|
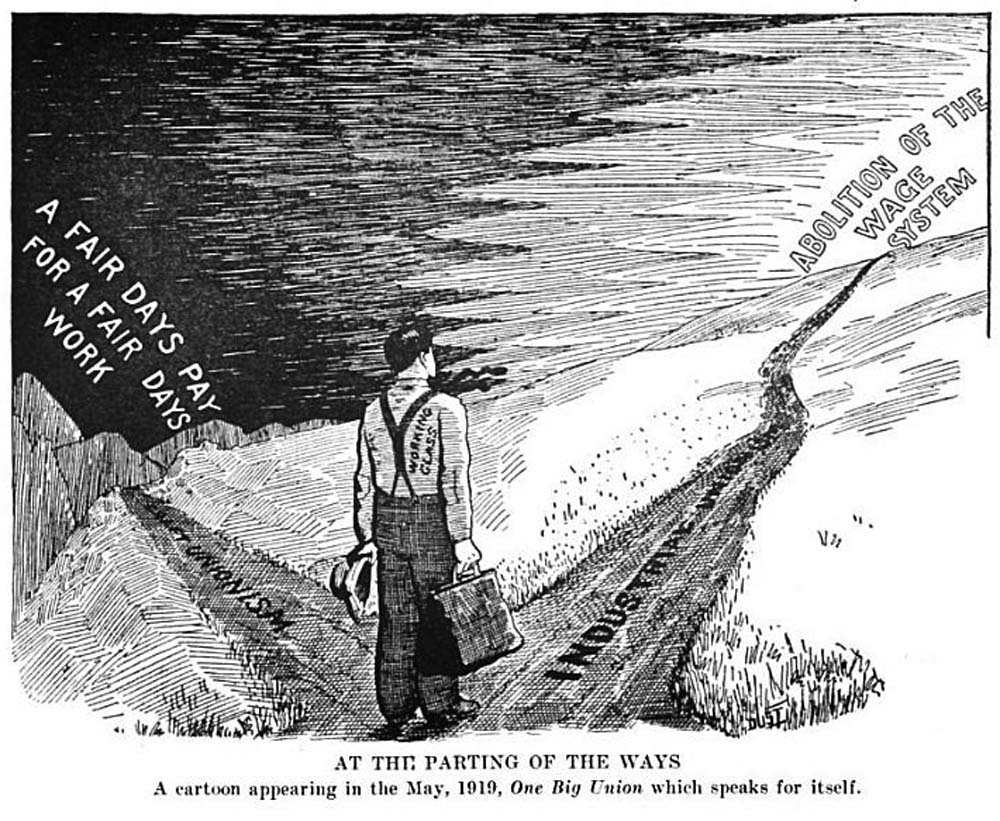
A Fair Day's Wage For A Fair Day's Work
A fair day's wage for a fair day's work is an objective of the labor movement, trade unions and other workers' groups, to increase pay, and adopt reasonable hours of work. It is a motto of the American Federation of Labor. Critique In 1881 Frederick Engels criticised the slogan in the first issue of ''The Labour Standard''. He argued that workers exchange their full labour power for a day in return for the subsistence necessary to maintain them for a day: "The workman gives as much, the Capitalist gives as little, as the nature of the bargain will admit." He also points out that capitalists can force a better bargain as they can live off their capital, but workers, without reserves, will be forced to accept work at a less advantageous rate. As innovation continually replaces workers with machines, he argues, workers come to form an industrial reserve army. Further, he argues that the wealth of capitalists has been accumulated through the exploitation of workers. He ends up calling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parting Of Tthe Ways
Parting may refer to: *Parting (film), ''Parting'' (film), a 2016 Afghan-Iranian film *Parting.com, a funeral home directory *Parting tradition *Cleavage (crystal)#Parting *Side-parting, a common male hairstyle: see Regular haircut *PartinG (gamer), a South Korean ''StarCraft II'' player *''The Parting'', an opera by Tom Cipullo *Gold parting or just parting, a final stage in gold extraction See also * *Part (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motto
A motto (derived from the Latin , 'mutter', by way of Italian , 'word' or 'sentence') is a sentence or phrase expressing a belief or purpose, or the general motivation or intention of an individual, family, social group, or organisation. Mottos (or mottoes) are usually found predominantly in written form (unlike slogans, which may also be expressed orally), and may stem from long traditions of social foundations, or from significant events, such as a civil war or a revolution. A motto may be in any language, but Latin has been widely used, especially in the Western world. Heraldry In heraldry, a motto is often found below the shield in a banderole; this placement stems from the Middle Ages, in which the vast majority of nobles possessed a coat of arms complete with a motto. In the case of Scottish heraldry, it is mandated to appear above the crest. Spanish coats of arms may display a motto in the bordure of the shield. In heraldic literature, the terms 'rallying cry' res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Federation Of Labor
The American Federation of Labor (A.F. of L.) was a national federation of labor unions in the United States that continues today as the AFL-CIO. It was founded in Columbus, Ohio, in 1886 by an alliance of craft unions eager to provide mutual support and disappointed in the Knights of Labor. Samuel Gompers was elected the full-time president at its founding convention and reelected every year, except one, until his death in 1924. He became the major spokesperson for the union movement. The A.F. of L. was the largest union grouping, even after the creation of the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) by unions that were expelled by the A.F. of L. in 1935. The Federation was founded and dominated by craft unions. especially the building trades. In the late 1930s craft affiliates expanded by organizing on an industrial union basis to meet the challenge from the CIO. The A.F. of L. and CIO competed bitterly in the late 1930s, but then cooperated during World War II and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Labour Standard
The Labour Standard was a short-lived trade unionist newspaper in London, published between May 1881 and July 1885. It described itself as 'the recognised industrial journal of the organised trades of the United Kingdom'. The paper's initial editor was George Shipton, Secretary of the London Trades Council. In February 1884 Shipton was replaced by William Barnett, who edited it until its closure.Harrison, ''British Labour Periodicals'', p. 268. The paper was published every Saturday and sold for one penny. Each edition consisted of eight pages. The paper is principally remembered for publishing a number of articles by Frederick Engels. Engels ceased to be a contributor after Shipton complained that an article by Karl Kautsky was "too strong"; Engels remarked that as some of his own articles would be even stronger, it would be best if he did not submit further articles. ''The Labour Standard'' online *A Fair Day's Wages for a Fair Day's Work Fredrick Engels No. 1 7 May 1881 * Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labour Power
Labour power (in german: Arbeitskraft; in french: force de travail) is a key concept used by Karl Marx in his critique of capitalist political economy. Marx distinguished between the capacity to do work, labour power, from the physical act of working, labour. Labour power exists in any kind of society, but on what terms it is traded or combined with means of production to produce goods and services has historically varied greatly. Under capitalism, according to Marx, the ''productive powers of labour'' appear as the ''creative power of capital''. Indeed, "labour power at work" becomes a component of capital, it functions as working capital. Work becomes just work, workers become an abstract labour force, and the control over work becomes mainly a management prerogative. Definition Karl Marx introduces the concept in chapter 6 of the first volume of ''Capital'', as follows: :"By labour-power or capacity for labour is to be understood the aggregate of those mental and physical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Reserve Army
Reserve army of labour is a concept in Karl Marx's critique of political economy. It refers to the unemployed and Underemployment, underemployed in Capitalist mode of production (Marxist theory), capitalist society. It is synonymous with "industrial reserve army" or "relative surplus population", except that the unemployed can be defined as those actually looking for work and that the relative surplus population also includes people unable to work. The use of the word "army" refers to the workers being conscripted and regimented in the workplace in a hierarchy under the Commanding heights of the economy, command or authority of the owners of Capital (economics), capital. Marx did not invent the term "reserve army of labour". It was already being used by Friedrich Engels in his 1845 book ''The Condition of the Working Class in England''. What Marx did was theorize the reserve army of labour as a necessary part of the capitalist organization of work. Prior to what Marx regarded as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Workers Of The World
The Industrial Workers of the World (IWW), members of which are commonly termed "Wobblies", is an international labor union that was founded in Chicago in 1905. The origin of the nickname "Wobblies" is uncertain. IWW ideology combines general unionism with industrial unionism, as it is a general union, subdivided between the various industries which employ its members. The philosophy and tactics of the IWW are described as "revolutionary industrial unionism", with ties to socialist, syndicalist, and anarchist labor movements. In the 1910s and early 1920s, the IWW achieved many of their short-term goals, particularly in the American West, and cut across traditional guild and union lines to organize workers in a variety of trades and industries. At their peak in August 1917, IWW membership was estimated at more than 150,000, with active wings in the United States, the UK, Canada, and Australia. The extremely high rate of IWW membership turnover during this era (estimated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Political Catchphrases
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |