from the pitot static system, such as altitude, is potentially safety-critical. Several commercial airline disasters have been traced to a failure of the pitot-static system. Pitot-static pressure The pitot-static system of instruments uses the principle of air pressure gradient. It works by measuring pressures or pressure differences and using these values to assess the speed and altitude. These pressures can be measured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuselage as the reference line (and also as the longitudinal axis). Some a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
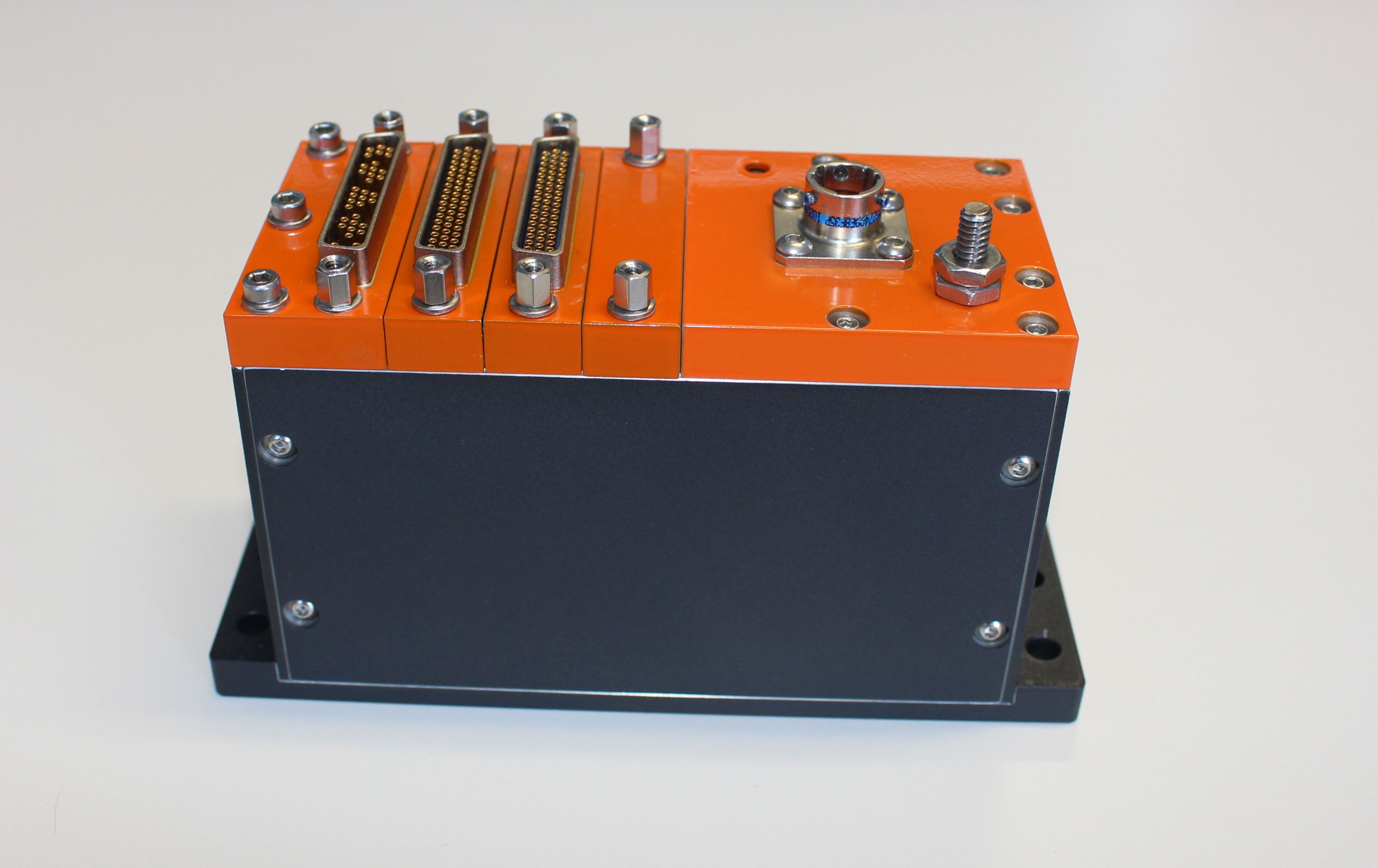
Flight Test Instrumentation
Flight test instrumentation (FTI) is monitoring and recording equipment fitted to aircraft during flight test. It is mainly used on experimental aircraft, prototype aircraft and development aircraft - both military and civil, and can monitor various parameters from the temperatures of specific components to the speed of the engines. This may be displayed in the cockpit or cabin to allow the aircrew to monitor the aircraft in flight, and is usually recorded to allow the data to be analysed later. FTI typically monitors between 10 and 120000 parameters - for example temperatures inside the cargo and pressure distribution along the wing. FTI sources could be temperature sensors, pressure probes, voltages, current transducers, potentiometers, strain gauges, aircraft data buses or cameras. These sensors may be digitalized and acquired by the data acquisition Data acquisition is the process of sampling signals that measure real-world physical conditions and converting the resulting sampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Test
Flight testing is a branch of aeronautical engineering that develops specialist equipment required for testing aircraft behaviour and systems. Instrumentation systems are developed using proprietary transducers and data acquisition systems. Data is sampled during the flight of an aircraft, or atmospheric testing of launch vehicles and reusable spacecraft. This data is validated for accuracy and analyzed before being passed to specialist engineering groups for further analysis to validate the design of the vehicle. The flight test phase accomplishes two major tasks: 1) finding and fixing any design problems and then 2) verifying and documenting the vehicle capabilities for government certification or customer acceptance. The flight test phase can range from the test of a single new system for an existing vehicle to the complete development and certification of a new aircraft, launch vehicle, or reusable spacecraft. Therefore, the duration of a particular flight test program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UTC Aerospace Systems
UTC Aerospace Systems (UTAS) was one of the world’s largest suppliers of aerospace and defense products, headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina, United States. The company was formed in August 2012 when parent United Technologies Corporation merged their existing subsidiary Hamilton Sundstrand with the newly-acquired Goodrich Corporation. In 2018, UTC acquired Rockwell Collins which was merged to form Collins Aerospace. Products UTC Aerospace Systems was engaged in designing, manufacturing and servicing systems and components for commercial, regional, business and military aircraft, helicopters and other platforms. UTC Aerospace Systems was also a major supplier to international space programs. UTC Aerospace Systems had two main segments: Aircraft Systems and Power, Control & Sensing Systems. These segments were then broken down into several business units. The Aircraft Systems consisted of Actuation & Propeller Systems, Aerostructures, Air Management Systems, Interiors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceAge Control
SpaceAge Control is a design, manufacturing, and service company focused on 3D displacement sensing and measurement. The company has supplied precision displacement sensors to industries worldwide since 1969. During its history, the company created ongoing displacement sensing innovations starting with miniature and subminiature string potentiometers (1968) and 2D and 3D cable-actuated displacement sensors (1974). History SpaceAge Control was established in 1968 to design, develop, and manufacture pilot protection devices in support of space-based and high-performance test aircraft programs. In 1970, the company was awarded a NASA contract to produce precision, small-format position transducers for aircraft flight control testing. The successful completion of this contract led to the development and production of a complete line of innovative, small-size position transducers. In 1974, the company was tasked with producing a multi-dimensional "swivel head" air data probe to en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
100600-style Air Data Boom Diagram
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Air Temperature
In aviation, stagnation temperature is known as total air temperature and is measured by a temperature probe mounted on the surface of the aircraft. The probe is designed to bring the air to rest relative to the aircraft. As the air is brought to rest, kinetic energy is converted to internal energy. The air is compressed and experiences an adiabatic increase in temperature. Therefore, total air temperature is higher than the static (or ambient) air temperature. Total air temperature is an essential input to an air data computer in order to enable the computation of static air temperature and hence true airspeed. The relationship between static and total air temperatures is given by: \frac = where: *T_= static air temperature, SAT (kelvins or degrees Rankine) *T_\mathrm= total air temperature, TAT (kelvins or degrees Rankine) *M_= Mach number *\gamma\ =\, ratio of specific heats, approx 1.400 for dry air In practice, the total air temperature probe will not perfectly recover t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |