|
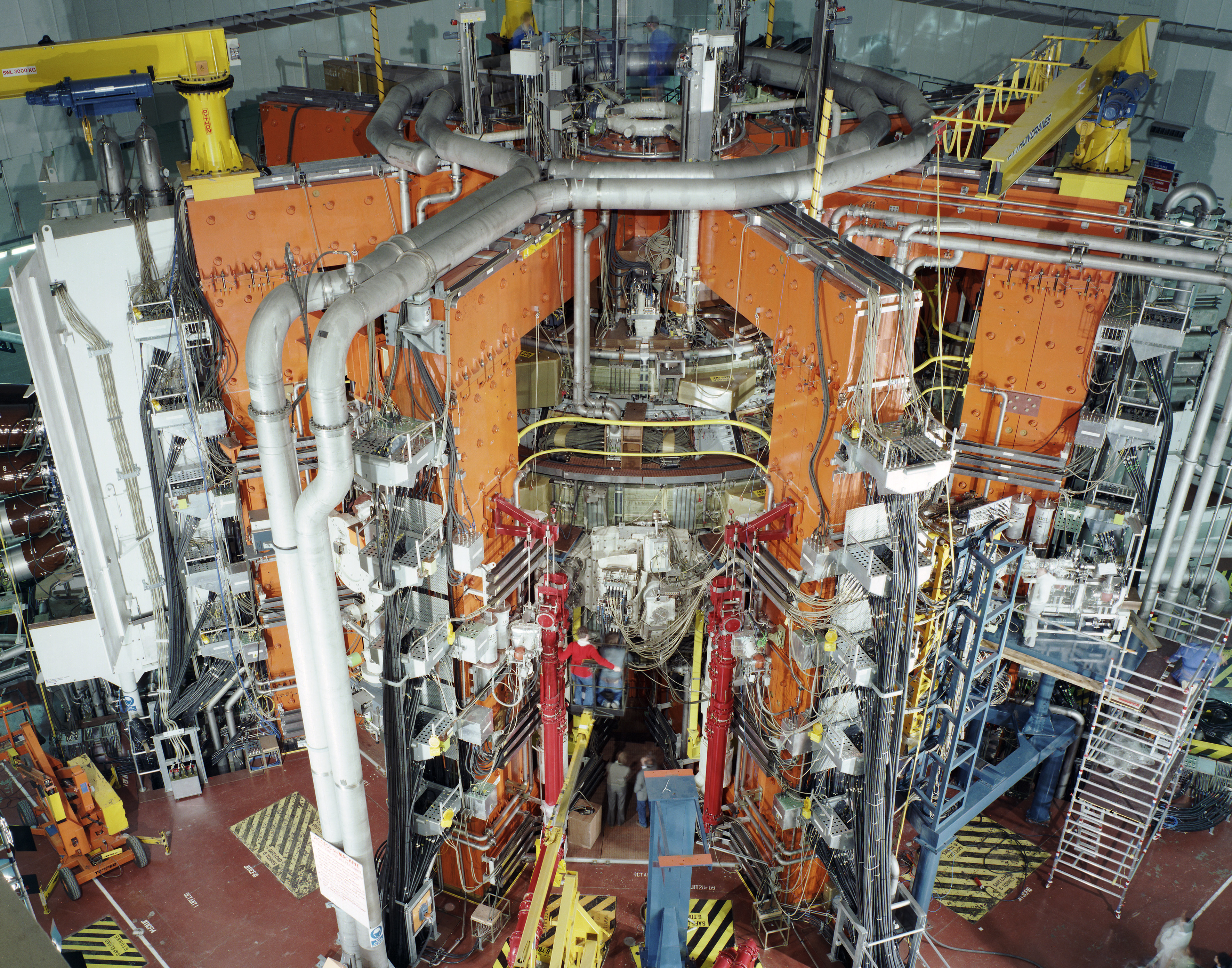
ARC Fusion Reactor
The ARC fusion reactor (affordable, robust, compact) is a design for a compact fusion reactor developed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Plasma Science and Fusion Center (PSFC). ARC aims to achieve an engineering breakeven of three (to produce three times the electricity required to operate the machine). The key technical innovation is to use high-temperature superconducting magnets in place of ITER's low-temperature superconducting magnets. The proposed device would be about half the diameter of the ITER reactor and cheaper to build. The ARC has a conventional advanced tokamak layout. ARC uses rare-earth barium copper oxide (REBCO) high-temperature superconductor magnets in place of copper wiring or conventional low-temperature superconductors. These magnets can be run at much higher field strengths, 23 T, roughly doubling the magnetic field on the plasma axis. The confinement time for a particle in plasma varies with the square of the linear size, and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Reactor
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2022, only one design, an inertial confinement laser-driven fusion machine at the US National Ignition Facility, has conclusively produced a positive fusion energy gain factor, i.e. more power output than input. Fusion processes require fuel and a confined environment with sufficient temperature, pressure, and confinement time to create a plasma in which fusion can occur. The combination of these figures that results in a power-producing system is known as the Lawson criterion. In stars, the most common fuel is hydrogen, and gravity provides extremely long confinement times that reach the conditions needed for fusion e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equinor
Equinor ASA (formerly Statoil and StatoilHydro) is a Norwegian state-owned multinational energy company headquartered in Stavanger. It is primarily a petroleum company, operating in 36 countries with additional investments in renewable energy. In the 2020 Forbes Global 2000, Equinor was ranked as the 169th-largest public company in the world. the company has 21,126 employees. The current company was formed by the 2007 merger of Statoil with the oil and gas division of Norsk Hydro. As of 2017, the Government of Norway is the largest shareholder with 67% of the shares, while the rest is public stock. The ownership interest is managed by the Norwegian Ministry of Petroleum and Energy. The company is headquartered and led from Stavanger, while most of their international operations are currently led from Fornebu, outside Oslo. The name ''Equinor'' was adopted in 2018 and is formed by combining ''equi'', the root for words such as ''equity'', ''equality'', and ''equilibrium'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Helium
Liquid helium is a physical state of helium at very low temperatures at standard atmospheric pressures. Liquid helium may show superfluidity. At standard pressure, the chemical element helium exists in a liquid form only at the extremely low temperature of . Its boiling point and critical point depend on which isotope of helium is present: the common isotope helium-4 or the rare isotope helium-3. These are the only two stable isotopes of helium. See the table below for the values of these physical quantities. The density of liquid helium-4 at its boiling point and a pressure of one atmosphere (101.3 kilopascals) is about , or about one-eighth the density of liquid water. Liquefaction Helium was first liquefied on July 10, 1908, by the Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes at the University of Leiden in the Netherlands. At that time, helium-3 was unknown because the mass spectrometer had not yet been invented. In more recent decades, liquid helium has been used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neon
Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypton and xenon) in 1898 as one of the three residual rare inert elements remaining in dry air, after nitrogen, oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide were removed. Neon was the second of these three rare gases to be discovered and was immediately recognized as a new element from its bright red emission spectrum. The name neon is derived from the Greek word, , neuter singular form of (), meaning 'new'. Neon is chemically inert, and no uncharged neon compounds are known. The compounds of neon currently known include ionic molecules, molecules held together by van der Waals forces and clathrates. During cosmic nucleogenesis of the elements, large amounts of neon are built up from the alpha-capture fusion process in stars. Although neon is a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form. To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully liquid state at atmospheric pressure, H2 needs to be cooled to .IPTS-1968 iupac.org, accessed 2020-01-01 A common method of obtaining liquid hydrogen involves a compressor resembling a jet engine in both appearance and principle. Liquid hydrogen is typically used as a concentrated form of hydrogen storage. Storing it as liquid takes less space than storing it as a gas at normal temperature and press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
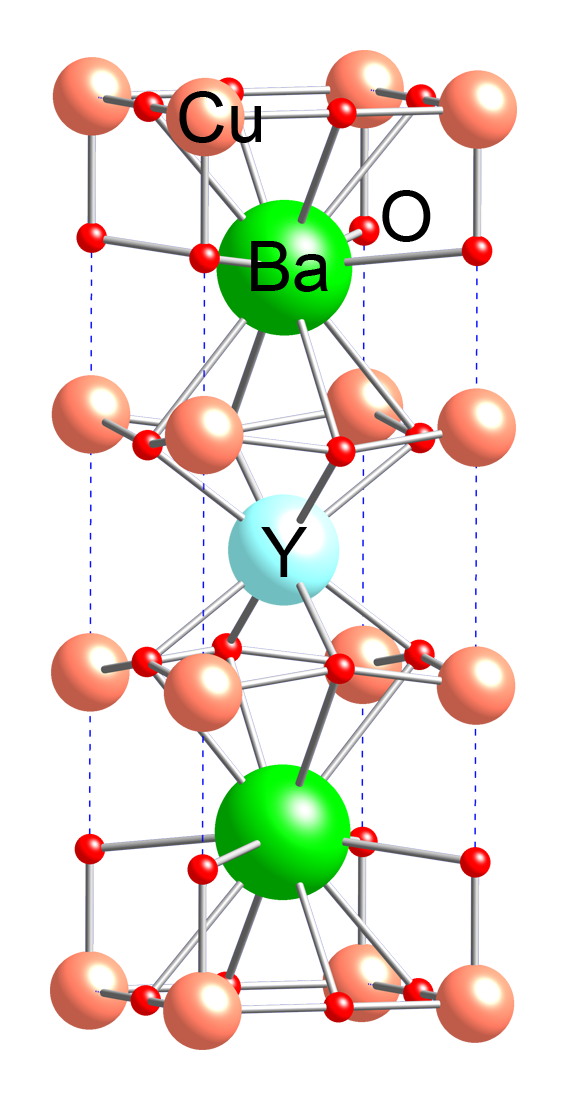
Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide
Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a family of crystalline chemical compounds that display high-temperature superconductivity; it includes the first material ever discovered to become superconducting above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen (77 K) at about 93 K. Many YBCO compounds have the general formula Y Ba2 Cu3 O7−''x'' (also known as Y123), although materials with other Y:Ba:Cu ratios exist, such as Y Ba2 Cu4 Oy (Y124) or Y2 Ba4 Cu7 Oy (Y247). At present, there is no singularly recognised theory for high-temperature superconductivity. It is part of the more general group of rare-earth barium copper oxides (ReBCO) in which, instead of yttrium, other rare earths are present. History In April 1986, Georg Bednorz and Karl Müller, working at IBM in Zurich, discovered that certain semiconducting oxides became superconducting at relatively high temperature, in particular, a lanthanum barium copper oxide becomes superconducting at 35 K. This oxide was an oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma ()πλάσμα , Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek English Lexicon'', on Perseus is one of the four fundamental states of matter. It contains a significant portion of charged particles – ions and/or s. The presence of these charged particles is what primarily sets plasma apart from the other fundamental states of matter. It is the most abundant form of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Field
Toroidal describes something which resembles or relates to a torus or toroid: Mathematics *Torus * Toroid, a surface of revolution which resembles a torus * Toroidal polyhedron *Toroidal coordinates, a three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system *Toroidal and poloidal coordinates, directions relative to a torus of reference *Toroidal graph, a graph whose vertices can be placed on a torus such that no edges cross *Toroidal grid network, where an n-dimensional grid network is connected circularly in more than one dimension Engineering * Toroidal inductors and transformers, a type of electrical device * Toroidal and poloidal, directions in magnetohydrodynamics *Toroidal engine, an internal combustion engine with pistons that rotate within a toroidal space *Toroidal CVT, a type of continuously variable transmission *Toroidal reflector, a parabolic reflector which has a different focal distance depending on the angle of the mirror Other uses *Toroidal ring model in theoretical phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconducting Tape
Superconducting wires are electrical wires made of superconductive material. When cooled below their transition temperatures, they have zero electrical resistance. Most commonly, conventional superconductors such as niobium-titanium are used, but high-temperature superconductors such as YBCO are entering the market. Superconducting wire's advantages over copper or aluminum include higher maximum current densities and zero power dissipation. Its disadvantages include the cost of refrigeration of the wires to superconducting temperatures (often requiring cryogens such as liquid nitrogen or liquid helium), the danger of the wire quenching (a sudden loss of superconductivity), the inferior mechanical properties of some superconductors, and the cost of wire materials and construction. Its main application is in superconducting magnets, which are used in scientific and medical equipment where high magnetic fields are necessary. Important parameters The construction and operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare-earth Barium Copper Oxide
Rare-earth barium copper oxide (also referred to as ReBCO) is a family of chemical compounds known for exhibiting high temperature superconductivity (HTS). ReBCO superconductors have the potential to sustain stronger magnetic fields than other superconductor materials. Due to their stronger magnetic field and relatively high superconducting critical temperature, this materials are proposed for future use in technical applications. This includes magnetic confinement fusion reactors such as the ARC reactor, allowing a more compact and potentially more economical construction, and superconducting magnets to use in future particle accelerators to come after the LHC at CERN which utilizes low-temperature superconductors. The most famous of these is yttrium barium copper oxide, YBa2Cu3O7−x (or Y123), the first superconductor found with a critical temperature above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. Its molar ratio is 1 to 2 to 3 for yttrium, barium, and copper and it has a un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritium
Tritium ( or , ) or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with half-life about 12 years. The nucleus of tritium (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the common isotope hydrogen-1 (''protium'') contains one proton and zero neutrons, and that of hydrogen-2 (''deuterium'') contains one proton and one neutron. Naturally occurring tritium is extremely rare on Earth. The atmosphere has only trace amounts, formed by the interaction of its gases with cosmic rays. It can be produced artificially by irradiating lithium metal or lithium-bearing ceramic pebbles in a nuclear reactor and is a low-abundance byproduct in normal operations of nuclear reactors. Tritium is used as the energy source in radioluminescent lights for watches, gun sights, numerous instruments and tools, and even novelty items such as self-illuminating key chains. It is used in a medical and scientific setting as a rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom of deuterium among all atoms of hydrogen (see heavy water). Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% by number (0.0312% by mass) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another (see Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water). (Tritium is yet another hydrogen isotope, with two neutrons, that is far more rare and is radioactive.) The name ''deuterium'' is derived from the Greek , meaning "second", to denot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |