|
Acropora Nasuta
''Acropora nasuta'' is a species of branching stony coral in the family Acroporidae. It is native to the western and central Indo-Pacific where it is found in shallow reef habitats. Like other corals of the genus ''Acropora'', it is susceptible to coral bleaching and coral diseases and the IUCN has listed it as being "Near Threatened". Description ''Acropora nasuta'' is a small colonial coral that grows in clumps which tend to develop flat tops. The branches are tapering and up to wide. The radial corallites usually form neat rows, sometimes being long and slender and sometimes appressed. The axial corallites may be larger or the same size as the radial corallites. The colour of this coral is creamy-white or pale brown and the branch tips are sometimes bluish. File:Acropora nasuta (Hard coral).jpg, Fish often hide among the branches File:Acropora nasuta Maldives 3.JPG, ''A. nasuta'' in the Maldives File:Acropora nasuta, isla Johnston.jpg, Close up Distribution and habitat ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Dwight Dana
James Dwight Dana Royal Society of London, FRS FRSE (February 12, 1813 – April 14, 1895) was an American geologist, mineralogist, volcanologist, and zoologist. He made pioneering studies of mountain-building, volcano, volcanic activity, and the origin and structure of continents and oceans around the world. His zoological author abbreviation is Dana. Early life and career Dana was born February 12, 1813, in Utica, New York. His father was merchant James Dana (1780–1860) and his mother was Harriet Dwight (1792–1870). Through his mother he was related to the Dwight New England family of missionaries and educators including uncle Harrison Gray Otis Dwight and first cousin Henry Otis Dwight. He showed an early interest in science, which had been fostered by Fay Edgerton, a teacher in the Utica high school, and in 1830 he entered Yale College in order to study under Benjamin Silliman the elder. Graduating in 1833, for the next two years he was teacher of mathematics to midshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tentacle
In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work mainly like muscular hydrostats. Most forms of tentacles are used for grasping and feeding. Many are sensory organs, variously receptive to touch, vision, or to the smell or taste of particular foods or threats. Examples of such tentacles are the eyestalks of various kinds of snails. Some kinds of tentacles have both sensory and manipulatory functions. A tentacle is similar to a cirrus, but a cirrus is an organ that usually lacks the tentacle's strength, size, flexibility, or sensitivity. A nautilus has cirri, but a squid has tentacles. Invertebrates Molluscs Many molluscs have tentacles of one form or another. The most familiar are those of the pulmonate land snails, which usually have two sets of tentacles on the head: when extended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Fauna Of Africa
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean. Marine or marines may refer to: Ocean * Maritime (other) * Marine art * Marine biology * Marine debris * Marine habitats * Marine life * Marine pollution Military * Marines, a naval-based infantry force ** United States Marine Corps ** Royal Marines of the UK ** Brazilian Marine Corps ** Spanish Marine Infantry ** Fusiliers marins (France) ** Indonesian Marine Corps ** Republic of China Marine Corps ** Republic of Korea Marine Corps ** Royal Thai Marine Corps *"Marine" also means "navy" in several languages: ** Austro-Hungarian Navy () ** Belgian Navy (, , ) ** Royal Canadian Navy () *** Provincial Marine (1796–1910), a predecessor to the Royal Canadian Navy ** Navy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo () ** Royal Danish Navy () ** Finnish Navy (, ) ** French Navy () ** Gabonese Navy () ** German Navy () ** Royal Moroccan Navy () ** Royal Netherlands Navy () ** Swedish Navy () Places * Marines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of The Red Sea
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Greek equivalent of fauna. ''Fauna'' is also the word for a book that catalogues the animals in such a manner. The term was first used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of The Indian Ocean
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is ''funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Greek equivalent of fauna. ''Fauna'' is also the word for a book that catalogues the animals in such a manner. The term was first used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnidarians Of The Pacific Ocean
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter. Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that they use mainly for capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians mostly have two basic body forms: swimming medusae and sessile polyps, both of which are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes. Both forms have a single orifice and body cavity that are used for digestion and respiration. Many cnidarian species produce colonies that are single organisms composed of medusa-like or polyp-like zooids, or both (hence they are trimorphic). Cnidarians' activities are coordinated by a decentralized nerve net and simple receptors. Several free-swimming species of Cubozoa and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
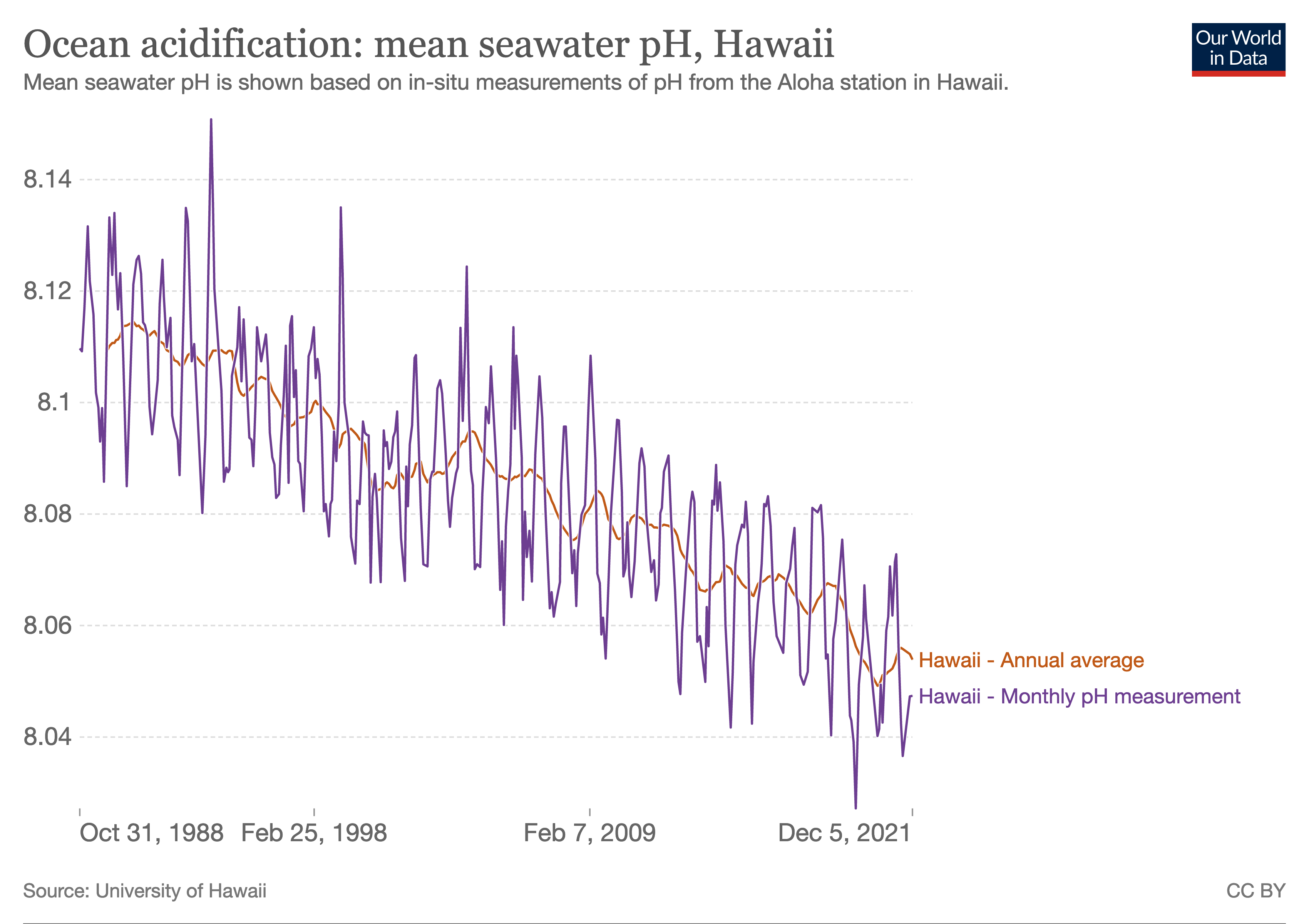
Ocean Acidification
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxide emissions from human activities which have led to atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels of more than 410 ppm (in 2020). The oceans absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. This leads to the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) which dissociates into a bicarbonate ion () and a hydrogen ion (H+). The free hydrogen ions (H+) decrease the pH of the ocean, therefore increasing acidity (this does not mean that seawater is acidic yet; it is still alkaline, with a pH higher than 8). A decrease in pH corresponds to a decrease in the concentration of carbonate ions, which are the main building block for calcium carbonate (CaCO3) shells and skeletons. Marine calcifying organisms, like mollusks, oysters and corals, are particularly affected by this as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reef Aquarium
A reef aquarium or reef tank is a marine aquarium that prominently displays live corals and other marine invertebrates as well as fish that play a role in maintaining the tropical coral reef environment. A reef aquarium requires appropriately intense lighting, turbulent water movement, and more stable water chemistry than fish-only marine aquaria, and careful consideration is given to which reef animals are appropriate and compatible with each other. Components Reef aquariums consist of a number of components, in addition to the livestock, including: *Display tank: The primary tank in which the livestock are kept and shown. *Stand: A stand allows for placement of the display tank at eye level and provides space for storage of the accessory components. *Sump: An accessory tank in which mechanical equipment is kept. A remote sump allows for a clutter-free display tank. *Refugium: An accessory tank dedicated to the cultivation of beneficial macroalgae and microflora/fauna. The re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Bleaching
Coral bleaching is the process when corals become white due to various stressors, such as changes in temperature, light, or nutrients. Bleaching occurs when coral polyps expel the zooxanthellae (dinoflagellates that are commonly referred to as algae) that live inside their tissue, causing the coral to turn white. The zooxanthellae are photosynthetic, and as the water temperature rises, they begin to produce reactive oxygen species. This is toxic to the coral, so the coral expels the zooxanthellae. Since the zooxanthellae produce the majority of coral colouration, the coral tissue becomes transparent, revealing the coral skeleton made of calcium carbonate. Most bleached corals appear bright white, but some are blue, yellow, or pink due to pigment proteins in the coral. The leading cause of coral bleaching is rising ocean temperature due to climate change. A temperature about 1 °C (or 2 °F) above average can cause bleaching. According to the United Nations Environment Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
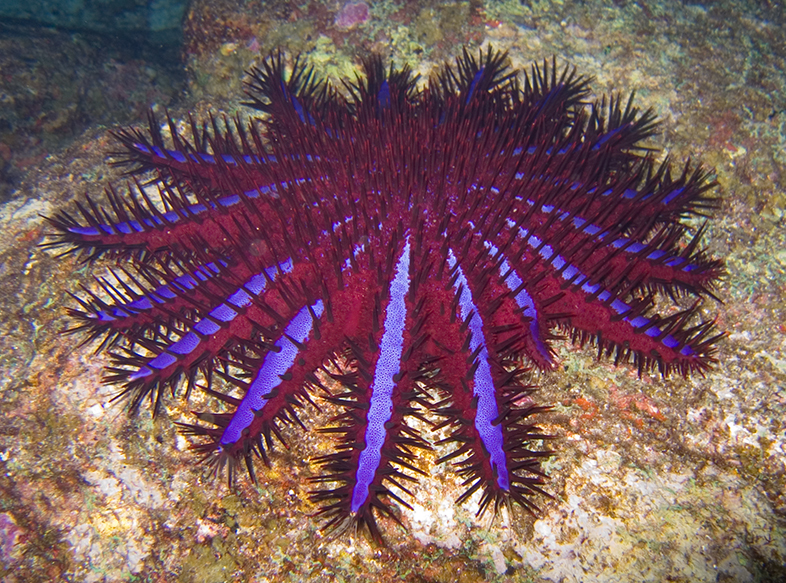
Crown-of-thorns Starfish
The crown-of-thorns starfish (frequently abbreviated to COTS), ''Acanthaster planci'', is a large starfish that preys upon hard, or stony, coral polyps (Scleractinia). The crown-of-thorns starfish receives its name from venomous thorn-like spines that cover its upper surface, resembling the biblical crown of thorns. It is one of the largest starfish in the world. ''A. planci'' has a very wide Indo-Pacific distribution. It is perhaps most common around Australia, but can occur at tropical and subtropical latitudes from the Red Sea and the East African coast across the Indian Ocean, and across the Pacific Ocean to the west coast of Central America. It occurs where coral reefs or hard coral communities occur in the region. Description The body form of the crown-of-thorns starfish is fundamentally the same as that of a typical starfish, with a central disk and radiating arms. Its special traits, however, include being disc-shaped, multiple-armed, flexible, prehensile, and heavily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
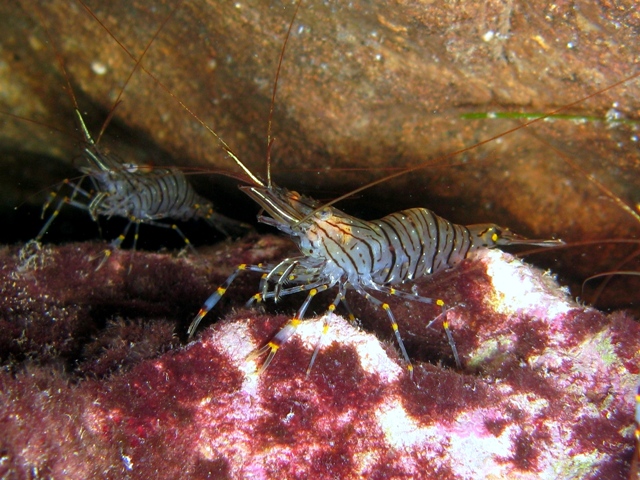
Shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are referred to as "shrimp". More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either group or to only the marine species. Under a broader definition, ''shrimp'' may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails (abdomens), long whiskers ( antennae), and slender legs. Any small crustacean which resembles a shrimp tends to be called one. They swim forward by paddling with swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks with the tail driving them backwards very quickly. Crabs and lobsters have strong walking legs, whereas shrimp have thin, fragile legs which they use primarily for perching.Rudloe & Rudloe (2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the world's oceans, in freshwater, and on land, are generally covered with a thick exoskeleton, and have a single pair of pincers. They first appeared during the Jurassic Period. Description Crabs are generally covered with a thick exoskeleton, composed primarily of highly mineralized chitin, and armed with a pair of chelae (claws). Crabs vary in size from the pea crab, a few millimeters wide, to the Japanese spider crab, with a leg span up to . Several other groups of crustaceans with similar appearances – such as king crabs and porcelain crabs – are not true crabs, but have evolved features similar to true crabs through a process known as carcinisation. Environment Crabs are found in all of the world's oceans, as well as in fresh w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)