|
Ackermann Steering Geometry
The Ackermann steering geometry is a geometric arrangement of linkages in the steering of a car or other vehicle designed to solve the problem of wheels on the inside and outside of a turn needing to trace out circles of different radii. It was invented by the German carriage builder Georg Lankensperger in Munich in 1817, then patented by his agent in England, Rudolph Ackermann (1764–1834) in 1818 for horse-drawn carriages. Erasmus Darwin may have a prior claim as the inventor dating from 1758. He devised his steering system because he was injured when a carriage tipped over. Advantages The intention of Ackermann geometry is to avoid the need for tires to slip sideways when following the path around a curve. The geometrical solution to this is for all wheels to have their axles arranged as radii of circles with a common centre point. As the rear wheels are fixed, this centre point must be on a line extended from the rear axle. Intersecting the axes of the front wheels on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ackermann Turning
Ackermann may also refer to the following: * Ackermann (surname), for many people with this name *Several mathematical objects named after Wilhelm Ackermann **Ackermann function **Ackermann ordinal **Ackermann set theory *Ackermann steering geometry, in mechanical engineering * Ackermann's formula, in control engineering *''Der Ackermann aus Böhmen'', or "The Ploughman from Bohemia", a work of poetry in Early New High German by Johannes von Tepl, written around 1401 *'' Ackermannviridae'', virus family named in honor of H.-W. Ackermann See also * Ackerman (other) *Ackermans (other) *Akkerman (other) Akkerman may refer to: Places * Bilhorod-Dnistrovskyi, a city in Ukraine * Akkerman Oblast, a region in Ukraine *Akerman Fortress; see Tyras Other uses * Akkerman (surname) * Akkerman Inc., a construction equipment manufacturer in Brownsdale, ... * Åkerman {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Rod
A tie rod or tie bar (also known as a hanger rod if vertical) is a slender structural unit used as a tie and (in most applications) capable of carrying tensile loads only. It is any rod or bar-shaped structural member designed to prevent the separation of two parts, as in a vehicle. Subtypes and examples of applications * In airplane structures, tie rods are sometimes used in the fuselage or wings. * Tie rods are often used in steel structures, such as bridges, industrial buildings, tanks, towers, and cranes. * Sometimes tie rods are retrofitted to bowing or subsiding masonry walls (brick, block, stone, etc.) to keep them from succumbing to lateral forces. * The rebar used in reinforced concrete is not referred to as a "tie rod", but it essentially performs some of the same tension-force-counteracting purposes that tie rods perform. * In automobiles, the ''tie rods'' are part of the steering mechanism. They differ from the archetypal tie rod by both pushing and pulling (operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
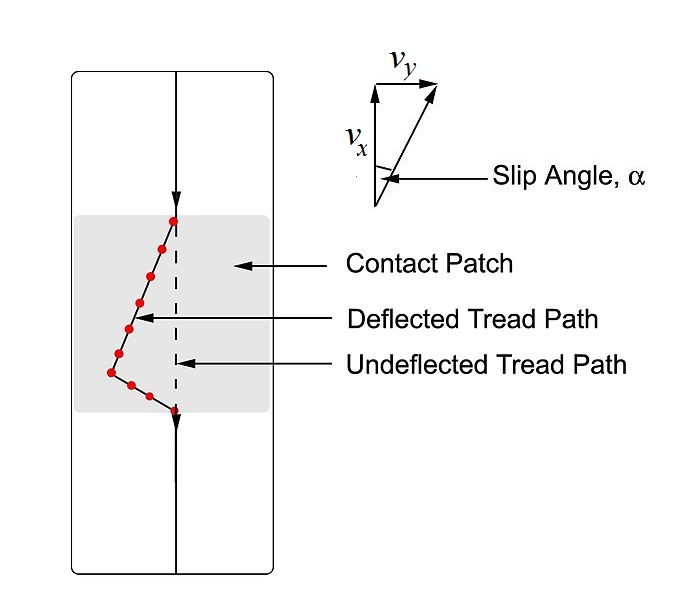
Slip Angle
In vehicle dynamics, slip angle or sideslip angle is the angle between the direction in which a wheel is pointing and the direction in which it is actually traveling (i.e., the angle between the forward velocity vector v_x and the vector sum of wheel forward velocity v_x and lateral velocity v_y, as defined in the image to the right). This slip angle results in a force, the cornering force, which is in the plane of the contact patch and perpendicular to the intersection of the contact patch and the midplane of the wheel. This cornering force increases approximately linearly for the first few degrees of slip angle, then increases non-linearly to a maximum before beginning to decrease. The slip angle, \alpha is defined as \alpha \triangleq -\arctan\left(\frac\right) Causes A non-zero slip angle arises because of deformation in the tire carcass and tread. As the tire rotates, the friction between the contact patch and the road results in individual tread 'elements' (finit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rack And Pinion
A rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular gear (the '' pinion'') engaging a linear gear (the ''rack''). Together, they convert rotational motion into linear motion. Rotating the pinion causes the rack to be driven in a line. Conversely, moving the rack linearly will cause the pinion to rotate. A rack and pinion drive can use both straight and helical gears. Though some suggest helical gears are quieter in operation, no hard evidence supports this theory. Helical racks, while being more affordable, have proven to increase side torque on the datums, increasing operating temperature leading to premature wear. Straight racks require a lower driving force and offer increased torque and speed per percentage of gear ratio which allows lower operating temperature and lessens viscal friction and energy use. The maximum force that can be transmitted in a rack and pinion mechanism is determined by the tooth pitch and the size of the pinion as well as the gear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tie Rod
A tie rod or tie bar (also known as a hanger rod if vertical) is a slender structural unit used as a tie and (in most applications) capable of carrying tensile loads only. It is any rod or bar-shaped structural member designed to prevent the separation of two parts, as in a vehicle. Subtypes and examples of applications * In airplane structures, tie rods are sometimes used in the fuselage or wings. * Tie rods are often used in steel structures, such as bridges, industrial buildings, tanks, towers, and cranes. * Sometimes tie rods are retrofitted to bowing or subsiding masonry walls (brick, block, stone, etc.) to keep them from succumbing to lateral forces. * The rebar used in reinforced concrete is not referred to as a "tie rod", but it essentially performs some of the same tension-force-counteracting purposes that tie rods perform. * In automobiles, the ''tie rods'' are part of the steering mechanism. They differ from the archetypal tie rod by both pushing and pulling (operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingpin (automotive Part)
The kingpin (also king-pin, king pin and k pin) is the main pivot in the steering mechanism of a car or other vehicle. The term is also used to refer to part of a fifth wheel coupling apparatus for a semi and its trailer or other load. History Originally, with the 'turntable' steering of horse-drawn wagons, this was a single pin on which the moveable axle was pivoted beneath the wagon's frame. This located the axle from side to side, but the weight of the wagon was carried on a circular wooden ring turntable surrounding this. Similar centre pivot steering was used by steam traction engines, the kingpin being mounted on the 'perch bracket' beneath the boiler. Some early cars also used centre pivot steering, although it became apparent that it was unsuitable for their increasing speeds. Ackermann steering separates the steering movement into two pivots, one near the hub of each front wheel. The beam axle between them remains fixed relative to the chassis, linked by the suspens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toe (automotive)
In automotive engineering, toe, also known as tracking, is the symmetric angle that each wheel makes with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle, as a function of static geometry, and kinematic and compliant effects. This can be contrasted with steer, which is the antisymmetric angle, i.e. both wheels point to the left or right, in parallel (roughly). Negative toe, or toe out, is the front of the wheel pointing away from the centreline of the vehicle. Positive toe, or toe in, is the front of the wheel pointing towards the centreline of the vehicle. Historically, and still commonly in the United States, toe was specified as the linear difference (either inches or millimeters) of the distance between the two front-facing and rear-facing tire centerlines at the outer diameter and axle-height; since the toe angle in that case depends on the tire diameter, the linear dimension toe specification for a particular vehicle is for specified tires. Description In a rear-wheel drive vehic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erasmus Darwin
Erasmus Robert Darwin (12 December 173118 April 1802) was an English physician. One of the key thinkers of the Midlands Enlightenment, he was also a natural philosopher, physiologist, slave-trade abolitionist, inventor, and poet. His poems included much natural history, including a statement of evolution and the relatedness of all forms of life. He was a member of the Darwin–Wedgwood family, which includes his grandsons Charles Darwin and Francis Galton. Darwin was a founding member of the Lunar Society of Birmingham, a discussion group of pioneering industrialists and natural philosophers. He turned down an invitation from George III to become Physician to the King. Early life and education Darwin was born in 1731 at Elston Hall, Nottinghamshire, near Newark-on-Trent, England, the youngest of seven children of Robert Darwin of Elston (1682–1754), a lawyer and physician, and his wife Elizabeth Hill (1702–97). The name Erasmus had been used by a number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steering
Steering is a system of components, linkages, and other parts that allows a driver to control the direction of the vehicle. Introduction The most conventional steering arrangement allows a driver to turn the front wheels of a vehicle using a hand–operated steering wheel positioned in front of the driver. The steering wheel is attached to a steering column, which is linked to rods, pivots and gears that allow the driver to change the direction of the front wheels. Other arrangements are sometimes found on different types of vehicles; for example, a tiller or rear-wheel steering. Tracked vehicle Continuous track is a system of vehicle propulsion used in tracked vehicles, running on a continuous band of treads or track plates driven by two or more wheels. The large surface area of the tracks distributes the weight of the vehicle ...s such as bulldozers and tanks usually employ differential steering, where the tracks are made to move at different speeds or even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolph Ackermann
Rudolph Ackermann (20 April 1764 in Schneeberg, Electorate of Saxony – 30 March 1834 in Finchley, London) was an Anglo-German bookseller, inventor, lithographer, publisher and businessman. Biography He attended the Latin school in Stollberg, but his wish to study at the university was made impossible by lack of financial means, and he therefore became a saddler like his father. He worked as a saddler and coach-builder in different German cities, moved from Dresden to Basel and Paris, and then, 23 years old, settled in London. He established himself in Long Acre, the centre of coach-making in London and close to the market at Covent Garden. His extraordinary business instinct, as well as his flair for design and talent for self-promotion, won him the £200 contract to design the ceremonial coach for the Lord Chancellor of Ireland, John FitzGibbon, 1st Earl of Clare. After this he designed ''The Royal Sailor'', an 8-wheel omnibus that ran between Charing Cross, Green ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Lankensperger
Georg Lankensperger (also: Lankensberger), (31 March 1779 – 11 July 1847) was a German wheelwright who invented the steering mechanism that is today known as Ackermann steering geometry. He patented the invention in Germany, but his agent Rudolph Ackermann filed for the patent in the U.K. Early life Lankensperger was born in Marktl in the district of Oberbayern in Germany. Career Lankensperger invented his steering mechanism in 1816 as Hofwagner (''Head waggoner'') in Munich, to allow the front wheels of a carriage to individually follow the natural arc of its turning circle, rather than skidding and slipping when they are forced to each share a common arc with the conventional pivoted axle. It continues to be used in horse-drawn carriages and passenger cars to this day..Veröffentlicht: ''„Wöchentlicher Anzeiger für Kunst- und Gewerbfleiß im Königreich Baiern“, No. 24, 15. Juni 1816, Spalte 394'' Death He died at Birkenstein near Berlin Berlin is Capital of Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |