|
Ahmose Called Turo
Ahmose called Turo (also Ture, Thure or Thuwre) was Viceroy of Kush under Amenhotep I and Thutmose I. George A. Reisner, ''The Viceroys of Ethiopia'', The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology, Vol. 6, No. 1. (Jan. 1920), pp. 28-55. Ahmose called Turo was a son of Ahmose called Si-Tayit. Turo's son Ahmose called Patjenna would continue to serve the royal family during the reigns of Hatshepsut and Thutmose III. Turo served under pharaoh Ahmose I as Commander of Buhen. Later he served as King's Son (of the Southern Region) under Amenhotep I (inscriptions in Semna, Uronarti). He served under Thutmose I according to inscriptions dating to year 1 and 3. Turo is mentioned in an inscription at West Silsila belonging to the vizier User. This inscription dates to the reign of Hatshepsut. This may be a posthumous mention of the Viceroy. It's possible there were family connections between Turo and User; Turo is shown leading Vizier Amethu's daughters in procession. (Amethu was User's father). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmose Called Si-Tayit
Ahmose called Si-Tayit was possibly the first Viceroy of Kush. It is possible that the position was held by a son of Pharaoh Ahmose I before Ahmose called Si-Tayit was appointed Viceroy, but there is no conclusive evidence for such a Viceroy.Edwards, The Cambridge ancient history, Volumes 1-3, 2000, pg 299, 348 Before Si-Tayit the power in Kush seems to have been in the hands of a dignitary named Hormeni, who was the mayor of Hierakonpolis. Ahmose called Si-Tayit served as Viceroy under both Ahmose I and Amenhotep I. Early in the reign of Amenhotep I, the position passed from Si-Tayit to his son Ahmose called Turo Ahmose called Turo (also Ture, Thure or Thuwre) was Viceroy of Kush under Amenhotep I and Thutmose I. George A. Reisner, ''The Viceroys of Ethiopia'', The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology, Vol. 6, No. 1. (Jan. 1920), pp. 28-55. Ahmose called Turo .... The position of Viceroy was not hereditary, and the position did not pass to Turo's son Patjenna.Boston Museum Bulle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Useramen
Useramen (also called User, Amenuser, or Useramun) was an ancient Egyptian vizier under pharaohs Hatshepsut and Thutmose III of the 18th Dynasty. Family Useramen was the son of the vizier Amethu called Ahmose, who served during the reign of Thutmose II and the early years of the combined reigns of Hatshepsut and Thutmose III.Hatshepsut by Anneke Bart His mother's name was Ta-amenthu. Useramen was married to a lady named Tuiu, and the couple is known from their tombs to have had at least four daughters and a son.Porter,B. and Moss R.L.B., Topographical Bibliography of Ancient Egyptian Hieroglyphic Texts, Reliefs and Paintings: The Theban Necropolis, Part One: Private Tombs. Second Edition. Griffith Institute. Oxford. 1994 Useramen came from a very influential family. His father was vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labib Habachi
Labib Habachi (لبيب حبشي) (April 18, 1906 – February 18, 1984) was an influential Coptic Egyptian Egyptologist. Dr Habachi spent 30 years in the Antiquities Department of the Egyptian Government, ending his career as Chief inspector. During this period he spent an enormous amount of time in numerous dig sites in Egypt and the Sudan. He left government work to accept a position at the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago as an Archaeological Consultant to its Nubian Expedition. Tell el-Dab'a Between 1929 and 1939, Pierre Montet excavated at Tanis, finding the royal necropolis of the Twenty-first and Twenty-second Dynasties — the finds there almost equalled that of Tutankhamun's tomb in the Valley of the Kings. He believed that he found the location of Avaris, and this opinion was widely accepted at the time. Yet Habachi was not convinced. In 1941-42 he worked at Tell el-Dab'a for the Egyptian Antiquities Service and came to the conclusion that thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
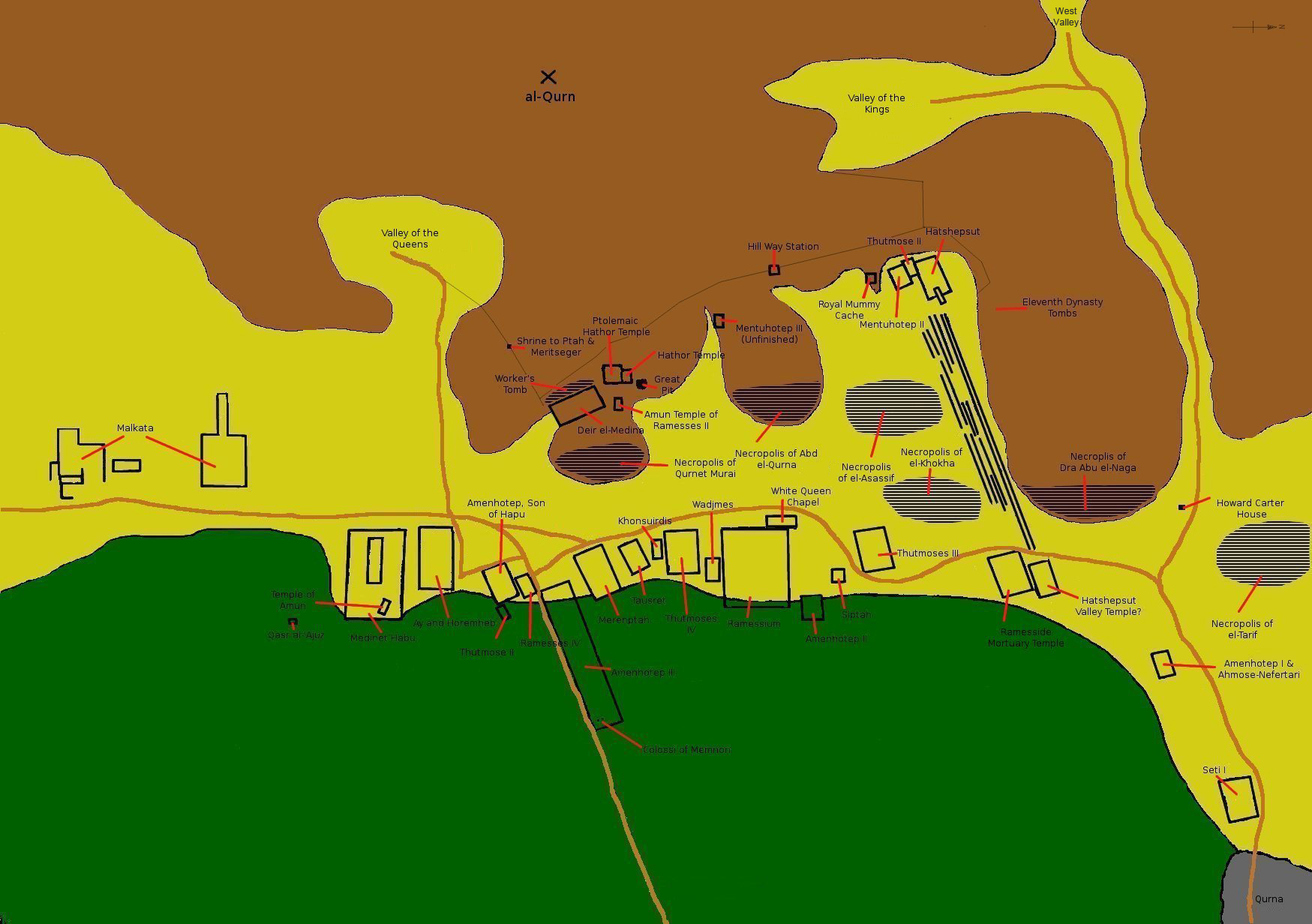
Theban Necropolis
The Theban Necropolis is a necropolis on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes (Luxor) in Upper Egypt. It was used for ritual burials for much of the Pharaonic period, especially during the New Kingdom. Mortuary temples * Deir el-Bahri ** Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut ** Mortuary temple of Mentuhotep II ** Mortuary temple of Thutmose III * Medinet Habu ** Mortuary temple and palace of Ramesses III ** Mortuary Temple of Ay & Horemheb * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep III ** Colossi of Memnon * Mortuary Temple of Merneptah * Mortuary Temple of Ramesses IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose III * Mortuary Temple of Twosret * Temple of Nebwenenef * Qurna ** Mortuary Temple of Seti I * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep II * Ramesseum (Mortuary Temple of Ramesses II) Royal Necropolis * Valley of the Kings (Modern: "''Wadi el-Muluk''") * Valley of the Queens (Modern: "''Biban el-Harim''") * Royal Cache * Bab el-Gasus Necropolis * Deir el-Medina ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funerary Cone
Funerary cones were small cones made from clay that were used in ancient Egypt, almost exclusively in the Theban Necropolis. The items were placed over the entrance of the chapel of a tomb. Early examples have been found from the Eleventh Dynasty. However, they are generally undecorated. During the New Kingdom, the cones were smaller in size and inscribed in hieroglyphs with the title and name of the tomb owner, often with a short prayer. The exact purpose of the cones is unknown, but hypotheses exist that they variously served as passports, architectural features, and symbolic offerings, among others. Funerary cones were first organized into a corpus by Davies and Macadam (1957). This catalog was later supplemented by Vivo and Costa (1997). In the 21st century, Dibley and Lipkin (2009) and Zenihiro (2009) have compiled more complete publications, with Theis (2017) contributing additional cones from books, articles, auction and exhibition catalogues for consideration. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deir El-Bahari
Deir el-Bahari or Dayr al-Bahri ( ar, الدير البحري, al-Dayr al-Baḥrī, the Monastery of the North) is a complex of mortuary temples and tombs located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the city of Luxor, Egypt. This is a part of the Theban Necropolis. The first monument built at the site was the mortuary temple of Mentuhotep II of the Eleventh Dynasty. It was constructed during the 21st century BC. During the Eighteenth Dynasty, Amenhotep I and Hatshepsut also built extensively at the site. Mortuary temple of Nebhepetre Mentuhotep Mentuhotep II, the Eleventh Dynasty king who reunited Egypt at the beginning of the Middle Kingdom, built a very unusual funerary complex. His mortuary temple was built on several levels in the great bay at Deir el-Bahari. It was approached by a 16-metre-wide (50-ft) causeway leading from a valley temple which no longer exists. The mortuary temple itself consists of a forecourt and entrance gate, enclosed by walls on three si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Egypt
, image = Decorated pillars of the temple at Karnac, Thebes, Egypt. Co Wellcome V0049316.jpg , alt = , caption = Pillars of the Great Hypostyle Hall, in '' The Holy Land, Syria, Idumea, Arabia, Egypt, and Nubia'' , map_type = Egypt , map_alt = , map_size = , relief = yes , coordinates = , location = Luxor, Luxor Governorate, Egypt , region = Upper Egypt , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = , abandoned = , epochs = , cultures = , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = , excavations = , archaeologists = , condition = , ownership = , management = , public_access = , website = , notes = , designation1 = WHS , designation1_offname = Ancient T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Cataract
The Cataracts of the Nile are shallow lengths (or whitewater rapids) of the Nile river, between Khartoum and Aswan, where the surface of the water is broken by many small boulders and stones jutting out of the river bed, as well as many rocky islets. In some places, these stretches are punctuated by whitewater, while at others the water flow is smoother but still shallow. The Six Cataracts Counted going upstream (from north to south): In Egypt: *The First Cataract cuts through Aswan (). Its former location was selected for the construction of Aswan Low Dam, the first dam built across the Nile. In Sudan: *The Second Cataract (or Great Cataract) was in Nubia and is now submerged under Lake Nasser. () *The Third Cataract is at Tombos (Nubia), Tombos/Hannek. () *The Fourth Cataract is in the Dar al-Manasir, Manasir Desert, and since 2008, is submerged under the reservoir of Merowe Dam. () *The Fifth Cataract is near the confluence of the Nile and Atbarah Rivers. () *The Sixth Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senusret III
Khakaure Senusret III (also written as Senwosret III or the hellenised form, Sesostris III) was a pharaoh of Egypt. He ruled from 1878 BC to 1839 BC during a time of great power and prosperity, and was the fifth king of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. He was a great pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty and is considered to be, perhaps, the most powerful Egyptian ruler of the dynasty. Consequently, he is regarded as one of the sources for the legend about Sesostris. His military campaigns gave rise to an era of peace and economic prosperity that reduced the power of regional rulers and led to a revival in craftwork, trade, and urban development."''The Pyramids: Their Archeology and History''", Miroslav Verner, Translated by Steven Rendall,p386-387 & p416-421, Atlantic, Senusret III was among the few Egyptian kings who were deified and honored with a cult during their own lifetime. Family Senusret III was the son of Senusret II and Khenemetneferhedjet I, also called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sehel Island
Sehel Island () is located in the Nile, about southwest of Aswan in southern Egypt. It is a large island, and is roughly halfway between the city and the upstream Aswan Low Dam. Geography Sehel Island, spanning 3/4 the width of the Nile, is the primary large island below the Nile's First Cataract and the Aswan Low Dam (1902). Following downriver, the next major islands after Sehel are: Saluga, Ambunarti, Elephantine, and then Kitchener's Island. There are a dozen smaller islands scattered around them. Archaeological artefacts The island was known in ancient tiles as ''Setet'', and there are many archaeological sites, including sacred places, such as the temple of Anuket, the Egyptian water goddess, and goddess of the Nile's cataracts. Seheil was home to a stone quarry for granite used during various Ancient Egyptian eras, and there are many inscriptions in the island's granite boulders. These inscriptions were usually left by travellers marking either the start or end of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Henry Breasted
James Henry Breasted (; August 27, 1865 – December 2, 1935) was an American archaeologist, Egyptologist, and historian. After completing his PhD at the University of Berlin in 1894, he joined the faculty of the University of Chicago. In 1901 he became director of the Haskell Oriental Museum at the university, where he continued to concentrate on Egypt. In 1905 Breasted was promoted to full professor, and held the first chair in Egyptology and Oriental History in the United States. In 1919 he founded the Oriental Institute at the University of Chicago, a center for interdisciplinary study of ancient civilizations. Breasted was a committed field researcher, and had a productive interest in recording and interpreting ancient writings, especially from sources and structures that he feared may be lost forever. Early life and education James Henry Breasted was born on August 27, 1865, the son of a small hardware business owner and his wife, in Rockford, Illinois. His ancestors went ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
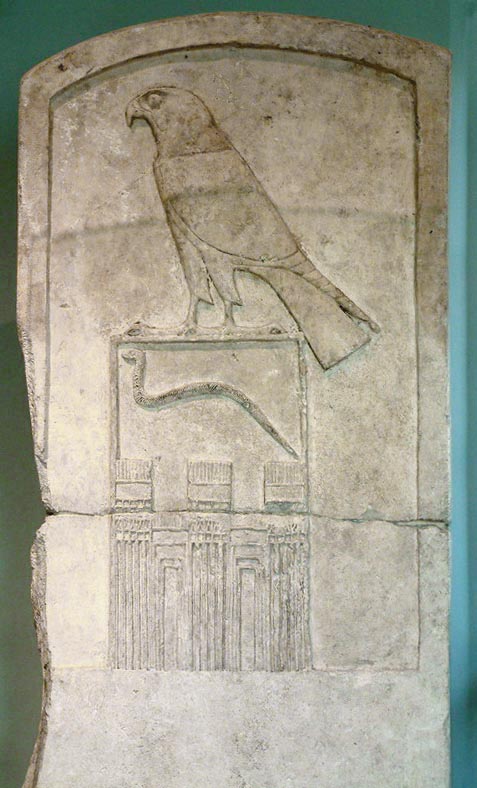
Ancient Egyptian Royal Titulary
The royal titulary or royal protocol is the standard naming convention taken by the pharaohs of ancient Egypt. It symbolised worldly power and holy might, also acting as a sort of mission statement for the duration of a monarch's reign (although sometimes it even changed during the reign). The full titulary, consisting of five names, did not come into standard usage until the Middle Kingdom but remained in use as late as the Roman Empire. Origins In order that the pharaoh, who held divine office, could be linked to the people and the gods, special epithets were created for them at their accession to the throne. These titles also served to demonstrate one's qualities and link them to the terrestrial realm. The five names were developed over the centuries beginning with the Horus name. This name identified the figure as a representative of the god Horus. The Nebty name was the second part of the royal titular of Upper and Lower Egypt. This name placed the king under the protecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |