|
Absorption Wavemeter
An absorption wavemeter is a simple electronic instrument used to measure the frequency of radio waves. It is an older method of measuring frequency, widely used from the birth of radio in the early 20th century until the 1970s, when the development of inexpensive frequency counters, which have far greater accuracy, made it largely obsolete. A wavemeter consists of an adjustable resonant circuit calibrated in frequency, with a meter or other means to measure the voltage or current in the circuit. When adjusted to resonance with the unknown frequency, the resonant circuit absorbs energy, which is indicated by a dip on the meter. Then the frequency can be read from the dial. Wavemeters are used for frequency measurements that do not require high accuracy, such as checking that a radio transmitter is operating within its correct frequency band, or checking for harmonics in the output. Many radio amateurs keep them as a simple way to check their output frequency. Similar devices can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from '' angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one event per second. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute (2 hertz), the period, —the interval at which the beats repeat—is half a second (60 seconds divided by 120 beats). Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals ( sound), radio waves, and light. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples of simple harmonic motion, the term ''frequency'' is defined as the number of cycles or vibrations per unit of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonant
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamic system, the system will oscillate at a higher amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies. Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are also known as resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies of the system. Small periodic forces that are near a resonant frequency of the system have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations in the system due to the storage of vibrational energy. Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, orbital resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measuring Instruments
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Established standard objects and events are used as units, and the process of measurement gives a number relating the item under study and the referenced unit of measurement. Measuring instruments, and formal test methods which define the instrument's use, are the means by which these relations of numbers are obtained. All measuring instruments are subject to varying degrees of instrument error and measurement uncertainty. These instruments may range from simple objects such as rulers and stopwatches to electron microscopes and particle accelerators. Virtual instrumentation is widely used in the development of modern measuring instruments. Time In the past, a common time measuring instrument was the sundial. Today, the usual measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grid Dip Oscillator
:''"Dip meter" can also refer to an influential early commercial expert system called Dipmeter Advisor; or may refer to an instrument that measures the magnetic dip angle of Earth's magnetic field, the field line angle in a vertical plane.'' Grid dip oscillator (GDO), also called grid dip meter, gate dip meter, dip meter, or just dipper, is a type of electronic instrument that measures the resonant frequency of nearby unconnected radio frequency tuned circuits. It is a variable-frequency oscillator that circulates a small-amplitude signal through an exposed coil, whose electromagnetic field can interact with adjacent circuitry. The oscillator loses power when its coil is near a circuit that resonates at the same frequency. A meter on the GDO registers the amplitude drop, or "dip", hence the name. Dip oscillators have been widely used by amateur radio operators for measuring the properties of resonant circuits, filters, and antennas. They can also be used for transmission lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
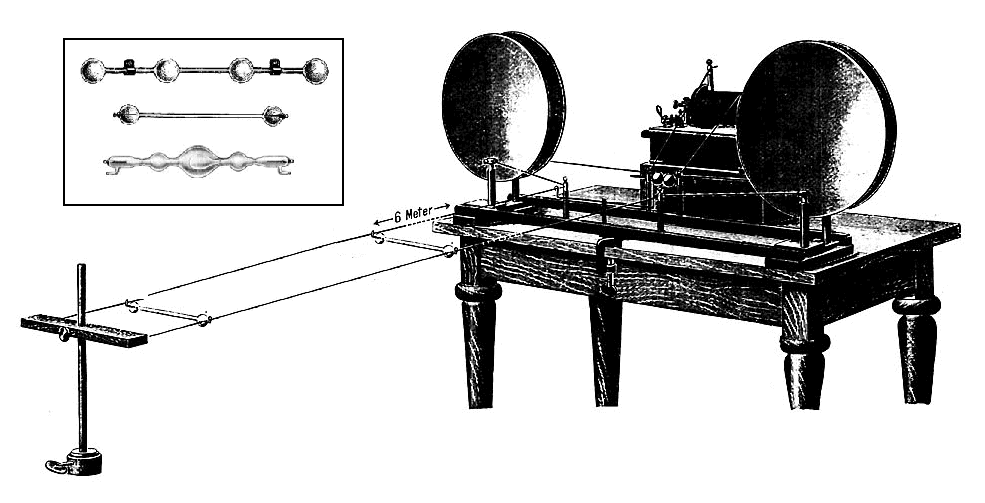
Lecher Lines
In electronics, a Lecher line or Lecher wires is a pair of parallel wires or rods that were used to measure the wavelength of radio waves, mainly at VHF, UHF and microwave frequencies. They form a short length of balanced transmission line (a resonant stub). When attached to a source of radio-frequency power such as a radio transmitter, the radio waves form standing waves along their length. By sliding a conductive bar that bridges the two wires along their length, the length of the waves can be physically measured. Austrian physicist Ernst Lecher, improving on techniques used by Oliver Lodge and Heinrich Hertz, developed this method of measuring wavelength around 1888. Lecher lines were used as frequency measuring devices until frequency counters became available after World War 2. They were also used as components, often called " resonant stubs", in VHF, UHF and microwave radio equipment such as transmitters, radar sets, and television sets, serving as tank circuits, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave Cavity
A microwave cavity or ''radio frequency (RF) cavity'' is a special type of resonator, consisting of a closed (or largely closed) metal structure that confines electromagnetic fields in the microwave region of the spectrum. The structure is either hollow or filled with dielectric material. The microwaves bounce back and forth between the walls of the cavity. At the cavity's resonant frequencies they reinforce to form standing waves in the cavity. Therefore, the cavity functions similarly to an organ pipe or sound box in a musical instrument, oscillating preferentially at a series of frequencies, its resonant frequencies. Thus it can act as a bandpass filter, allowing microwaves of a particular frequency to pass while blocking microwaves at nearby frequencies. A microwave cavity acts similarly to a resonant circuit with extremely low loss at its frequency of operation, resulting in quality factors (Q factors) up to the order of 106, compared to 102 for circuits mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-band
The X band is the designation for a band of frequencies in the microwave radio region of the electromagnetic spectrum. In some cases, such as in communication engineering, the frequency range of the X band is rather indefinitely set at approximately 7.0–11.2 GHz. In radar engineering, the frequency range is specified by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) as 8.0–12.0 GHz. The X band is used for radar, satellite communication, and wireless computer networks. Radar X band is used in radar applications including continuous-wave, pulsed, single-polarization, dual-polarization, synthetic aperture radar, and phased arrays. X band radar frequency sub-bands are used in civil, military, and government institutions for weather monitoring, air traffic control, maritime vessel traffic control, defense tracking, and vehicle speed detection for law enforcement. X band is often used in modern radars. The shorter wavelengths of the X band allo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stripline
Stripline is a transverse electromagnetic (TEM) transmission line medium invented by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Force Cambridge Research Centre in the 1950s. Stripline is the earliest form of planar transmission line. Description A stripline circuit uses a flat strip of metal which is sandwiched between two parallel ground planes. The insulating material of the substrate forms a dielectric. The width of the strip, the thickness of the substrate and the relative permittivity of the substrate determine the characteristic impedance of the strip which is a transmission line. As shown in the diagram, the central conductor need not be equally spaced between the ground planes. In the general case, the dielectric material may be different above and below the central conductor. To prevent the propagation of unwanted modes, the two ground planes must be shorted together. This is commonly achieved by a row of vias running parallel to the strip on each side. Like coaxial cable, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumped Component
The lumped-element model (also called lumped-parameter model, or lumped-component model) simplifies the description of the behaviour of spatially distributed physical systems, such as electrical circuits, into a Topology (electrical circuits), topology consisting of discrete entities that approximate the behaviour of the distributed system under certain assumptions. It is useful in electrical network, electrical systems (including electronics), mechanical multibody systems, heat transfer, acoustics, etc. This may be contrasted to distributed parameter systems or models in which the behaviour is distributed spatially and cannot be considered as localized into discrete entities. Mathematically speaking, the simplification reduces the State space (controls), state space of the system to a counting number, finite dimension, and the partial differential equations (PDEs) of the continuous (infinite-dimensional) time and space model of the physical system into ordinary differential equa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galvanometer
A galvanometer is an electromechanical measuring instrument for electric current. Early galvanometers were uncalibrated, but improved versions, called ammeters, were calibrated and could measure the flow of current more precisely. A galvanometer works by deflecting a pointer in response to an electric current flowing through a coil in a constant magnetic field. Galvanometers can be thought of as a kind of actuator. Galvanometers came from the observation, first noted by Hans Christian Ørsted in 1820, that a magnetic compass's needle deflects when near a wire having electric current. They were the first instruments used to detect and measure small amounts of current. André-Marie Ampère, who gave mathematical expression to Ørsted's discovery, named the instrument after the Italian electricity researcher Luigi Galvani, who in 1791 discovered the principle of the frog galvanoscope – that electric current would make the legs of a dead frog jerk. Galvanometers have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Wave
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz ( GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (shorter than a grain of rice); at 30 Hz the corresponding wavelength is (longer than the radius of the Earth). Like all electromagnetic waves, radio waves in a vacuum travel at the speed of light, and in the Earth's atmosphere at a close, but slightly lower speed. Radio waves are generated by charged particles undergoing acceleration, such as time-varying electric currents. Naturally occurring radio waves are emitted by lightning and astronomical objects, and are part of the blackbody radiation emitted by all warm objects. Radio waves are generated artificially by an electronic device called a transmitter, which is connected to an antenna which radiates the waves. They are received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |