|
Administrative Division Codes Of The People's Republic Of China
The administrative division codes of the People's Republic of China identify the administrative divisions of China at county level and above. They are published by the National Bureau of Statistics of China with the latest version issued on September 30, 2015. Coding scheme Reading from left to right, administrative division codes contain the following information: * The first and second digits identify the highest level administrative division, which may be a province, autonomous region, municipality or Special Administrative Region (SAR). * Digits three and four show summary data for the associated prefecture-level city, prefecture (地区 ''dìqū''), autonomous prefecture, Mongolian league, municipal city district or county. Codes 01 – 20 and 51 – 70 identify provincial level cities, codes 21 – 50 represent prefectures, autonomous prefectures and Mongolian leagues. *The fifth and sixth digits represent the county-level division – city district, county-level ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North China Administrative Division Codes Of The PRC (Division 1)
List of Administrative division codes of the People's Republic of China, administrative division codes of the PRC in Division 1 or North China. Beijing (11) Tianjin (12) Hebei (13) Shanxi (14) Inner Mongolia (15) {, class="wikitable" align="center" width="1000" , ----- style="background:#FFDF80" , 150000, , Inner Mongolia AR, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , - style="background:#606060; height:2pt" , colspan="10" , , ----- style="background:#CCFFFF" , 150100, , Hohhot city, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ----- style="background:#D3D3D3" , rowspan="2", 150101, , rowspan="2", ''District'', , 150102, , Xincheng District, Hohhot, Xincheng, , 150103, , Huimin District, Huimin, , 150104, , Yuquan District, Yuquan, , 150105, , Saihan District, Saihan , ----- style="background:#D3D3D3" , , , , , , , , , bgcolor="#FFC0CB", 150120, , , , , , , - , 150121, , Tumed Left Banner, Tumedzuo Ban., , 150122, , Togtoh County, Togtoh Co., , 150123, , Horinger County, Horinger Co., , 1501 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Prefecture
Autonomous prefectures ( zh, c=自治州, p=zìzhìzhōu) are one type of autonomous administrative divisions of China, autonomous administrative division in China, existing at the Prefecture-level divisions of China, prefectural level, with either list of ethnic groups in China and Taiwan, ethnic minorities forming over 50% of the population or being, most commonly, the historic home of significant minorities. The official name of an autonomous prefecture includes the most significant minority in that region, sometimes two, rarely three. For example, a prefecture with a large number of Kazakhs (''Kazak'' in official naming system) may be called a ''Kazak Autonomous Prefecture''. Like all other prefectural level divisions, autonomous prefectures are divided into County-level division, county level divisions. There is one exception: Ili Kazak Autonomous Prefecture contains two prefectures of its own. Under the Constitution of the People's Republic of China, autonomous prefectures ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Standards Of The People's Republic Of China
The National Standards of the People's Republic of China (), coded as , are the standards issued by the Standardization Administration of China under the authorization of Article 10 of the Standardization Law of the People's Republic of China. According to Article 2 of the Standardization Law, national standards are divided into mandatory national standards and recommended national standards. Mandatory national standards are prefixed "GB". Recommended national standards are prefixed "". Guidance technical documents are prefixed with "GB/Z", but are not legally part of the national standard system. Mandatory national standards are the basis for the product testing which products must undergo during the China Compulsory Certificate (CCC or 3C) certification. If there is no corresponding mandatory national standard, CCC is not required. Nomenclature A Chinese standard code has three parts: the prefix, the sequential number, and the year number. For example, GB 2312-1980 refers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OKATO
Russian Classification on Objects of Administrative DivisionThe English name of the document is given per the English title included on the document's first page. (), or OKATO (), also called All-Russian classification on units of administrative and territorial distribution in English,''Country Report of the Russian Federation'' submitted to the 12th session of the UN ESCAP Committee on Statistics (pdf) is one of several |
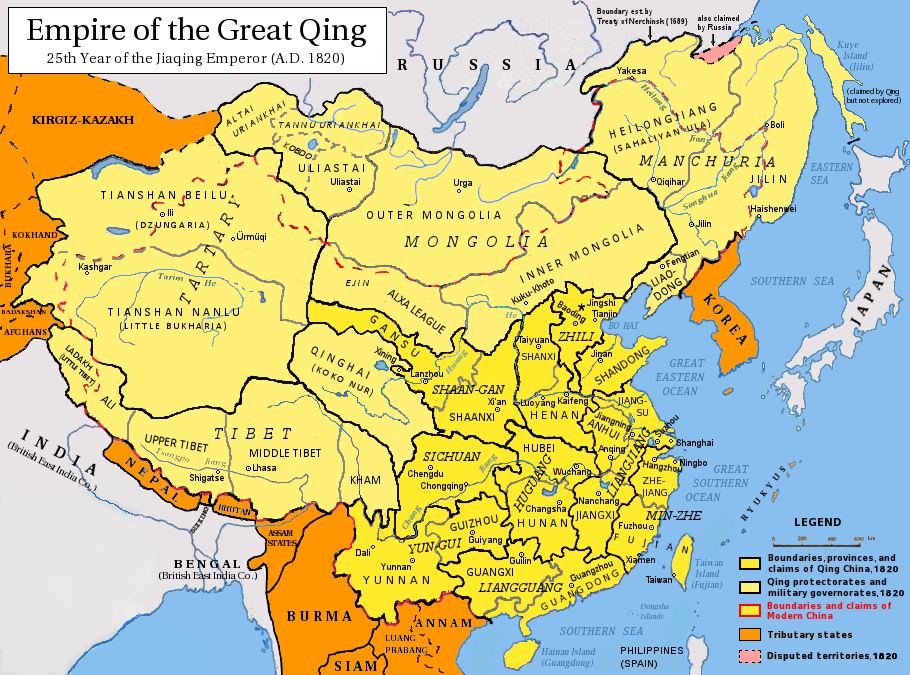
Administrative Divisions Of China
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since 1412, due to mainland China's large population and geographical area. In the People's Republic of China, the constitution provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there are five levels of local government; the provincial (province, autonomous region, municipality, and special administrative region), prefecture, county, township, and village. Since the 17th century, provincial boundaries in mainland China have remained largely static. Major changes since then have been the reorganization of provinces in the northeast after the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949 and the formation of autonomous regions, based on Soviet ethnic policies. The provinces serve an important cultural role in China, as people tend to identify with their native province. Levels The Constitution of the People's Republic of China provides for three levels: the provincial, the county le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuetan Community
{{Beijing-geo-stub ...
The Temple of the Moon () is an altar located in Fuchengmen, Xicheng District, in western Beijing, China. The altar was built in 1530 during the Ming Dynasty for use in ritual sacrifice to the Moon by the Emperor of China. The altar and the surrounding grounds are within a public park. The altar itself is no longer intact, though the surrounding walls remain. See also *Temple of Heaven * Temple of Earth * Temple of the Sun References Buildings and structures completed in 1530 Religious buildings and structures completed in 1530 Major National Historical and Cultural Sites in Beijing Taoist temples in Beijing China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuetan Subdistrict
Yuetan Subdistrict () is a subdistrict on the western side of Xicheng District, Beijing, China. As of 2020, its total population is 97,771. The subdistrict was named after the Temple of the Moon within it. History Administrative Division As of 2021, there are a total of 26 communities A community is a Level of analysis, social unit (a group of people) with a shared socially-significant characteristic, such as place (geography), place, set of Norm (social), norms, culture, religion, values, Convention (norm), customs, or Ide ... within Yuetan Subdistrict: Landmarks * Temple of the Moon * White Cloud Temple * Capital Museum See also * List of township-level divisions of Beijing References External links Official website (Archived) {{authority control Xicheng District Subdistricts of Beijing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xicheng District
Xicheng () is a district of the city of Beijing. Its cover the western half of the old city (largely inside the 2nd Ring Road; the eastern half is Dongcheng District, Beijing, Dongcheng District), and has 1,106,214 inhabitants (2020 Census). Its List of postal codes in China, postal code is 100032. Xicheng is subdivided into 15 subdistricts of the city proper of Beijing. The former Xuanwu District, Beijing, Xuanwu District was merged into Xicheng in July 2010. The Xidan commercial district, Beijing Financial Street, Beihai Park, Jingshan Park, Shichahai, and Zhongnanhai are all within its jurisdiction. The popular Houhai bar area is also in Xicheng Precinct. Before the 1911 Revolution, most royalty and aristocrats resided in the precinct. The oldest Catholic church in Beijing, the Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception, Beijing, Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception is located in Xicheng. Administrative divisions There are 15 Subdistricts of China, subdistricts in the distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages Of China
Villages (), formally village-level divisions () in China, serve as a fundamental organizational unit for its rural population (census, mail system). Basic local divisions like neighborhoods and communities are not informal, but have defined boundaries and designated heads (one per area). In 2000, China's densely populated villages (>100 persons/square km) had a population greater than 500 million and covered more than 2 million square kilometers, or more than 20% of China's total area. By 2020, all incorporated villages (with proper conditions making it possible) had road access, the last village to be connected being a remote village in Sichuan province's Butuo County. Types of villages Urban * Residential community () ** Residents' committee () *** Residential groups ( ;Note: Urban village () one that spontaneously and naturally exists within urban area, which is not an administrative division. Rural * Administrative village or Village () * Hamlet or Band () * Gacha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Division
Administrative divisions (also administrative units, administrative regions, subnational entities, or constituent states, as well as many similar generic terms) are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divided. Such a unit usually has an administrative authority with the power to take administrative or policy decisions for its area. Administrative divisions are often used as polygons in geospatial analysis. Description Usually, sovereign states have several levels of administrative division. Common names for the principal (largest) administrative divisions include: Federated state, states (subnational states, rather than sovereign states), provinces, States of Germany#States, lands, oblasts and Region#Administrative regions, regions. These in turn are often subdivided into smaller administrative units known by names such as comarcas, raions or districts, which are further subdivided into municipality, municipalities, Commune (administrativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banners Of Inner Mongolia
A banner (; ) is an administrative division of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in China, equivalent to a county-level administrative division. Banners were first used during the Qing dynasty, which organized the Mongols into banners, except those who belonged to the Eight Banners. Each banner had sums as nominal subdivisions. In Inner Mongolia, several banners made up a league. In the rest, including Outer Mongolia, northern Xinjiang, and Qinghai Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xin ..., Aimag (Аймаг) was the largest administrative division. While it restricted the Mongols from crossing banner borders, the dynasty protected Mongolia from population pressure from China proper. After the Mongolian People's Revolution, the banners of Outer Mongolia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County-level City
A county-level city () is a County-level divisions of China, county-level administrative division of the China, People's Republic of China. County-level cities have judiciary, judicial but no legislature, legislative rights over their own local ordinance, local law and are usually governed by Administrative divisions of China#Prefectural level (2nd), prefecture-level divisions, but a few are governed directly by Administrative divisions of China#Provincial level (1st), province-level divisions. A county-level city is a "city" () and "county" () that have been merged into one unified jurisdiction. As such, it is simultaneously a city, which is a municipal entity, and a county, which is an administrative division of a prefecture. Most county-level cities were created in the 1980s and 1990s by replacing denser populated Counties of China, counties. County-level cities are not "city, cities" in the strictest sense of the word, since they usually contain rural areas many times the size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |