|
Achaemenid Family Tree
The Achaemenid Empire was the first Persian empire, founded in 550 BC by Cyrus the Great Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced .... This article contains the Achaemenid family tree. Family tree See also :Template:Cyrus-tree Notes :*: Unconfirmed rulers, due to the Behistun Inscription. References * {{Cyrus the Great Dynasty genealogy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smerdis Of Persia
Bardiya or Smerdis ( peo, 𐎲𐎼𐎮𐎡𐎹 ; grc, Σμέρδις ; possibly died 522 BC), also named as Tanyoxarces ( grc, Τανυοξάρκης ) by Ctesias, was a son of Cyrus the Great and the younger brother of Cambyses II, both Persian kings. There are sharply divided views on his life. Bardiya either ruled the Achaemenid Empire for a few months in 522 BC, or was impersonated by a magus called Gaumāta ( peo, 𐎥𐎢𐎶𐎠𐎫); whose name is given by Ctesias as Sphendadates ( peo, Spantadātaʰ; grc, Σφενδαδάτης ), until he was toppled by Darius the Great. Name and sources The prince's name is listed variously in the historical sources. In Darius the Great's Behistun inscription, his Persian name is Bardiya or Bardia. Herodotus calls him Smerdis, which is the prevalent Greek form of his name; the Persian name has been assimilated to the Greek (Asiatic) name ''Smerdis'' or ''Smerdies'', a name which also occurs in the poems of Alcaeus and Anacreo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artazostre
Artazostre (or Artozostre) (Old Persian *''Artazauštrī'') was a Persian princess, daughter of king Darius the Great (521-485 BC) by Artystone, daughter of Cyrus the Great. According to the Greek historian Herodotus (VI, 43) Artazostre was given in marriage to Mardonius, young son of the noble Gobryas, not much before he took the command of the Persian army in Thrace and Macedon (c. 493/492 BC). Artazostre seems not to be mentioned by name in the Persepolis Fortification Tablets (administrative documents found at Persepolis), but there are references (in tablets dated on the year 498 BC) to a "wife of Mardonius, daughter of the king", who received rations for a trip she made with Gobryas and a woman called ''Radušnamuya'' or ''Ardušnamuya'', perhaps Gobryas' wife. However, another interpretation of the text suggests that ''Ardušnamuya'' was actually the anonymous "wife of Mardonius" See Lendering. Mardonius had a son, probably by Artazostre, named Artontes. Notes Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenes (satrap)
Achaemenes ( peo, 𐏃𐎧𐎠𐎶𐎴𐎡𐏁 ;M. A. Dandamayev, “Achaemenes,” Encyclopædia Iranica, I/4, p. 414; an updated version is available online at http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/achaemenes-greek grc, Ἀχαιμένης , also incorrectly called Achaemenides by Ctesias) was an Achaemenid general and satrap of ancient Egypt during the early 5th century BC, at the time of the 27th Dynasty of Egypt. Career A son of king Darius I by his queen Atossa and thus a full brother of Xerxes I, Achaemenes was appointed satrap of Egypt some time between 486 and 484 BC, shortly after Xerxes' accession. At the time, Egypt was revolting against Achaemenid rule, and it appears likely that the previous satrap Pherendates lost his life in the turmoil. The rebellion, possibly led by a self-proclaimed pharaoh named Psammetichus IV, was eventually quelled by Achaemenes around 484 BC. After the victory, Achaemenes adopted a more repressive policy in order to discourage new re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masistes
Masistes (Old Persian 𐎶𐎰𐎡𐏁𐎫, ''Maθišta''; Greek Μασίστης, ''Masístēs''; Old Iranian *''Masišta'') (?- c. 478 BC) was a Persian prince of the Achaemenid Dynasty, son of king Darius I (reign: 520-486 BC) and of his wife Atossa, and full brother of king Xerxes I (reign: 486-465 BC). He was satrap (governor) of Bactria during his brother's reign, where he attempted to start a revolt in 478 BC. Chief marshal Masistes was one of the six chief marshals of the Greek campaigns of Xerxes (480-479 BC). Along with general Mardonius, he commanded the army column that crossed Thrace along the coast; however, he was almost completely absent during the course of the war, including the battles of Salamis and Plataea. He reappeared close to the end of the war, when he fought in the Battle of Mycale (479 BC). According to Herodotus, the battle was just about to take place at sea, but the Persians decided to come ashore in Ionia, Asia Minor, and fight on land. The G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariabignes
Ariabignes ( peo, Ariyabigna, el, Ἀριαβίγνης) was one of the sons of the Persian king Darius I and his mother was a daughter of Gobryas (). He participated in the Second Persian invasion of Greece, as one of the four admirals of the fleet of his brother Xerxes I, and was killed in the Battle of Salamis in 480 BC. Ariabignes was the commander of the Carian and Ionian forces. Plutarch calls him, Ariamenes (),Plutarch ''Parallel Lives'' "Themistocles", 14 and speaks of him as a brave man and the most just of the brothers of Xerxes. The same writer relates that this Ariamenes laid claim to the throne on the death of Darius, as the eldest of his sons, but was opposed by Xerxes, who maintained that he had a right to the crown as the eldest of the sons born after Darius had become king. The Persians appointed Artabanus to decide the dispute; and upon his declaring in favour of Xerxes, Ariamenes immediately saluted his brother as king, and was treated by him with great resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gobryas
Gobryas ( grc, Γοβρύας; peo, 𐎥𐎢𐎲𐎽𐎢𐎺 g-u-b-ru-u-v, reads as ''Gaub(a)ruva''?; Elamite: ''Kambarma'') was a common name of several Persian noblemen. Gobryas (Cyrus the Great's general) This Gobryas is mentioned in the Cyropedia of Xenophon as a general who helped in the conquering of Babylon. The A.K. Grayson translation of the Nabonidus Chronicle, based on that of T.G. Pinches, considers both the names ''Ugbaru'' and ''Gubaru'' found in the latter to be references to this Gobryas. However the names are distinct in the text and refer to two different individuals, the one called ''Gubaru'' being the ruler placed over Babylon thus corresponding to Cyaxares of the Cyropedia, not Gobryas. ''Ugbaru'' remains a candidate for Gobryas being described as the ruler of the region of Gutium dying soon after the conquest of Babylon similarly to Xenophon's portrayal of Gobryas as an elderly "Assyrian" ruler. According to William H. Shea Ugbaru and Gubaru is the same pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariomardus
Ariomardus was the name of a number of people from classical antiquity: * A son of the Persian King Darius I and his wife Parmys.Lendering, J:Parmys, in http://www.livius.org He attended Xerxes I into Greece, being in command of the Moschi and Tibareni. * The brother of Artuphius, who commanded the Caspii in the army of Xerxes I. * The ruler of Thebes in Egypt, and one of the commanders of the Egyptians in the army of Xerxes.Aeschylus, ''The Persians'' 38, 313. References Further reading The history of Herodotus, Volume 2at Project Gutenberg Project Gutenberg (PG) is a Virtual volunteering, volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks." It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the ... Persian people of the Greco-Persian Wars 5th-century BC Iranian people {{AncientNearEast-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parmys
Parmys (Old Persian ''(H)uparviyā'', Elamite ''Uparmiya'') was a Persian princess, the only daughter of Bardiya (Smerdis), son of Cyrus the Great.Herodotus, '' Histories'', book 3, chapter 88section 3 She was the granddaughter of Cyrus the Great, and Cassandane. When Darius the Great (Darius I) seized the Achaemenid throne, he married two daughters (Atossa and Artystone) of Cyrus the Great and later on his granddaughter (Parmys). Parmys bore him a son called Ariomardus. References {{reflist Sources *Herodotus, III, 88; VII, 78 *Persepolis Fortification Tablets The Persepolis Fortification Archive and Persepolis Treasury Archive are two groups of clay administrative archives — sets of records physically stored together – found in Persepolis dating to the Achaemenid Persian Empire. The discover ... (where she is called Uparmiya) *Brosius, M: ''Women in Ancient Persia, 559-331 BC'', Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1998. *Lendering, J:Parmys, in http://www.livius.orgPersepoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerxes I Of Persia
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius the Great () and his mother was Atossa, a daughter of Cyrus the Great (), the founder of the Achaemenid empire. Like his father, he ruled the empire at its territorial peak. He ruled from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC at the hands of Artabanus, the commander of the royal bodyguard. Xerxes I is notable in Western history for his invasion of Greece in 480 BC. His forces temporarily overran mainland Greece north of the Isthmus of Corinth until losses at Salamis and Plataea a year later reversed these gains and ended the second invasion decisively. However, Xerxes successfully crushed revolts in Egypt and Babylon. Xerxes also oversaw the completion of various construction projects at Susa and Persepolis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabazus
Megabazus (Old Persian: ''Bagavazdā'' or ''Bagabāzu'', grc, Μεγαβάζος), son of Megabates, was a highly regarded Persian general under Darius, to whom he was a first-degree cousin. Most of the information about Megabazus comes from '' The Histories'' by Herodotus. Scythian campaign (513 BC) Megabazus led the army of the Persian King Darius I in 513 BC during his European Scythian campaign. After this had to be discontinued without result, Megabazos was left as commander-in-chief of an 80,000-man army in Europe, with the mission of subjugating the Greek cities on the Hellespont. The Persian troops first subjugated gold-rich Thrace after capturing Perinthos and the coastal Greek cities, and then defeated the powerful Paeonians, many of whom he deported to Phrygia. Subjugation of Macedon Finally, Megabazus sent envoys to Amyntas I, king of Macedon, demanding acceptance of Persian domination, which the king accepted. Megabazus received the present of "Earth and Wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
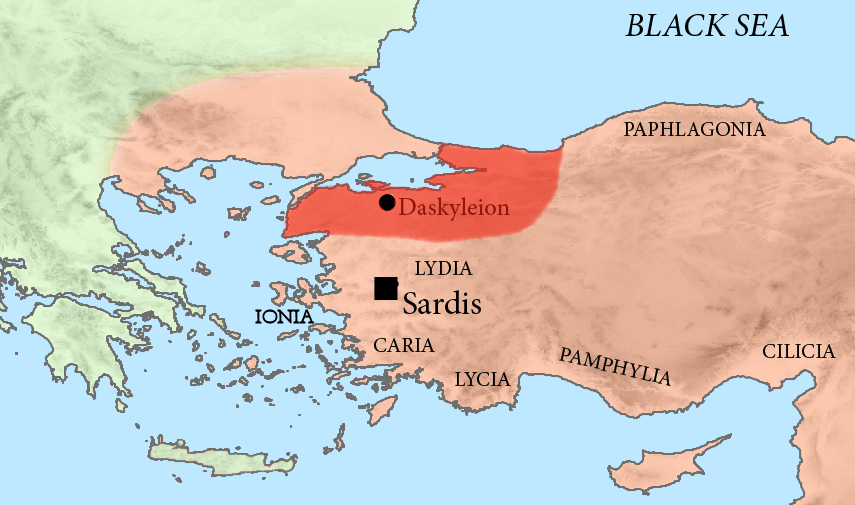
Artaphernes
Artaphernes ( el, Ἀρταφέρνης, Old Persian: Artafarna, from Median ''Rtafarnah''), flourished circa 513–492 BC, was a brother of the Achaemenid king of Persia, Darius I, satrap of Lydia from the capital of Sardis, and a Persian general. In his position he had numerous contacts with the Greeks, and played an important role in suppressing the Ionian Revolt. Biography First contacts with Athens (507 BC) In 507 BC, Artaphernes, as brother of Darius I and Satrap of Asia Minor in his capital Sardis, received an embassy from Athens, probably sent by Cleisthenes, which was looking for Persian assistance in order to resist the threats from Sparta. Artaphernes asked the Athenians for "Earth and Water", a symbol of submission, if they wanted help from the Achaemenid king. The Athenians ambassadors apparently accepted to comply, and to give "Earth and Water". Artaphernes also advised the Athenians that they should receive back the Athenian tyrant Hippias. The Persians threat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |