|
Accusative Case
The accusative case (abbreviated ) of a noun is the grammatical case used to mark the direct object of a transitive verb. In the English language, the only words that occur in the accusative case are pronouns: 'me,' 'him,' 'her,' 'us,' and ‘them’. The spelling of those words will change depending on how they are used in a sentence. For example, the pronoun ''they'', as the subject of a sentence, is in the nominative case ("They wrote a book"); but if the pronoun is instead the object, it is in the accusative case and ''they'' becomes ''them'' ("The book was written by them"). The accusative case is used in many languages for the objects of (some or all) prepositions. It is usually combined with the nominative case (for example in Latin). The English term, "accusative", derives from the Latin , which, in turn, is a translation of the Greek . The word may also mean "causative", and this may have been the Greeks' intention in this name, but the sense of the Roman translation has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glossing Abbreviations
This article lists common abbreviations for grammatical terms that are used in linguistic interlinear glossing of oral languages in English. The list provides conventional glosses as established by standard inventories of glossing abbreviations such as the Leipzig Glossing rules, the most widely known standard. These will generally be the glosses used on Wikipedia. Synonymous glosses are listed as alternatives for reference purposes. In a few cases, long and short standard forms are listed, intended for texts where that gloss is rare or common. Conventions * Grammatical abbreviations are generally written in full or small caps to visually distinguish them from the translations of lexical words. For instance, capital or small-cap (frequently abbreviated to ) glosses a grammatical past-tense morpheme, while lower-case 'past' would be a literal translation of a word with that meaning. Similarly, (small) cap might be a locative suffix used in nominal inflections, prototypically in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Language
Ukrainian ( uk, украї́нська мо́ва, translit=ukrainska mova, label=native name, ) is an East Slavic language of the Indo-European language family. It is the native language of about 40 million people and the official state language of Ukraine in Eastern Europe. Written Ukrainian uses the Ukrainian alphabet, a variant of the Cyrillic script. The standard Ukrainian language is regulated by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (NANU; particularly by its Institute for the Ukrainian Language), the Ukrainian language-information fund, and Potebnia Institute of Linguistics. Comparisons are often drawn to Russian, a prominent Slavic language, but there is more mutual intelligibility with Belarusian,Alexander M. Schenker. 1993. "Proto-Slavonic," ''The Slavonic Languages''. (Routledge). pp. 60–121. p. 60: " hedistinction between dialect and language being blurred, there can be no unanimity on this issue in all instances..."C.F. Voegelin and F.M. Voegelin. 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oblique Case
In grammar, an oblique (abbreviated ; from la, casus obliquus) or objective case (abbr. ) is a nominal case other than the nominative case, and sometimes, the vocative. A noun or pronoun in the oblique case can generally appear in any role except as subject, for which the nominative case is used. The term ''objective case'' is generally preferred by modern English grammarians, where it supplanted Old English's dative and accusative. When the two terms are contrasted, they differ in the ability of a word in the oblique case to function as a possessive attributive; whether English has an oblique rather than an objective case then depends on how "proper" or widespread one considers the dialects where such usage is employed. An oblique case often contrasts with an unmarked case, as in English oblique ''him'' and ''them'' versus nominative ''he'' and ''they''. However, the term ''oblique'' is also used for languages without a nominative case, such as ergative–absolutive langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declension
In linguistics, declension (verb: ''to decline'') is the changing of the form of a word, generally to express its syntactic function in the sentence, by way of some inflection. Declensions may apply to nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, and article (grammar), articles to indicate grammatical number, number (e.g. singular, dual, plural), grammatical case, case (e.g. nominative case, accusative case, genitive case, dative case), grammatical gender, gender (e.g. masculine, neuter, feminine), and a number of other grammatical categories. Meanwhile, the inflectional change of verbs is called Grammatical conjugation, ''conjugation''. Declension occurs in many of the world's languages. It is an important aspect of language families like Quechuan languages, Quechuan (i.e., languages native to the Andes), Indo-European languages, Indo-European (e.g. German language, German, Baltic language, Lithuanian, Latvian, Slavic languages, Slavic, Sanskrit, Latin, Ancient Greek, Modern Greek, Clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8th and 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telicity
In linguistics, telicity (; ) is the property of a verb or verb phrase that presents an action or event as having a specific endpoint. A verb or verb phrase with this property is said to be ''telic''; if the situation it describes is ''not'' heading for any particular endpoint, it is said to be ''atelic''. Testing for telicity in English One common way to gauge whether an English verb phrase is telic is to see whether such a phrase as ''in an hour'', in the sense of "within an hour", (known as a ''time-frame adverbial'') can be applied to it. Conversely, a common way to gauge whether the phrase is atelic is to see whether such a phrase as ''for an hour'' (a ''time-span adverbial'') can be applied to it. This can be called the ''time-span/time-frame test''. According to this test, the verb phrase ''built a house'' is telic, whereas the minimally different ''built houses'' is atelic: : Fine: "John built a house in a month." : Bad: *"John built a house for a month." :: → ''buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphosyntactic Alignment
In linguistics, morphosyntactic alignment is the grammatical relationship between Argument (linguistics), arguments—specifically, between the two arguments (in English, subject and object) of transitive verbs like ''the dog chased the cat'', and the single argument of intransitive verbs like ''the cat ran away''. English has a ''subject (grammar), subject,'' which merges the more active argument of transitive verbs with the argument of intransitive verbs, leaving the ''object (grammar), object'' distinct; other languages may have different strategies, or, rarely, make no distinction at all. Distinctions may be made morphology (linguistics), morphologically (through grammatical case, case and agreement (linguistics), agreement), syntax, syntactically (through word order), or both. Terminology Arguments Dixon (1994) The following notations will be used to discuss the various types of alignment: *S (from ''sole''), the Subject (grammar), subject of an intransitive verb ; *A (from ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitive Case
The partitive case (abbreviated , , or more ambiguously ) is a grammatical case which denotes "partialness", "without result", or "without specific identity". It is also used in contexts where a subgroup is selected from a larger group, or with numbers. Finnic languages In the Finnic languages, such as Finnish and Estonian, this case is often used to express unknown identities and irresultative actions. For example, it is found in the following circumstances, with the characteristic ending of ''-a'' or ''-ta'': * After numbers, in singular: "kolme taloa" → "three houses" (cf. plural, where both are used, e.g. ''sadat kirjat'' "the hundreds of books", ''sata kirjaa'' "hundred books" as an irresultative object.) * For atelic actions (possibly incomplete) and ongoing processes: "luen kirjaa" → "I'm reading a book" ** Compare with telic actions in accusative case: "luen kirjan" → "I will read the (entire) book" * With atelic verbs, particularly those indicating emotions: " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
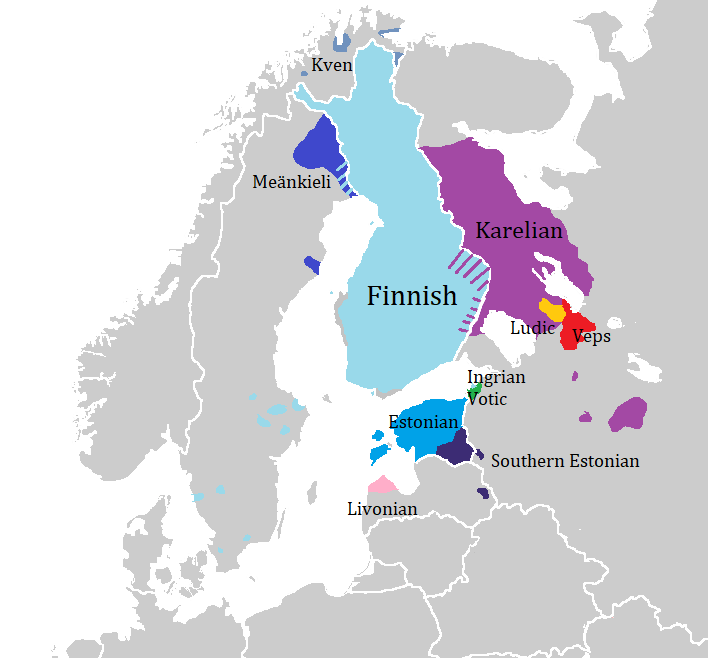
Balto-Finnic Languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Language
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal written m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitic Languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant and expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis. Semitic languages occur in written form from a very early historical date in West Asia, with East Semitic Akkadian and Eblaite texts (written in a script adapted from Sumerian cuneiform) appearing from the 30th century BCE and the 25th century BCE in Mesopotamia and the north eastern Levant respectively. The only earlier attested languages are Sumerian and Elamite (2800 BCE to 550 BCE), both language isolates, and Egyptian (a sister branch of the Afroasiatic family, related to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India. Malayalam was designated a "Classical Language of India" in 2013. Malayalam has official language status in Kerala, and Puducherry ( Mahé), and is also the primary spoken language of Lakshadweep, and is spoken by 34 million people in India. Malayalam is also spoken by linguistic minorities in the neighbouring states; with significant number of speakers in the Kodagu and Dakshina Kannada districts of Karnataka, and Kanyakumari, district of Tamil Nadu. It is also spoken by the Malayali Diaspora worldwide, especially in the Persian Gulf countries, due to large populations of Malayali expatriates there. There are significant population in each cities in India including Mumbai, Bengaluru, Delhi, Kolkata, Pune etc. The origin of Malayalam remains a matter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)