|
ARC (file Format)
ARC is a lossless data compression and archival format by System Enhancement Associates (SEA). The file format and the program were both called ARC. The format is known as the subject of controversy in the 1980s, part of important debates over what would later be known as open formats. ARC was extremely popular during the early days of the dial-up BBS. ARC was convenient as it combined the functions of the SQ program to compress files and the LU program to create .LBR archives of multiple files. The format was later replaced by the ZIP format, which offered better compression ratios and the ability to retain directory structures through the compression/decompression process. The .arc filename extension is often used for several unrelated file archive-like file types. For example, the Internet Archive used its own ARC format to store multiple web resources into a single file. The FreeArc archiver also uses .arc extension, but uses a completely different file format. Nintendo u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Enhancement Associates
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences. Systems have several common properties and characteristics, including structure, function(s), behavior and interconnectivity. Etymology The term ''system'' comes from the Latin word ''systēma'', in turn from Greek ''systēma'': "whole concept made of several parts or members, system", literary "composition"."σύστημα" Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, '' |
Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley (Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems (SunOS/Solaris (operating system), Solaris), Hewlett-Packard, HP/Hewlett Packard Enterprise, HPE (HP-UX), and IBM (IBM AIX, AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Archive Formats
This is a list of file formats used by archivers and compressors used to create archive files. Archiving only Compression only Archiving and compression Data recovery Comparison Containers and compression Notes While the original tar format uses the ASCII character encoding, current implementations use the UTF-8 (Unicode) encoding, which is backwards compatible with ASCII. Supports the external Parchive program (par2). From 3.20 release RAR can store modification, creation and last access time with the precision up to 0.0000001 second (= 0.1 µs) The PAQ family (with its lighter weight derivative LPAQ) went through many revisions, each revision suggested its own extension. For example: ".paq9a". WIM can store the ciphertext of encrypted files on an NTFS volume, but such files can only by decrypted if an administrator extracts the file to an NTFS volume, and the decryption key is available (typically from the file's original owner on the same Windows installation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PKZIP
PKZIP is a file archiving computer program, notable for introducing the popular ZIP file format. PKZIP was first introduced for MS-DOS on the IBM-PC compatible platform in 1989. Since then versions have been released for a number of other architectures and operating systems. PKZIP was originally written by Phil Katz and marketed by his company PKWARE, Inc starting in 1986. The company bears his initials: 'PK'. History By the 1970s, file archiving programs were distributed as standard utilities with operating systems. They include the Unix utilities ar, shar, and tar. These utilities were designed to gather a number of separate files into a single archive file for easier copying and distribution. These archives could optionally be passed through a stream compressor utility, such as compress and others. Other archivers also appeared during the 1980s, including ARC by System Enhancement Associates, Inc. (SEA), Rahul Dhesi's ZOO, Dean W. Cooper's DWC, LHarc by Haruhiko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative Work
In copyright law, a derivative work is an expressive creation that includes major copyrightable elements of an original, previously created first work (the underlying work). The derivative work becomes a second, separate work independent in form from the first. The transformation, modification or adaptation of the work must be substantial and bear its author's personality sufficiently to be original and thus protected by copyright. Translations, Film adaptation, cinematic adaptations and Arrangement, musical arrangements are common types of derivative works. Most countries' legal systems seek to protect both original and derivative works. They grant authors the right to impede or otherwise control their integrity and the author's commercial interests. Derivative works and their authors benefit in turn from the full protection of copyright without prejudicing the rights of the original work's author. Definition Berne The Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PKWare
PKWARE, Inc. is an enterprise data protection software company that provides discovery, classification, masking and encryption solutions, along with data compression software, used by organizations in financial services, manufacturing, military, healthcare and government. The company's products are intended to assist other companies in complying with various data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. The company is headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin with additional offices in the US, UK and India. PKWARE was founded in 1986 by Phil Katz, co-inventor of the ZIP standard. As of May 13, 2020, Thompson Street Capital Partners has acquired PKWARE Inc. History Compression software (1986–2000) PKWARE was founded in 1986 by Phil Katz, a software developer who had begun distributing a new file compression utility, called PKARC, as shareware. PKARC represented a radical improvement over existing compression software (including the ARC utility, on which it was based) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software (abbreviated to AV software), also known as anti-malware, is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware. Antivirus software was originally developed to detect and remove computer viruses, hence the name. However, with the proliferation of other malware, antivirus software started to protect from other computer threats. In particular, modern antivirus software can protect users from malicious browser helper objects (BHOs), browser hijackers, ransomware, keyloggers, backdoors, rootkits, trojan horses, worms, malicious LSPs, dialers, fraud tools, adware, and spyware. Some products also include protection from other computer threats, such as infected and malicious URLs, spam, scam and phishing attacks, online identity (privacy), online banking attacks, social engineering techniques, advanced persistent threat (APT), and botnet DDoS attacks. History 1949–1980 period (pre-antivirus days) Although the roots of the computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phil Katz
Phillip Walter Katz (November 3, 1962 – April 14, 2000) was a computer programmer best known as the co-creator of the Zip file format for data compression, and the author of PKZIP, a program for creating zip files that ran under DOS. A copyright lawsuit between System Enhancement Associates (SEA) and Katz's company, PKWARE, Inc., was widely publicized in the BBS community in the late 1980s. Phil Katz's software business was very successful, but he struggled with social isolation and chronic alcoholism in the last years of his life. Career Phil Katz was a graduate of Nicolet High School in Glendale, Wisconsin. Katz graduated from the Computer Science Engineering program at the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee. After his graduation, he was hired by the Allen-Bradley company as a programmer. He wrote code to run programmable logic controllers, which operated manufacturing equipment on shop floors worldwide for Allen-Bradley's customers. PKARC and PKWARE Katz left Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lempel–Ziv–Welch
Lempel–Ziv–Welch (LZW) is a universal lossless data compression algorithm created by Abraham Lempel, Jacob Ziv, and Terry Welch. It was published by Welch in 1984 as an improved implementation of the LZ78 algorithm published by Lempel and Ziv in 1978. The algorithm is simple to implement and has the potential for very high throughput in hardware implementations. It is the algorithm of the widely used Unix file compression utility compress and is used in the GIF image format. Algorithm The scenario described by Welch's 1984 paper encodes sequences of 8-bit data as fixed-length 12-bit codes. The codes from 0 to 255 represent 1-character sequences consisting of the corresponding 8-bit character, and the codes 256 through 4095 are created in a dictionary for sequences encountered in the data as it is encoded. At each stage in compression, input bytes are gathered into a sequence until the next character would make a sequence with no code yet in the dictionary. The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
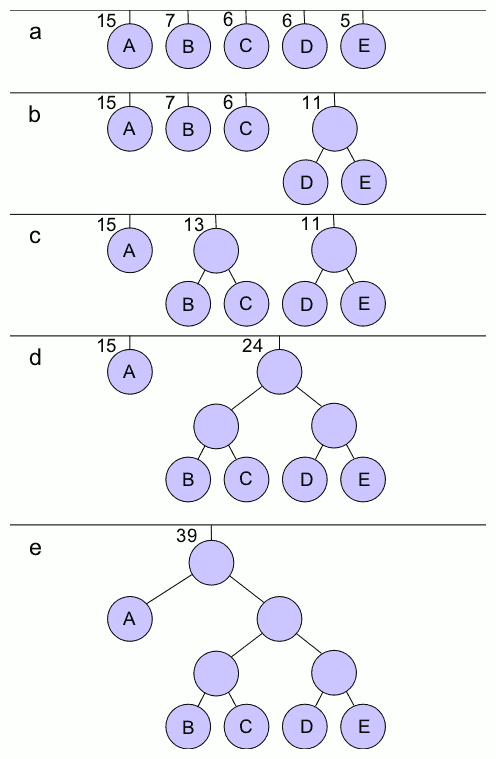
Huffman Coding
In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code proceeds by means of Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Sc.D. student at MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes". The output from Huffman's algorithm can be viewed as a variable-length code table for encoding a source symbol (such as a character in a file). The algorithm derives this table from the estimated probability or frequency of occurrence (''weight'') for each possible value of the source symbol. As in other entropy encoding methods, more common symbols are generally represented using fewer bits than less common symbols. Huffman's method can be efficiently implemented, finding a code in time linear to the number of input weights if these weights are sorted. However, although opt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LZ77 And LZ78
LZ77 and LZ78 are the two lossless data compression algorithms published in papers by Abraham Lempel and Jacob Ziv in 1977 and 1978. They are also known as LZ1 and LZ2 respectively. These two algorithms form the basis for many variations including LZW, LZSS, LZMA and others. Besides their academic influence, these algorithms formed the basis of several ubiquitous compression schemes, including GIF and the DEFLATE algorithm used in PNG and ZIP. They are both theoretically dictionary coders. LZ77 maintains a sliding window during compression. This was later shown to be equivalent to the ''explicit dictionary'' constructed by LZ78—however, they are only equivalent when the entire data is intended to be decompressed. Since LZ77 encodes and decodes from a sliding window over previously seen characters, decompression must always start at the beginning of the input. Conceptually, LZ78 decompression could allow random access to the input if the entire dictionary were known in ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM System/370
The IBM System/370 (S/370) is a model range of IBM mainframe computers announced on June 30, 1970, as the successors to the System/360 family. The series mostly maintains backward compatibility with the S/360, allowing an easy migration path for customers; this, plus improved performance, were the dominant themes of the product announcement. In September 1990, the System/370 line was replaced with the System/390. Evolution The original System/370 line was announced on June 30, 1970, with first customer shipment of the Models 155 and 165 planned for February 1971 and April 1971 respectively. The 155 first shipped in January 1971. System/370 underwent several architectural improvements during its roughly 20-year lifetime. The following features mentioned in Principles of Operation are either optional on S/360 but standard on S/370, introduced with S/370 or added to S/370 after announcement. *Branch and Save *Channel Indirect Data Addressing *Channel-Set Switching *Clear I/O *Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |