|
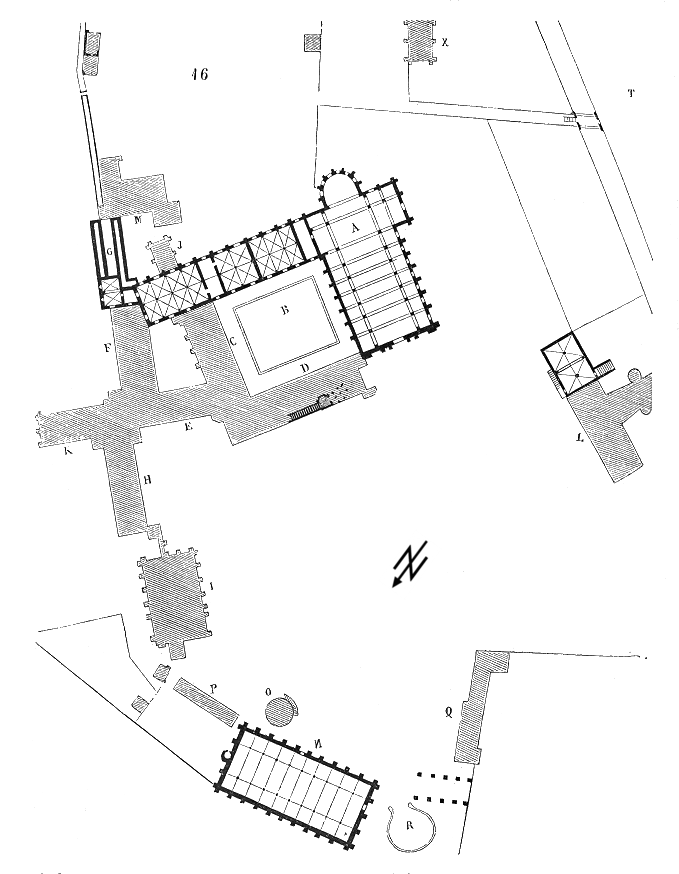
Abbey Of Maubuisson
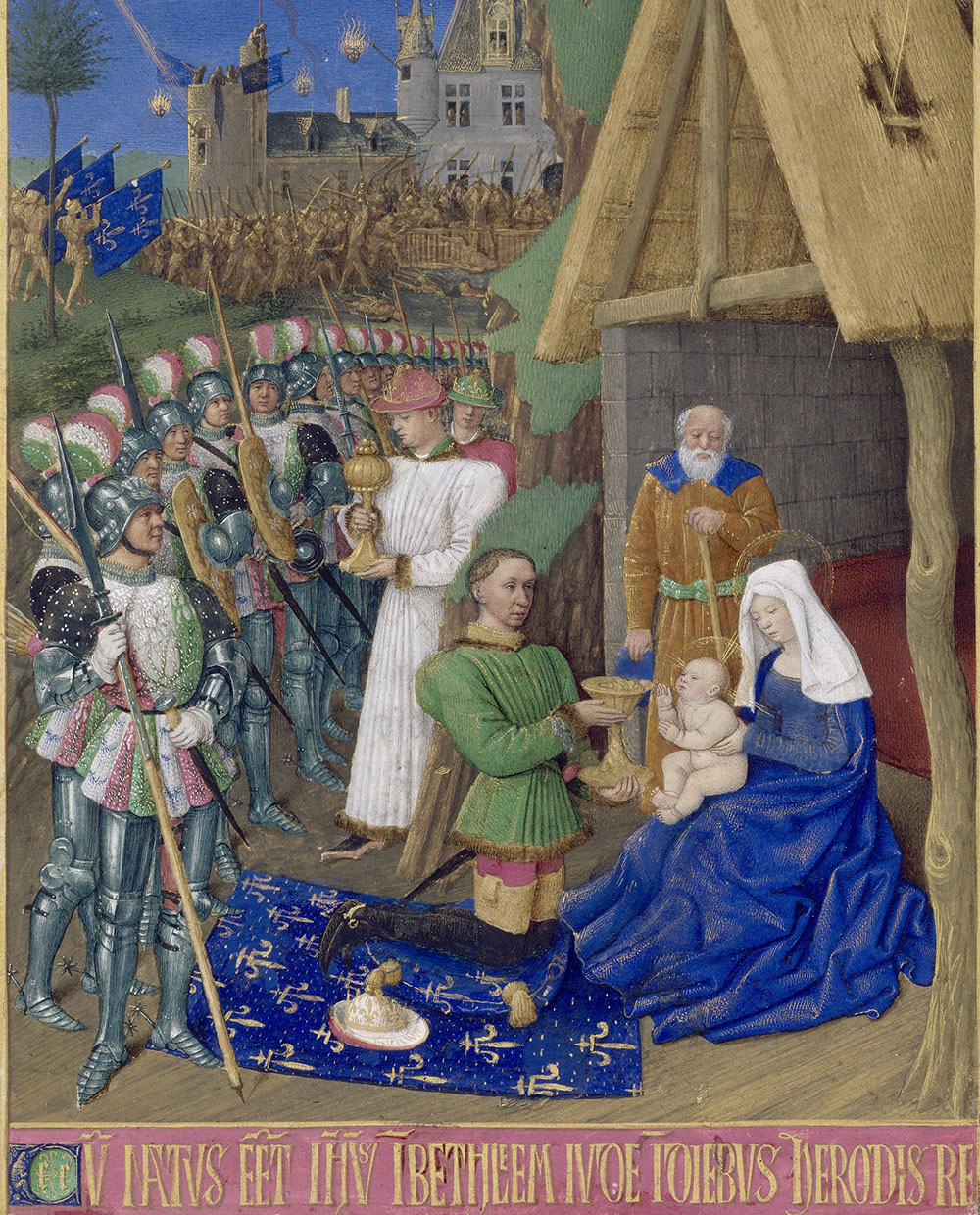
Maubuisson Abbey (french: Abbaye de Maubuisson or ) is a Cistercian nunnery at Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône, in the Val-d'Oise department of France. It was founded in A.D. 1236 by Blanche of Castile, Queen of France, who may have been buried there in 1252. The site is now within the north-western suburbs of Paris. The surviving buildings are listed as a ''monument historique''. History The abbey was founded in 1236 by Blanche of Castile, the queen consort of Louis VIII. It thrived financially under royal patronage until the Hundred Years' War. In the fifteenth century the nuns twice supported rival abbesses. After a century of decline the abbey was disbanded in 1787 by order of Louis XVI. From foundation to the Hundred Years War As part of an effort to strengthen the ties between royalty and the abbeys, Blanche of Castile decided to finance and build her own abbey. In 1236 she annexed the lands of Pontoise and Saint-Ouen, which only became Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône much later. These lands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône
Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône () is a commune in the northwestern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the center of Paris, in the "new town" of Cergy-Pontoise, created in the 1960s. Population Transport Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône is served by two interchange stations on Paris RER C line and on the Transilien Paris-Nord suburban rail line: Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône-Liesse and Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône. Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône is also served by two other stations on the Transilien Paris-Nord suburban rail line: Épluches and Pont-Petit. Finally, Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône is also served by Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône-Quartier de l'Église station on the Transilien Paris-Saint-Lazare suburban rail line. Education Schools in the commune include: *Four sets of preschools (''maternelles'') and elementary schools: Matisse, Prairie, Jean Effel, Le Nôtre [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. France originated as West Francia (''Francia Occidentalis''), the western half of the Carolingian Empire, with the Treaty of Verdun (843). A branch of the Carolingian dynasty continued to rule until 987, when Hugh Capet was elected king and founded the Capetian dynasty. The territory remained known as ''Francia'' and its ruler as ''rex Francorum'' ("king of the Franks") well into the High Middle Ages. The first king calling himself ''rex Francie'' ("King of France") was Philip II, in 1190, and officially from 1204. From then, France was continuously ruled by the Capetians and their cadet lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angélique D'Estrées
Angelique or Angélique may refer to: * Angélique (given name), a French feminine name Arts and entertainment Music * Angélique (instrument), a string instrument of the lute family * ''Angélique'', a 1927 opéra bouffe by Jacques Ibert * "Angelique" (song), the Danish entry in the Eurovision Song Contest 1961, performed by Dario Campeotto * "Angélique", a song by Theatre of Tragedy from the album '' Aégis'' * "Angelique", a song by Badfinger from the album ''Magic Christian Music'' * "Angelique", a song by Mike Oldfield from the album ''Light + Shade'' * ''Angelique'', the debut album by Yukie Nishimura Other uses in arts and entertainment * ''Angélique'' (novel series), by Anne Golon ** ''Angélique, Marquise des Anges'', a 1964 film adaptation directed by Bernard Borderie ** ''Angélique'' (film), a 2013 film adaptation directed by Ariel Zeitoun * ''Angélique'' (play), by Lorena Gale * ''Angelique'' (video game series), a cross-media franchise including video g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Wars Of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estimates, between two and four million people died from violence, famine or diseases which were directly caused by the conflict; additionally, the conflict severely damaged the power of the French monarchy. The fighting ended in 1598 when Henry of Navarre, who had converted to Catholicism in 1593, was proclaimed Henry IV of France and issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted substantial rights and freedoms to the Huguenots. However, the Catholics continued to have a hostile opinion of Protestants in general and they also continued to have a hostile opinion of him as a person, and his assassination in 1610 triggered a fresh round of Huguenot rebellions in the 1620s. Tensions between the two religions had been building since the 1530s, exacerba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône (95), Abbaye De Maubuisson, Grange, Mur Gouttereau Nord, Vue Vers Le Sud-est 4
Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône () is a commune in the northwestern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the center of Paris, in the "new town" of Cergy-Pontoise, created in the 1960s. Population Transport Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône is served by two interchange stations on Paris RER C line and on the Transilien Paris-Nord suburban rail line: Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône-Liesse and Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône. Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône is also served by two other stations on the Transilien Paris-Nord suburban rail line: Épluches and Pont-Petit. Finally, Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône is also served by Saint-Ouen-l'Aumône-Quartier de l'Église station on the Transilien Paris-Saint-Lazare suburban rail line. Education Schools in the commune include: *Four sets of preschools (''maternelles'') and elementary schools: Matisse, Prairie, Jean Effel, Le Nôtre [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XI Of France
Louis XI (3 July 1423 – 30 August 1483), called "Louis the Prudent" (french: le Prudent), was King of France from 1461 to 1483. He succeeded his father, Charles VII. Louis entered into open rebellion against his father in a short-lived revolt known as the Praguerie in 1440. The king forgave his rebellious vassals, including Louis, to whom he entrusted the management of the Dauphiné, then a province in southeastern France. Louis's ceaseless intrigues, however, led his father to banish him from court. From the Dauphiné, Louis led his own political establishment and married Charlotte of Savoy, daughter of Louis, Duke of Savoy, against the will of his father. Charles VII sent an army to compel his son to his will, but Louis fled to Burgundy, where he was hosted by Philip the Good, the Duke of Burgundy, Charles' greatest enemy. When Charles VII died in 1461, Louis left the Burgundian court to take possession of his kingdom. His taste for intrigue and his intense diplomatic ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trials Of The Knights Templar
The Knights Templar trace their beginnings to the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem in when nine Christian knights, under the auspices of King Baldwin II and the Patriarch Warmund, were given the task of protecting pilgrims on the roads to Jerusalem, which they did for nine years until elevated to a military order at the Council of Troyes in 1129. They became an elite fighting force in the Crusades known for their propensity not to retreat or surrender. Eventually, their rules of secrecy, their power, privileges and their wealth,During this time period money loaned to popes, kings and princes was not being repaid. The high costs of maintaining an army in the Holy Land, of castle building and rebuilding, expensive armour, weapons, and warhorses was catching up with the order. By 1307 it seems much of their great wealth had been expended. See Anne Gilmour-Bryson, ''The trial of the Templars in Cyprus: a complete English edition'' (Leiden, Boston, Köln: Brill, 1998), p. 4. made them vuln ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Cross
The True Cross is the cross upon which Jesus was said to have been crucified, particularly as an object of religious veneration. There are no early accounts that the apostles or early Christians preserved the physical cross themselves, although protective use of the sign of the cross was common by at least the 2nd century. Post-Nicene historians such as Socrates of Constantinople relate that Helena, the mother of the Roman emperor ConstantineI, travelled to the Holy Land in the years 326–328, founding churches and establishing relief agencies for the poor. The late 4th-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus claimed that while there she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, St. Dismas and Gestas, executed with him. To one cross was affixed the titulus bearing Jesus's name, but according to Rufinus, Helena was not sure until a miracle revealed that this was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross , colors_label = Attire , march = , mascot = Two knights riding a single horse , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = The Crusades, including: , anniversaries = , decorations = , battle_honours = , commander1 = Hugues de Payens , commander1_label = First Grand Master , commander2 = Jacques de Molay , commander2_label = Last Grand Master , commander3 = , commander3_label = , notable_commanders = The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon ( la, Pauperes commilitones Christi Templique Salomonici), also known as the Order of Solomon's Temple, the Knights Templar, or simply the Templars, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip IV Of France
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (french: Philippe le Bel), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre as Philip I from 1284 to 1305, as well as Count of Champagne. Although Philip was known to be handsome, hence the epithet ''le Bel'', his rigid, autocratic, imposing, and inflexible personality gained him (from friend and foe alike) other nicknames, such as the Iron King (french: le Roi de fer, link=no). His fierce opponent Bernard Saisset, bishop of Pamiers, said of him: "He is neither man nor beast. He is a statue." Philip, seeking to reduce the wealth and power of the nobility and clergy, relied instead on skillful civil servants, such as Guillaume de Nogaret and Enguerrand de Marigny, to govern the kingdom. The king, who sought an uncontested monarchy, compelled his upstart vassals by wars and restricted their feudal privileges, paving the way for the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choir (architecture)
A choir, also sometimes called quire, is the area of a church or cathedral that provides seating for the clergy and church choir. It is in the western part of the chancel, between the nave and the sanctuary, which houses the altar and Church tabernacle. In larger medieval churches it contained choir-stalls, seating aligned with the side of the church, so at right-angles to the seating for the congregation in the nave. Smaller medieval churches may not have a choir in the architectural sense at all, and they are often lacking in churches built by all denominations after the Protestant Reformation, though the Gothic Revival revived them as a distinct feature. As an architectural term "choir" remains distinct from the actual location of any singing choir – these may be located in various places, and often sing from a choir-loft, often over the door at the liturgical western end. In modern churches, the choir may be located centrally behind the altar, or the pulpit. The back-choir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabrielle D'Estrées
Gabrielle d'Estrées, Duchess of Beaufort and Verneuil, Marchioness of Monceaux (; 157310 April 1599) was a mistress, confidante and adviser of Henry IV of France. She persuaded Henry to renounce Protestantism in favour of Catholicism in 1593. Later she urged French Catholics to accept the Edict of Nantes, which granted certain rights to the Protestants. As it was legally impossible for the King to marry her as he was already married to Margaret of Valois, he controversially petitioned Pope Clement VIII for an annulment in February 1599 to end his childless first marriage, and announced his intention to marry Gabrielle and have her crowned the next Queen of France, while legitimizing their three children born out of wedlock. Her coronation and wedding never occurred due to her untimely and sudden death. Birth Gabrielle d'Estrées was born at either the Château de la Bourdaisière in Montlouis-sur-Loire in Touraine, or at the Château de Cœuvres in Picardy. Her parents were An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |