|
Aiptasia Pallida
''Exaiptasia'' is a genus of sea anemone in the family Aiptasiidae, native to shallow waters in the temperate western Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. It is monotypic with a single species, ''Exaiptasia diaphana,'' and commonly known as the brown anemone, glass anemone, pale anemone, or simply as Aiptasia. Description ''Exaiptasia diaphana'' has a slender brownish or whitish translucent column up to long, girdled by two rows of slits through which acontia (threads armed with nematocysts) can protrude. The oral disc, up to wide, has a central mouth surrounded by a whorl of up to 96 variable-length tentacles; a few of these are extra long, the majority are fairly long and a few are short. Distribution and habitat ''Exaiptasia diaphana'' is a common species of sea anemone occurring in the western Atlantic Ocean, round the coast of the United States from Maine to Florida, and throughout the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. It occurs in a range of hab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Agassiz
Jean Louis Rodolphe Agassiz ( ; ) FRS (For) FRSE (May 28, 1807 – December 14, 1873) was a Swiss-born American biologist and geologist who is recognized as a scholar of Earth's natural history. Spending his early life in Switzerland, he received a PhD at Erlangen and a medical degree in Munich. After studying with Georges Cuvier and Alexander von Humboldt in Paris, Agassiz was appointed professor of natural history at the University of Neuchâtel. He emigrated to the United States in 1847 after visiting Harvard University. He went on to become professor of zoology and geology at Harvard, to head its Lawrence Scientific School, and to found its Museum of Comparative Zoology. Agassiz is known for observational data gathering and analysis. He made institutional and scientific contributions to zoology, geology, and related areas, including multivolume research books running to thousands of pages. He is particularly known for his contributions to ichthyological classification, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
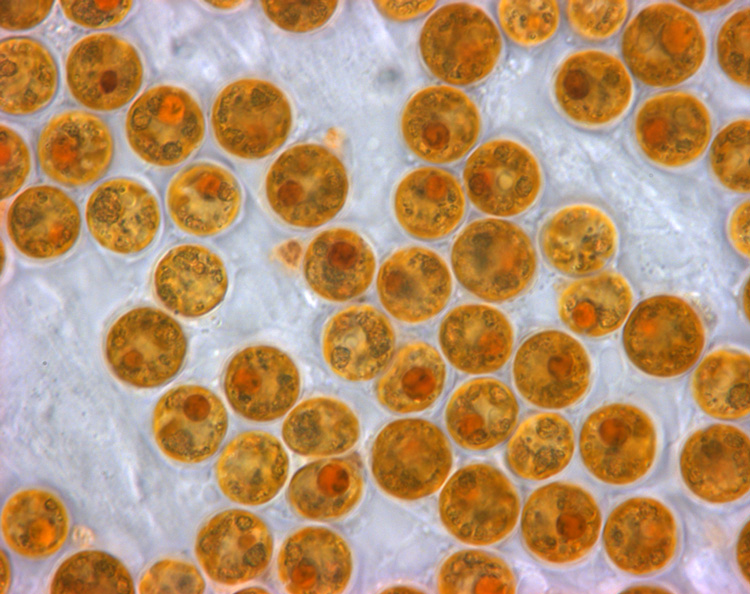
Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus '' Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexacorallia Genera
Hexacorallia is a class of Anthozoa comprising approximately 4,300 species of aquatic organisms formed of polyps, generally with 6-fold symmetry. It includes all of the stony corals, most of which are colonial and reef-forming, as well as all sea anemones, and zoanthids, arranged within five extant orders. The hexacorallia are distinguished from another class of Anthozoa, Octocorallia, in having six or fewer axes of symmetry in their body structure; the tentacles are simple and unbranched and normally number more than eight. These organisms are formed of individual soft polyps which in some species live in colonies and can secrete a calcite skeleton. As with all Cnidarians, these organisms have a complex life cycle including a motile planktonic phase and a later characteristic sessile phase. Hexacorallia also include the significant extinct order of rugose corals. Phylogeny Hexacorallia is considered to be monophyletic, that is all contained species are descended from a common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle sequenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reef Aquarium
A reef aquarium or reef tank is a marine aquarium that prominently displays live corals and other marine invertebrates as well as fish that play a role in maintaining the tropical coral reef environment. A reef aquarium requires appropriately intense lighting, turbulent water movement, and more stable water chemistry than fish-only marine aquaria, and careful consideration is given to which reef animals are appropriate and compatible with each other. Components Reef aquariums consist of a number of components, in addition to the livestock, including: *Display tank: The primary tank in which the livestock are kept and shown. *Stand: A stand allows for placement of the display tank at eye level and provides space for storage of the accessory components. *Sump: An accessory tank in which mechanical equipment is kept. A remote sump allows for a clutter-free display tank. *Refugium: An accessory tank dedicated to the cultivation of beneficial macroalgae and microflora/fauna. The re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spurilla Neapolitana
''Spurilla neapolitana'', the Neapolitan spurilla, is a species of sea slug, an aeolid nudibranch, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Aeolidiidae. It is native to the western Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. This species was first described as ''Eolis neapolitana'' by the Italian naturalist Stefano delle Chiaje in 1841. However, although some authorities quote the year as 1823, the species does not appear in the first volume of delle Chiaje's memoirs, which was published that year. The species was later reassigned to the genus '' Spurilla''. Distribution ''Spurilla neapolitana'' is found in shallow temperate waters in the Mediterranean Sea, the western Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico and Baja California. Molecular studies have shown that this is a species complex consisting of at least three species. The type ''Spurilla neapolitana'' is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, from Cape Verde and the Azores to Portugal, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berghia Stephanieae
''Berghia stephanieae'' is a species of sea slug, an aeolid nudibranch. It is a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Aeolidiidae. It was previously known as ''Aeolidiella stephanieae''. Distribution The range of this species is from the most northern point 25.7°N, to the most southern 25.09°N, and from the most western 80.44°W, to the most eastern 80.2°W."''Aeolidiella stephanieae'' Valdés, 2005" Malacolog Version 4.1.1. A Database of Western Atlantic Marine Mollusca, accessed 20 February 2010. This is one of the most commonly sold aeolid nudibranchs in the marine trade in |
Berghia Coerulescens
''Berghia coerulescens'' is a species of sea slug, a marine nudibranch in the family (biology), family Aeolidiidae.Gofas, S. (2010) ''Berghia coerulescens'' (Laurillard, 1830).In: Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S.; Rosenberg, G. (2010) World Marine Mollusca database. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species on 2011-03-10 It is the type speciesCarmona L., Pola M., Gosliner T.M. & Cervera J.L. (2014)The Atlantic-Mediterranean genus ''Berghia'' Trinchese, 1877 (Nudibranchia: Aeolidiidae): taxonomic review and phylogenetic analysis.Journal of Molluscan Studies. 80(5): 482-498. of the genus ''Berghia''. Distribution Originally described from the French Mediterranean coast, this species is also known from different localities along the central and western Mediterranean (including the Adriatic Sea). It also occurs in the Atlantic Ocean, from the Brittany coasts to the Canary Islands. The geographic distribution of this species has been controversial. Some specimens of ''Berghia marcusi'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nudibranch
Nudibranchs () are a group of soft-bodied marine gastropod molluscs which shed their shells after their larval stage. They are noted for their often extraordinary colours and striking forms, and they have been given colourful nicknames to match, such as "clown", "marigold", "splendid", "dancer", "dragon", or "sea rabbit". Currently, about 3,000 valid species of nudibranchs are known.Ocean Portal (2017)A Collage of Nudibranch Colors Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. Retrieved 17 April 2018. The word "nudibranch" comes from the Latin "naked" and the Ancient Greek () "gills". Nudibranchs are often casually called sea slugs, as they are a family of opistobranchs (sea slugs), within the phylum Mollusca (molluscs), but many sea slugs belong to several taxonomic groups which are not closely related to nudibranchs. A number of these other sea slugs, such as the photosynthetic ''Sacoglossa'' and the colourful Aglajidae, are often confused with nudibranchs. Distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey (phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, ''Oodinium'' and ''Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. The organisms, each termed a symbiont, must be of different species. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term was subject to a century-long debate about whether it should specifically denote mutualism, as in lichens. Biologists have now abandoned that restriction. Symbiosis can be obligatory, which means that one or more of the symbionts depend on each other for survival, or facultative (optional), when they can generally live independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. When symbionts form a single body it is called conjunctive symbiosis, while all other arrangements are called disjunctive symbiosis."symbiosis." Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |