|
Acarospora Schleicheri
''Acarospora schleicheri'', the soil paint lichen, is a bleached to bright yellow areolate to squamulose lichen that commonly grows to on soil (terricolous) in arid habitats of southern California and Baja California, also in Europe and Africa.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, ''Acarospora schleicheri'', Lichen Flora of the Greater Sonoran Desert Region. Vol 3., Nash, T.H., Ryan, B.D., Gries, C., Bugartz, F., (eds.) 2001/ref> It produces rhizocarpic acid as a secondary metabolite, which gives it a yellow coloration and serves to protect it from the sun. Its lower surface is also yellow. It can be greenish when moist. Roundish, angular, or irregularly shaped squamules are 0.5–4 mm in diameter. There are 0–1 (sometimes 2–3) apothecia embedded in the thallus, with 0.4–1.2 mm roundish black to reddish-brown, or dark brown discs, which sometimes fill the areola so as to be lecanorine. It divides vegetatively on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphonse Boistel
Alphonse Barthélémy Martin Boistel (24 December 1836, Paris – 21 September 1908) was a French law professor, who performed research in the fields of geology and lichenology. He studied law at Collège Rollin and at the University of Paris , image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg , image_size = 150px , caption = Coat of Arms , latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis , motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin) , mottoeng = Here and a ..., obtaining his law degree in 1864. From 1865 to 1870 he served as a professor to the faculty of law at Grenoble, then afterwards returned to Paris, where he was a professor of commercial law (1870–79) and civil law (1879–1907). As a lichenologist, he was the author of "''Nouvelle flore des lichens pour la détermination facile des espèces''" (2 volumes, 1896–1902). In 1906 he was named president of the Société géologique de France. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
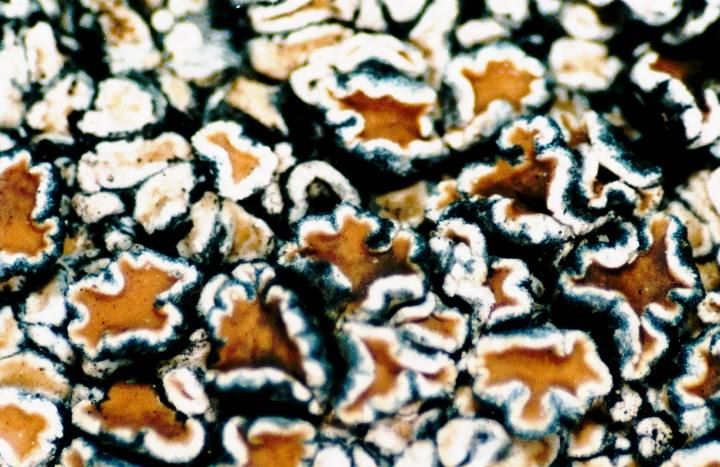
Lecanorine
A lichen has lecanorine fruiting body parts if they are shaped like a plate with a ring around them, and that ring is made of tissue similar to the main non-fruiting body part of the lichen.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, , page 279 The name comes from the name of the lichen genus ''Lecanora ''Lecanora'' is a genus of lichen commonly called rim lichens.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, Lichens in the genus ''Squamarina'' are also called rim lichens. Members of the genus have roughly ci ...'', whose members have such apothecia. If a lichen has lecanorine apothecia, the lichen itself is sometimes described as being lecanorine. References Lichenology {{lichen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Erik Acharius
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in '' Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichens Of North America
Irwin M. Brodo (born 1935) is an emeritus scientist at the Canadian Museum of Nature, in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. He is an authority on the identification and biology of lichens. Irwin Brodo was honored in 1994 with an Acharius Medal presented to him by the International Association for Lichenology. Brodo did his undergraduate studies at Columbia University, and received a master's degree from Cornell University. He earned a Ph.D. in lichenology under the supervision of Henry Imshaug at Michigan State University. He later went on to teach at Université Laval and the University of Alaska, and he also supervised master's students at the University of Ottawa and Carleton University. Brodo's list of publications includes 75 research papers, 8 popular articles, 22 reviews and 6 editorials and obituaries. In 1993, Brodie was awarded the Mary E. Elliot Service Award for his meritorious service to the Canadian Botanical Association. One of Irwin Brodo's great achievements was the public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichens Of Europe
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (); flat leaf-like structures ( |
Lichens Of Africa
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (); flat leaf-like structures ( |
Lichen Species
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (); flat leaf-like structures ( |
Acarospora
''Acarospora'' is a genus of mostly lichen-forming fungi in the family Acarosporaceae. Most species in the genus are crustose lichens that grow on rocks in open and arid places all over the world. They may look like a cobblestone road or cracked up old paint, and are commonly called cobblestone lichens or cracked lichens.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, They usually grow on rock (are "saxicolous"), but some grow on soil (terricolous) or on other lichens. Some species in the genus are fungi that live as parasites on other lichens (lichenicolous fungi). ''Acarospora'' is a widely distributed genus, with about 128 species according to a 2008 estimate. Species in ''Acarospora'' may be shiny as if covered with a glossy varnish, or dull and powdery looking. They have a diverse range of colors, from the brilliant yellow bright cobblestone lichen, to the dark reddish-brown mountain cobblestone lichen, or they can appear tan, gray, or w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GBIF
The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) is an international organisation that focuses on making scientific data on biodiversity available via the Internet using web services. The data are provided by many institutions from around the world; GBIF's information architecture makes these data accessible and searchable through a single portal. Data available through the GBIF portal are primarily distribution data on plants, animals, fungi, and microbes for the world, and scientific names data. The mission of the GBIF is to facilitate free and open access to biodiversity data worldwide to underpin sustainable development. Priorities, with an emphasis on promoting participation and working through partners, include mobilising biodiversity data, developing protocols and standards to ensure scientific integrity and interoperability, building an informatics architecture to allow the interlinking of diverse data types from disparate sources, promoting capacity building and catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen Spot Test
A spot test in lichenology is a spot analysis used to help identify lichens. It is performed by placing a drop of a chemical on different parts of the lichen and noting the colour change (or lack thereof) associated with application of the chemical. The tests are routinely encountered in dichotomous keys for lichen species, and they take advantage of the wide array of lichen products produced by lichens and their uniqueness among taxa. As such, spot tests reveal the presence or absence of chemicals in various parts of a lichen. They were first proposed by the botanist William Nylander in 1866. Three common spot tests use either 10% aqueous KOH solution (K test), saturated aqueous solution of bleaching powder or calcium hypochlorite (C test), or 5% alcoholic ''p''-phenylenediamine solution (P test). The colour changes occur due to presence of particular secondary metabolites in the lichen. There are several other less frequently used spot tests of more limited use that are employed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial ellipsoid (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascus
An ascus (; ) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. ''Monosporascus cannonballus''), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. ''Tympanis'') with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some ''Cordyceps'', also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the "bourrelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |