|
A Journey Made In The Summer Of 1794
''A Journey Made in the Summer of 1794, through Holland and the Western Frontier of Germany, with a Return Down the Rhine: to which are added Observations During a Tour to the Lakes of Lancashire, Westmoreland, and Cumberland'' is a travel narrative by Ann Radcliffe first published in 1795. Radcliffe at that time was the famous and successful author of four Gothic novels, largely set in Southern European locales which she never visited; this journey was her first time leaving England, and featured a Northern itinerary. The book was published by George Robinson, who published Radcliffe's bestselling ''The Mysteries of Udolpho ''The Mysteries of Udolpho'', by Ann Radcliffe, appeared in four volumes on 8 May 1794 from G. G. and J. Robinson of London. Her fourth and most popular novel, ''The Mysteries of Udolpho'' tells of Emily St. Aubert, who suffers misadventures th ...'' the preceding year. References Citations Works cited * * * External links {{travel-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travel Narrative
The genre of travel literature encompasses outdoor literature, guide books, nature writing, and travel memoirs. One early travel memoirist in Western literature was Pausanias, a Greek geographer of the 2nd century CE. In the early modern period, James Boswell's ''Journal of a Tour to the Hebrides'' (1786) helped shape travel memoir as a genre. History Early examples of travel literature include the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (generally considered a 1st century CE work; authorship is debated), Pausanias' ''Description of Greece'' in the 2nd century CE, ''Safarnama'' (Book of Travels) by Nasir Khusraw (1003-1077), the '' Journey Through Wales'' (1191) and '' Description of Wales'' (1194) by Gerald of Wales, and the travel journals of Ibn Jubayr (1145–1214), Marco Polo (1254–1354), and Ibn Battuta (1304–1377), all of whom recorded their travels across the known world in detail. As early as the 2nd century CE, Lucian of Samosata discussed history and tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ann Radcliffe
Ann Radcliffe (née Ward; 9 July 1764 – 7 February 1823) was an English novelist and a pioneer of Gothic fiction. Her technique of explaining apparently supernatural elements in her novels has been credited with gaining respectability for Gothic fiction in the 1790s.The British LibrarRetrieved 12 November 2016./ref> Radcliffe was the most popular writer of her day and almost universally admired; contemporary critics called her the mighty enchantress and the Shakespeare of romance-writers, and her popularity continued through the 19th century. Interest has revived in the early 21st century, with the publication of three biographies.Chawton House LibraryRuth Facer, "Ann Radcliffe (1764–1823)" retrieved 1 December 2012. Biography Early life Radcliffe was born Ann Ward in Holborn, London on 9 July 1764. She was the only child to William Ward (1737-1798) and Ann Oates (1726-1800), and her mother was 36 years old when she gave birth. Her father worked as a haberdasher in Lond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Fiction
Gothic fiction, sometimes called Gothic horror in the 20th century, is a loose literary aesthetic of fear and haunting. The name is a reference to Gothic architecture of the European Middle Ages, which was characteristic of the settings of early Gothic novels. The first work to call itself Gothic was Horace Walpole's 1764 novel ''The Castle of Otranto'', later subtitled "A Gothic Story". Subsequent 18th century contributors included Clara Reeve, Ann Radcliffe, William Beckford (novelist), William Thomas Beckford, and Matthew Gregory Lewis, Matthew Lewis. The Gothic influence continued into the early 19th century, works by the Romantic poetry, Romantic poets, and novelists such as Mary Shelley, Charles Maturin, Walter Scott and E. T. A. Hoffmann frequently drew upon gothic motifs in their works. The early Victorian literature, Victorian period continued the use of gothic, in novels by Charles Dickens and the Brontë family, Brontë sisters, as well as works by the American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
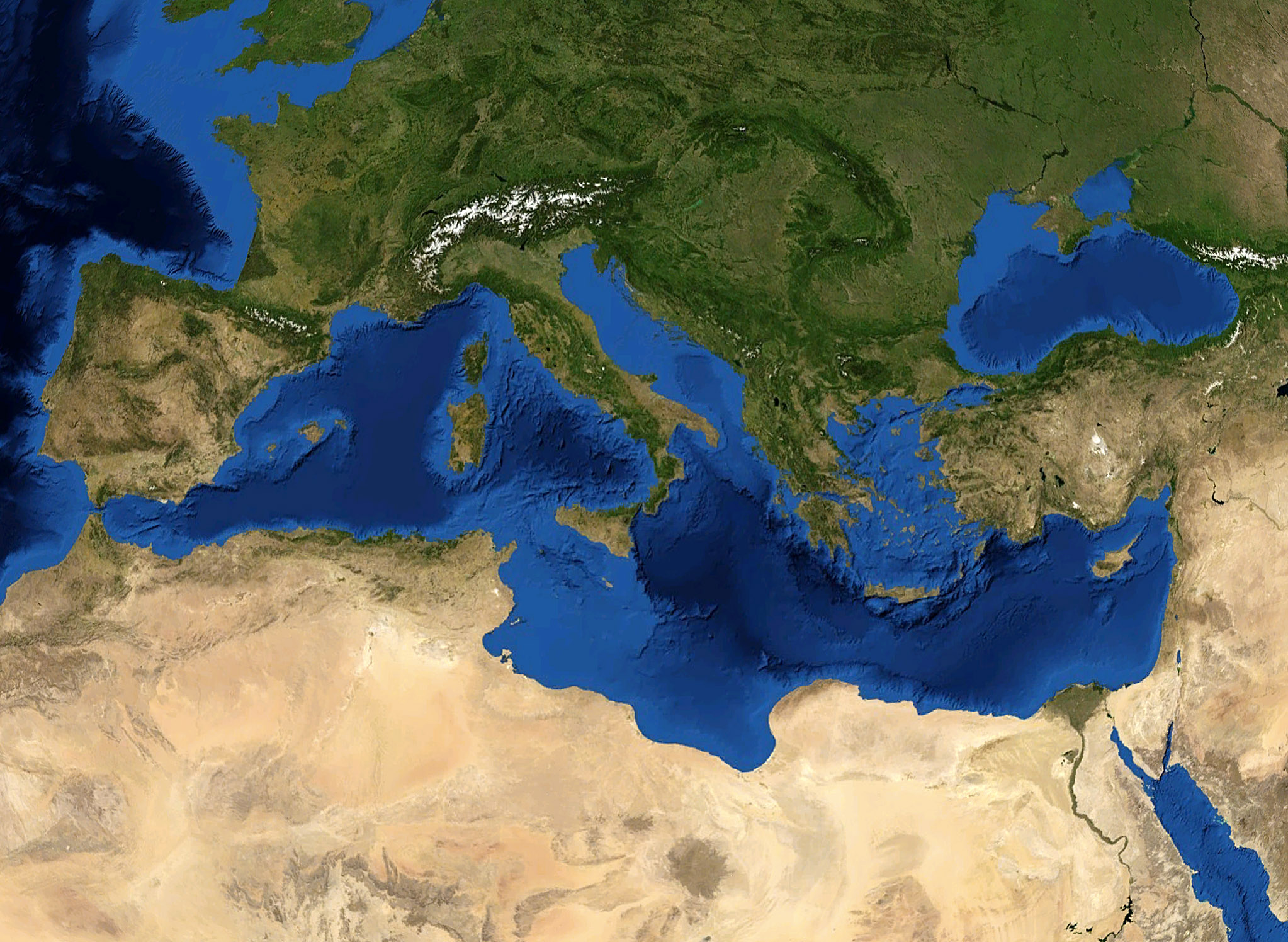
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern regions of Europe, region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, East Thrace, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy, Kosovo, Malta, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, Romania, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, Southern France, Spain, and Vatican City (the Holy See). Southern Europe is focused on the three peninsulas located in the extreme south of the European continent. These are the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, Apennine Peninsula, and the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. These three peninsulas are separated from the rest of Europe by towering mountain ranges, respectively by the Pyrenees, the Alps and the Balkan Mountains. The location of these peninsulas in the heart of the Mediterranean Sea, as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Robinson (bookseller)
George Robinson (bapt. 20 December 1736 – 6 June 1801) was an English bookseller and publisher working in London. Robinson published ''The Lady's Magazine'' and a serial reference work, '' The New Annual Register'', as well as fiction and non-fiction. He was also known for publishing books written by women. Life Robinson was baptised at Dalston, Cumberland, in December 1736,Henry Richard Tedder, "Robinson, George", in ''Dictionary of National Biography'', 1885-1900, Volume 49 and about 1755 migrated to London in search of work. John Nichols later said that Robinson came with "a decent education, and a great share of natural sense and shrewdness." John Nichols, ''Literary Anecdotes of the Eighteenth Century'', vol. 3pp. 445–448 He was an assistant to John Rivington (1720–1792), a publisher in St Paul's Churchyard, and later worked for a Mr. Johnstone on Ludgate Hill. In about 1763 he and a friend, John Roberts, went into business in Paternoster Row as booksellers. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Mysteries Of Udolpho
''The Mysteries of Udolpho'', by Ann Radcliffe, appeared in four volumes on 8 May 1794 from G. G. and J. Robinson of London. Her fourth and most popular novel, ''The Mysteries of Udolpho'' tells of Emily St. Aubert, who suffers misadventures that include the death of her mother and father, supernatural terrors in a gloomy castle, and machinations of an Italian brigand. Often cited as the archetypal Gothic novel, ''The Mysteries of Udolpho'' appears prominently in Jane Austen's 1817 novel ''Northanger Abbey'', where an impressionable young woman reader comes to see friends and acquaintances as Gothic villains and victims, with amusing results. Plot ''The Mysteries of Udolpho'' is a quintessential Gothic romance, replete with incidents of physical and psychological terror: remote crumbling castles, seemingly supernatural events, a brooding, scheming villain and a persecuted heroine. Modern editors note that only about a third of the novel is set in the eponymous Gothic castle, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travel Books
The genre of travel literature encompasses outdoor literature, guide books, nature writing, and travel memoirs. One early travel memoirist in Western literature was Pausanias, a Greek geographer of the 2nd century CE. In the early modern period, James Boswell's ''Journal of a Tour to the Hebrides'' (1786) helped shape travel memoir as a genre. History Early examples of travel literature include the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' (generally considered a 1st century CE work; authorship is debated), Pausanias' ''Description of Greece'' in the 2nd century CE, ''Safarnama'' (Book of Travels) by Nasir Khusraw (1003-1077), the '' Journey Through Wales'' (1191) and '' Description of Wales'' (1194) by Gerald of Wales, and the travel journals of Ibn Jubayr (1145–1214), Marco Polo (1254–1354), and Ibn Battuta (1304–1377), all of whom recorded their travels across the known world in detail. As early as the 2nd century CE, Lucian of Samosata discussed history and tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
