|
Abulfat Agha Javanshir
Abulfat agha Javanshir (; ) also known with his pen name ''Tuti'' () was an Iranian noble of Azerbaijani ethnicity. Early life He was born in 1766 to Ibrahim Khalil Khan of Karabakh and Rugan Khanum, an Armenian girl from Nakhichevanik village in Shusha. Had an excellent palace education and involved in affairs government since early age. Ibrahim Khalil Khan sent him to the Russian camp upon arrival of Valerian Zubov in 1796. This event was described by Mirza Jamal Javanshir, the vizier of the Karabakh Khanate and historian: He was sent as an hostage to Fath Ali Shah upon death of Agha Muhammad alongside his half-sister Aghabeyim agha Javanshir. He was later placed under Abbas Mirza, given the titular title of khan. Struggle for heirship He was called to Karabakh sometime in 1804 by his father when he had a fall out with his elder son and heir Mammad Hasan agha Javanshir. Since he was born of a "temporary wife" but had a royal favor, Mammad Hasan felt threatened and secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javanshir Clan
The Javanshirs ( az, Cavanşirlər; fa, جوانشیران – ''Javānširān'') are a Turkic clan from Karabakh, who belong to the Afshar tribe and are in turn a branch of the Oghuz Turks. Between 1748 and 1822, members of the Javanshir clan functioned as the head of the Karabakh Khanate. History Early years The greater Javanshir tribe is said to of came from Turkestan, as Reza-Qoli Khan Hedayat wrote in his book Rozvat-us-Safa, “the Javanshir elat came from Turkestan and belonged to the tribe of Oshir(Afshar) Khan, who was son of Ildyz Khan, the fourth son of Uguz(Oghuz) Khan.The Javanshir tribe joined the 120-thousand-strong army of Hulagu khan. Under Emir Timur, they came back from Rûm for the second time and spread across Turkestan, Kandahar, Kabul, and Iran. One of its branches led by Ibrahim Khalil Agha, who served Shah Abbas I, remained in Karabakh”Ismailov, Eldar, THE KHANS OF KARABAKH: THE ROOTS, SUBORDINATION TO THE RUSSIAN EMPIRE, AND LIQUIDATION OF THE KHANATE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehdigulu Khan Javanshir
Mehdigulu Khan Javanshir ( fa, مهدیقلی خان جوانشیر, translit=Mehdiqoli Xān Javānšir, az, مهدیقلو خان جاوانشیر; 1763 or 1772–1845) was the last Khan of the Karabakh Khanate, functioning as its head from 1806 to 1822. His only known issue was Khurshidbanu Natavan, a famous Azerbaijani poetess. Early life Mehdigulu Khan was born in 1763 to Ibrahim Khalil, the second Khan of Karabakh, and Khurshid Begum, daughter of Javad Khan and a granddaughter of Shahverdi Khan of Ganja. Although according to a report written by Tsitsianov on November 1805, he was 33 at time of writing - hence, possibly born . He lost half of his nose during fight against Qajars in his youth. Career under Ibrahim Khalil Khan He was sent together with his half-brother Mammad Hasan Agha Javanshir in pursuit of his cousin Muhammad Bey (son of Mehrali Bey), who seized rulership of Karabakh during chaos ensued due to Agha Muhammad Khan's death in 1797. In July 1805, he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
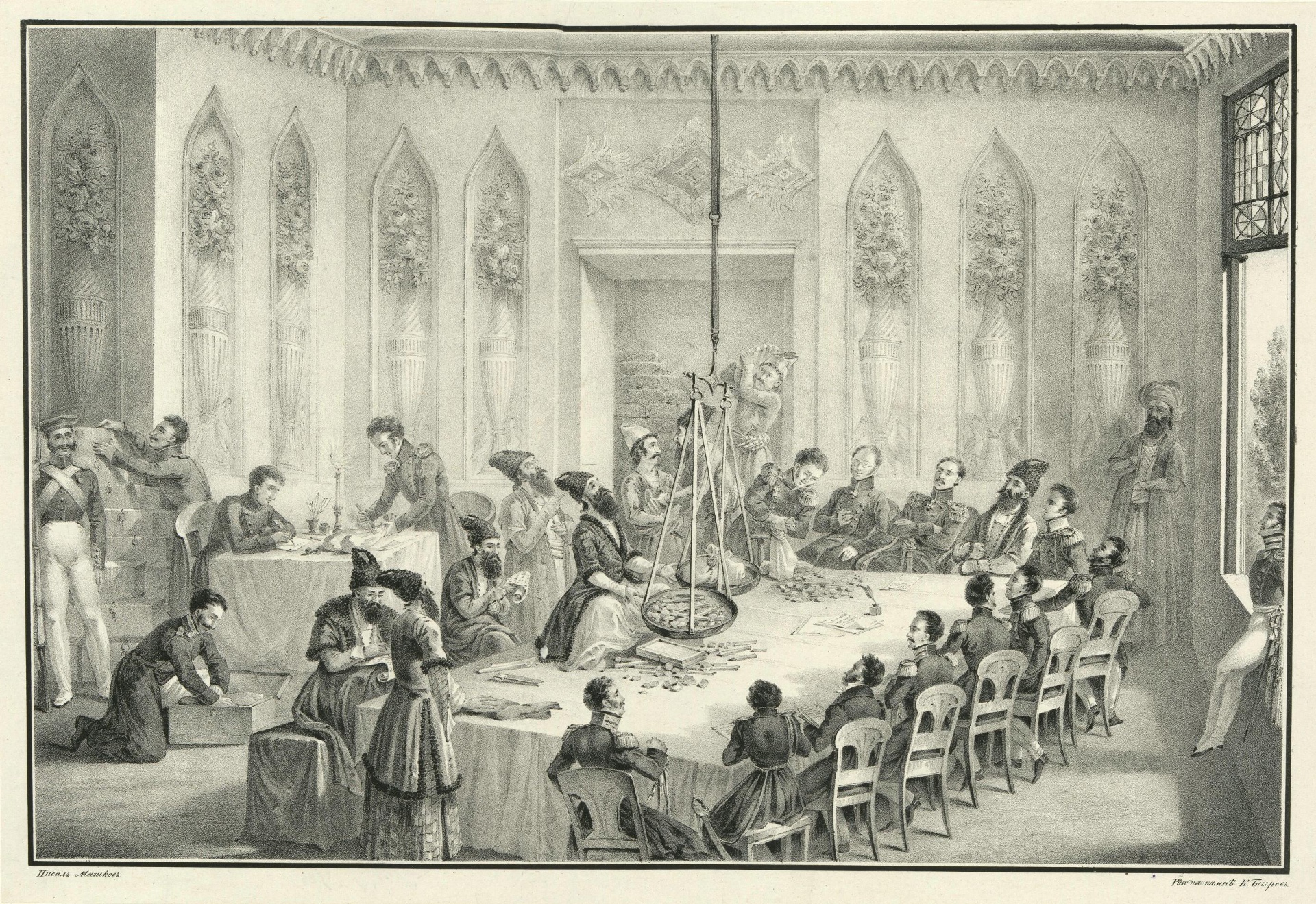
Treaty Of Turkmenchay
The Treaty of Turkmenchay ( fa, عهدنامه ترکمنچای; russian: Туркманчайский договор) was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–28). It was second of the series of treaties (the first was the 1813 Treaty of Gulistan and the last, the 1881 Treaty of Akhal) signed between Qajar Iran and Imperial Russia that forced Persia to cede or recognize Russian influence over the territories that formerly were Greater Iran, part of Iran. The treaty was signed on 21 February 1828 (5 Sha'ban 1243) in Torkamanchay (a village between Tabriz and Tehran). It made Persia cede the control of several areas in the South Caucasus to Russia: the Erivan Khanate, the Nakhichevan Khanate, Nakhchivan Khanate and the remainder of the Talysh Khanate. The boundary between Russia and Persia was set at the Aras (river), Aras River. The territories are now Armenia, the south of the Republic of Azerbaijan, Nakhchivan A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Persian War (1826–1828)
The Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828 was the last major military conflict between the Russian Empire and Persia. After the Treaty of Gulistan that concluded the previous Russo-Persian War in 1813, peace reigned in the Caucasus for thirteen years. However, Fath 'Ali Shah, constantly in need of foreign subsidies, relied on the advice of British agents, who advised him to reconquer the territories lost to the Russian Empire and pledged their support for military action. The matter was decided upon in spring 1826, when a bellicose party of Abbas Mirza prevailed in Tehran and the Russian minister, Aleksandr Sergeyevich Menshikov, was placed under house arrest. The war ended in 1828 following the occupation of Tabriz. The war had even more disastrous results for Persia than the 1804-1813 war, as the ensuing Treaty of Turkmenchay stripped Persia of its last remaining territories in the Caucasus, which comprised all of modern Armenia, the southern remainder of modern Azerbaijan, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Gulistan
The Treaty of Gulistan (russian: Гюлистанский договор; fa, عهدنامه گلستان) was a peace treaty concluded between the Russian Empire and Iran on 24 October 1813 in the village of Gulistan (now in the Goranboy District of Azerbaijan) as a result of the first full-scale Russo-Persian War (1804 to 1813). The peace negotiations were precipitated by the successful storming of Lankaran by General Pyotr Kotlyarevsky on 1 January 1813. It was the first of the series of treaties (the last being the Akhal Treaty) signed between Qajar Iran and Imperial Russia that forced Persia to cede or recognize Russian influence over the territories that formerly were part of Iran. The treaty confirmed the ceding and inclusion of what is now Dagestan, eastern Georgia, most of the Republic of Azerbaijan and parts of northern Armenia from Iran into the Russian Empire. The text was prepared by the British diplomat Sir Gore Ouseley, who served as a mediator and wielded a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jafargulu Agha Javanshir
Jafargulu agha Javanshir ( az, Cəfərqulu ağa Məhəmmədhəsən ağa oğlu Sarıcalı-Cavanşir; 1782 or 1787–1866) was an Azerbaijani poet, figure and a major-general of the Russian Army. Early life Jafargulu was born either in 1782/3 or in 1787, in Shusha. He was the elder son of Mammadhasan agha Javanshir - heir of Ibrahimkhalil khan of Karabakh - by Khayrunnisa begüm of Ganja. After his father's death on , he inherited all properties (about 36 villages), as well as leadership of his maternal clan of Jabrayillu and received the recognition as heir. He cooperated with Russian Empire under the orders of his grandfather during the 1804–1813 Russo-Persian War, routing Kurdish tribesmen of Karadagh. Dmitry Lisanevich, the Russian lieutenant-colonel who killed his grandfather in 1806, mentioned Jafargulu as one of the informants of treason of khan, he even claimed that Russian troops used Jafargulu's house as meeting point. Just a day after murder, Jafargulu rode wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hossein Khan Sardar
Hossein Qoli Khan Sardar Qajar ( fa, حسین قلی خان سردار قاجار), better simply known as Hossein Khan Sardar () (born ca. 1742 – died 1831) was an Iranian statesman in Qajar Iran, who was the last governor of the Erivan Khanate from 1807 to 1828. Around 1826–1828, he and Abbas Mirza, the crown prince, attempted to win back the Transcaucasian and Dagestanian possessions lost to Russia during the war of 1804-1813 which had ended with the Gulistan Treaty. However, using superior tactics and weapons developed since their defeat of Napoleon, the Tsar’s generals inflicted even greater losses on Iran. In addition to ceding further territories, the 1828 Treaty of Turkmenchay forced Iran to pay crippling reparations. The treaty also banned Hossein Khan and his younger brother, Hasan Khan, from ever venturing north of the Aras River, the new border. Hossein Khan belonged to the Qoyunlu branch of the Qajar clan, and was thus part of the royal Qajar dynasty. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanullah Khan Afshar
Amanallah Khan Khamseh-Afshar ( fa, امان الله خان خمسه افشار) was one of the most prominent commanders in the army of the Qajar shah (king) of Iran, Fath-Ali Shah Qajar (). A member of the Afshar clan of Zanjan (which he briefly governed), he was a son of Farajallah Khan Afshar. In 1806, during the Russo-Persian War of 1804–1813, Amanallah Khan was amongst the commanders assigned with the task to aid Ibrahim Khalil Khan, the khan (governor) of the Karabakh Khanate. However, by the time he had arrived, Ibrahim Khalil Khan had been murdered by the Russians. References Sources * * {{cite book , last1=Bournoutian, first1=George, author-link=George Bournoutian, title=From the Kur to the Aras: A Military History of Russia's Move into the South Caucasus and the First Russo-Iranian War, 1801–1813 , date=2021 , publisher=Brill Brill may refer to: Places * Brielle (sometimes "Den Briel"), a town in the western Netherlands * Brill, Buckinghamshire, a villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dizak
Dizak (), also known as Ktish after its main stronghold, was a medieval Armenian principality in the historical province of Artsakh and later one of the five melikdoms of Karabakh, which included the southern third of Khachen (present-day Nagorno-Karabakh) and from the 13th century also the canton of Baghk of Syunik. Robert H. Hewsen, ''Armenia: A Historical Atlas''. The University of Chicago Press, 2001, p. 163. The founder of this principality was Esayi Abu-Muse, in the 9th century. In the 16th-18th centuries, Dizak was ruled by the Armenian Melik-Avanian dynasty, a branch of the House of Syunik-Khachen. The seat of the princes of Dizak was the town of Togh (or Dogh) with the adjacent ancient fortress of Ktish. One of the last princes of Dizak, Esayi Melik-Avanian, was killed by Ibrahim Khalil Khan in 1781, after a long-lasting resistance in the fortress of Ktish. Today the name "Dizak" is often used to refer to the Hadrut Province of the Republic of Artsakh. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuğ
Tugh ( az, Tuğ) or Togh ( hy, Տող) is a village in the Khojavend District of Azerbaijan, in the Political status of Nagorno-Karabakh, disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh. The village had a mixed Armenian-Azerbaijani population before the First Nagorno-Karabakh War, the Azerbaijani inhabitants fled the fighting in 1991, and the Armenians, Armenian population fled the village during the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. History The village and the neighboring fortress of ''Ktish'' ( hy, Քթիշ), are first mentioned in the 9th century, as the capital of the Dizak, Principality of Dizak. In 854, Esayi Abu-Muse, the Prince of Dizak, resisted an Arab conquest of Armenia, Abbasid army under the command of Bugha al-Kabir at Ktish for more than a year.Tovma Artsruni and Anon, ''History of the House of Artruni'', Yerevan 1985, pp. 297–98. The 13th-century monastery of Gtichavank, and ruins of some churches including the 13th-century St. Stephen's Church are located near the village. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
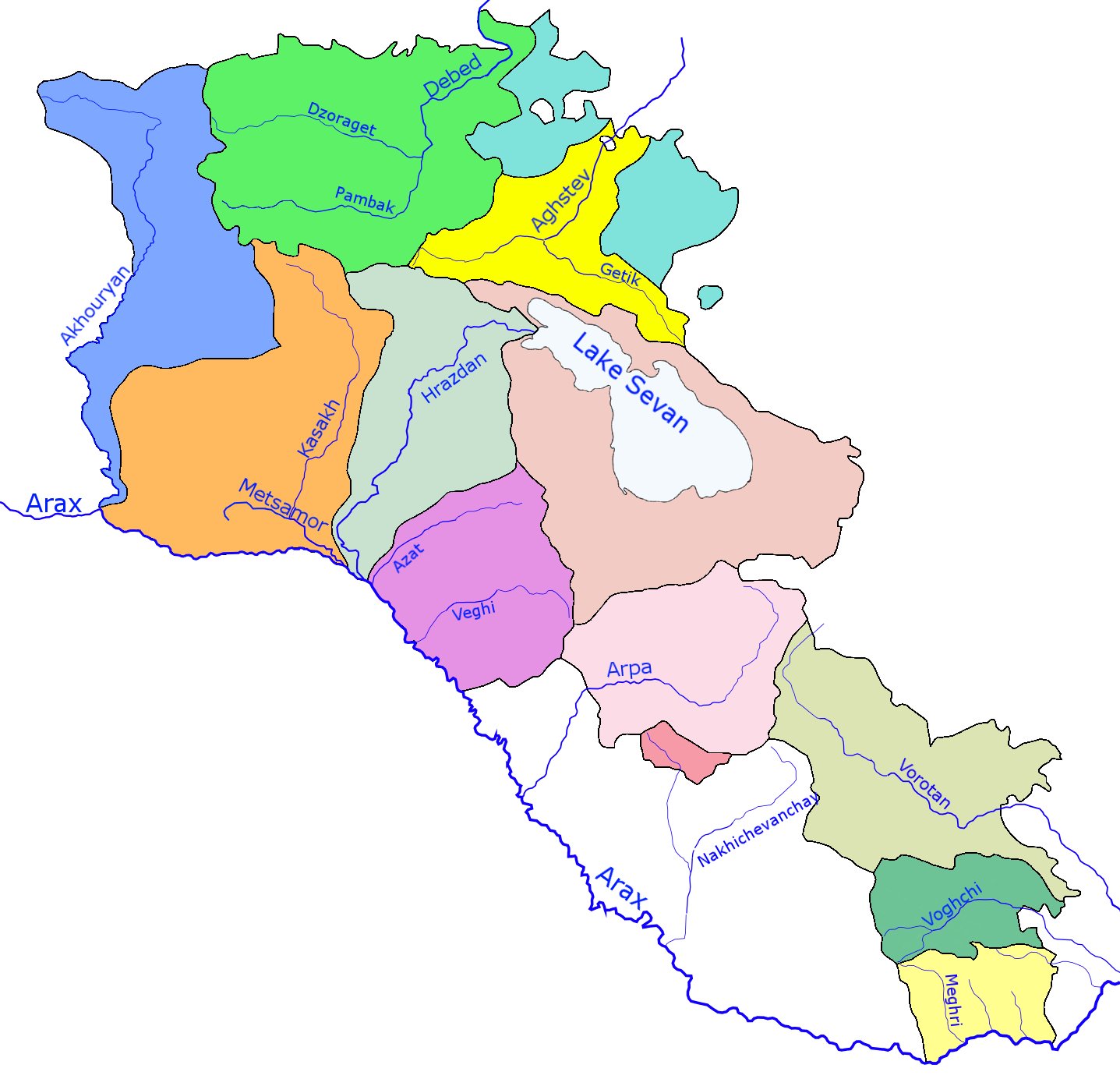
Vorotan (river)
The Vorotan (), or Bargushad () or Bazarchay ( az, Bazarçay), is a river in Transcaucasia that is the largest right tributary of the Hakari river. The river originates in the mountains of Azerbaijan's Kalbajar District and flows into Armenia's Syunik Province. It flows through Armenia for in a generally south-easterly direction. The river enters Azerbaijan again, flowing for through the districts of Qubadli and Zangilan. The lower section of the Hakari, from its confluence with the Vorotan until its confluence with the Aras river, is sometimes considered to be part of the Vorotan. Course of the river The river flows mostly through mountainous country and in several places has formed deep canyons. The towns of Sisian and Qubadli lie along its course. Six kilometers from Sisian, the river forms a waterfall — the "Shaki Waterfall" ( hy, Շաքիի ջրվեժ) — that is 18m high. The river forms a natural monument — the "Devil's Bridge" — near Tatev Monastery. There ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia (Republic of Dagestan) to the north, Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. Baku is the capital and largest city. The Azerbaijan Democratic Republic proclaimed its independence from the Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic in 1918 and became the first secular democratic Muslim-majority state. In 1920, the country was incorporated into the Soviet Union as the Azerbaijan SSR. The modern Republic of Azerbaijan proclaimed its independence on 30 August 1991, shortly before the dissolution of the Soviet Union in the same year. In September 1991, the ethnic Armenian majority of the Nagorno-Karabakh region formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |