|
Aftermath Of The Gulf War
The aftermath of Gulf War saw drastic and profoundly significant political, cultural, and social change across the Middle East and even in areas outside those that were directly involved. Palestinian community in Kuwait Significant demographic changes occurred in Kuwait as a result of the Gulf War. There were 400,000 Palestinians in Kuwait before the Gulf War. During the Iraqi occupation of Kuwait, 200,000 Palestinians left Kuwait due to various reasons (fear or persecution, food shortages, medical care difficulties, financial shortages, fear of arrest and mistreatment at roadblocks by Iraqis). After the Gulf War of 1991, nearly 200,000 Palestinians fled Kuwait, partly due to economic burdens, regulations on residence and fear of abuse by Kuwaiti security forces. Kuwait's lack of support for Palestinians after the Gulf War was a response to the alignment of Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat and the PLO with Saddam Hussein, who had earlier invaded Kuwait. On March 14, 1991, 200,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Kuwait
The Iraqi invasion of Kuwait was an operation conducted by Iraq on 2 August 1990, whereby it invaded the neighboring State of Kuwait, consequently resulting in a seven-month-long Iraqi military occupation of the country. The invasion and Iraq's subsequent refusal to withdraw from Kuwait by a deadline mandated by the United NationsUnited Nations Security Council Resolution 660 (Condemning the Invasion of Kuwait by Iraq), S.C. Res. 660, 45 U.N. SCOR at 19, U.N. Doc. S/RES/660 (1990) . umn.edu. Retrieved on 12 June 2011 led to a direct military intervention by a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop Grumman E-8 Joint STARS
The Northrop Grumman E-8 Joint Surveillance Target Attack Radar System (Joint STARS) is a United States Air Force airborne ground surveillance, battle management and command and control aircraft. It tracks ground vehicles and some aircraft, collects imagery, and relays tactical pictures to ground and air theater commanders. The aircraft is operated by both active duty U.S. Air Force and Air National Guard units and also carries specially trained U.S. Army personnel as additional flight crew. Development Joint STARS evolved from separate United States Army and Air Force programs to develop technology to detect, locate and attack enemy armor at ranges beyond the forward area of troops. August 2013. In 1982, the programs were merged and the U.S. Air Force became the lead agent. The concept and sensor technology for the E-8 was developed and tested on the Tacit Blue experimental aircraft. The prime contract was awarded to Grumman Aerospace Corporation in September 1985 for two E- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Peters (RAF)
Squadron Leader John Peters (born 1961) is a former pilot of the Royal Air Force (RAF). Early life He attended the independent Churcher's College in east Hampshire, leaving in 1980. By the age of 17, he had his pilot's licence. He attended the University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology (commonly known as UMIST, now part of the University of Manchester since 2004), gaining a BSc in Building Technology in 1983. He was an RAF university cadet, joining the RAF in 1979, training at RAF Woodvale with the Manchester and Salford Universities Air Squadron. He later graduated with an MBA from the University of Leicester. Career After his RAF training, he was based at RAF Chivenor, RAF Lossiemouth and RAF Laarbruch. He became a staff pilot in 1987 at the Air Navigation School (ANS) of No. 6 Flying Training School at RAF Finningley. In 1988, he moved to XV Squadron at RAF Laarbruch after converting to the Tornado GR1 as a Flight Lieutenant. Gulf War On his first missi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Nichol (RAF Officer)
Adrian John Nichol (born December 1963) is a retired Royal Air Force navigator who was shot down and captured during the Gulf War. Early life Adrian John Nichol was born in North Shields, and attended the St Cuthbert's Grammar School on Gretna Road in Newcastle upon Tyne. He joined the Royal Air Force (RAF) in February 1981 as an electronics technician; having signed up in 1980 and needing sufficient O levels. In the intervening period between school and the RAF, he worked in a large DIY store, although his employers were not aware of his military plans until they sought to promote him to management and he decided to tell them. RAF career Nichol was commissioned as a navigator in December 1986. He served with XV Squadron based at RAF Laarbruch, Germany. During Operation Granby in the Gulf War, the squadron was deployed to Muharraq Airfield in Bahrain. Nichol's first mission, on 17 January 1991, entailed flying as number two to Squadron Leader Paul "Pablo" Mason on an ultra-low- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panavia Tornado
The Panavia Tornado is a family of twin-engine, variable-sweep wing multirole combat aircraft, jointly developed and manufactured by Italy, the United Kingdom and West Germany. There are three primary Tornado variants: the Tornado IDS (interdictor/strike) fighter-bomber, the suppression of enemy air defences Tornado ECR (electronic combat/reconnaissance) and the Tornado ADV (air defence variant) interceptor aircraft. The Tornado was developed and built by Panavia Aircraft GmbH, a tri-national consortium consisting of British Aerospace (previously British Aircraft Corporation), MBB of West Germany, and Aeritalia of Italy. It first flew on 14 August 1974 and was introduced into service in 1979–1980. Due to its multirole design, it was able to replace several different fleets of aircraft in the adopting air forces. The Royal Saudi Air Force (RSAF) became the only export operator of the Tornado in addition to the three original partner nations. A tri-nation training and ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner Of War
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610. Belligerents hold prisoners of war in custody for a range of legitimate and illegitimate reasons, such as isolating them from the enemy combatants still in the field (releasing and repatriating them in an orderly manner after hostilities), demonstrating military victory, punishing them, prosecuting them for war crimes, exploiting them for their labour, recruiting or even conscripting them as their own combatants, collecting military and political intelligence from them, or indoctrinating them in new political or religious beliefs. Ancient times For most of human history, depending on the culture of the victors, enemy fighters on the losing side in a battle who had surrendered and been taken as prisoners of war could expect to be either slaughtered or enslaved. Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East Review Of International Affairs
''Middle East Review of International Affairs'' (MERIA) was a quarterly, peer-reviewed, journal on Middle East issues founded by the late Barry Rubin and edited by Dr. Jonathan Spyer. The journal is no longer active; the last published issue was Vol. 21, No. 3 (Fall/Winter 2017). MERIA was published by the Rubin Center for Research in International Affairs formerly known as Global Research in International Affairs Center (GLORIA) of the Interdisciplinary Center (IDC) in Herzliya, Israel. The Rubin Center for Research in International Affairs also published ''MERIA News'', a monthly magazine on Middle East studies; ''MERIA Research Guides''; and ''MERIABooks'', collections of articles from the journal and other sources. According to Rubin's website for MERIA, the mission of the publication is "to advance research on the Middle East and ofoster scholarly communication and cooperation," and MERIA is a "non-partisan publication involving people across the geographical and political ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Purification
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for human consumption (drinking water), but water purification may also be carried out for a variety of other purposes, including medical, pharmacological, chemical, and industrial applications. The history of water purification includes a wide variety of methods. The methods used include physical processes such as filtration, sedimentation, and distillation; biological processes such as slow sand filters or biologically active carbon; chemical processes such as flocculation and chlorination; and the use of electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light. Water purification can reduce the concentration of particulate matter including suspended particles, parasites, bacteria, algae, viruses, and fungi as well as reduce the concentration of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dick Cheney
Richard Bruce Cheney ( ; born January 30, 1941) is an American politician and businessman who served as the 46th vice president of the United States from 2001 to 2009 under President George W. Bush. He is currently the oldest living former U.S. vice president, following the death of Walter Mondale in 2021. Born in Lincoln, Nebraska, Cheney grew up there and in Casper, Wyoming. He attended Yale University before earning a Bachelor of Arts and Master of Arts in political science from the University of Wyoming. He began his political career as an intern for Congressman William A. Steiger, eventually working his way into the White House during the Nixon and Ford administrations. He served as White House chief of staff from 1975 to 1977. In 1978, he was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives, and represented Wyoming's at-large congressional district from 1979 to 1989, briefly serving as House minority whip in 1989. He was selected as Secretary of Defense during the pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Simpson (journalist)
John Cody Fidler-Simpson (born 9 August 1944) is an English foreign correspondent and world affairs editor of BBC News. He has spent all his working life with the BBC, and has reported from more than 120 countries, including thirty war zones, and interviewed many world leaders. He was educated at Magdalene College, Cambridge, where he read English and was editor of ''Granta'' magazine. Early life and education Simpson was born on 9 August 1944 in Cleveleys, Lancashire, but was taken to his mother's "bomb-damaged house in London" the following week. He says in his autobiography that his father was an anarchist. He spent ten years growing up in Dunwich in Suffolk. He was educated at Dulwich College Preparatory School and St Paul's School, followed by Magdalene College, Cambridge, where he read English and was editor of ''Granta'' magazine. In 1965 he was a member of the Magdalene ''University Challenge'' team. A year later Simpson started as a trainee sub-editor at BBC radio news ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
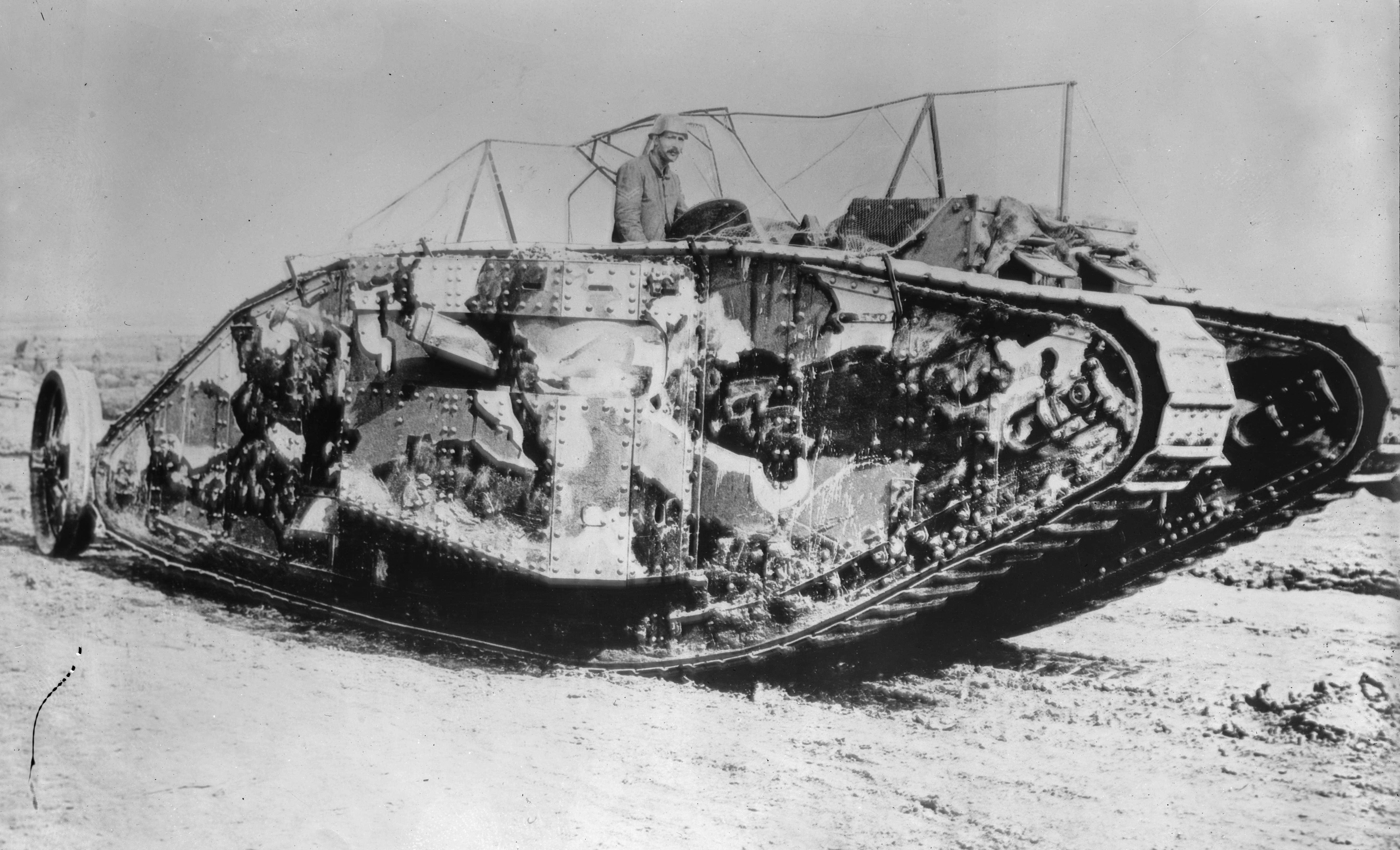
Tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; usually their main armament is mounted in a turret. They are a mainstay of modern 20th and 21st century ground forces and a key part of combined arms combat. Modern tanks are versatile mobile land weapons platforms whose main armament is a large-caliber tank gun mounted in a rotating gun turret, supplemented by machine guns or other ranged weapons such as anti-tank guided missiles or rocket launchers. They have heavy vehicle armour which provides protection for the crew, the vehicle's munition storage, fuel tank and propulsion systems. The use of tracks rather than wheels provides improved operational mobility which allows the tank to overcome rugged terrain and adverse conditions such as mud and ice/snow better than wheeled vehicles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plow
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or steel frame, with a blade attached to cut and loosen the soil. It has been fundamental to farming for most of history. The earliest ploughs had no wheels; such a plough was known to the Romans as an ''aratrum''. Celtic peoples first came to use wheeled ploughs in the Roman era. The prime purpose of ploughing is to turn over the uppermost soil, bringing fresh nutrients to the surface while burying weeds and crop remains to decay. Trenches cut by the plough are called furrows. In modern use, a ploughed field is normally left to dry and then harrowed before planting. Ploughing and cultivating soil evens the content of the upper layer of soil, where most plant-feeder roots grow. Ploughs were initially powered by humans, but the use of farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)

