|
ABO-incompatible Transplantation
ABO-incompatible (ABOi) transplantation is a method of allocation in organ transplantation that permits more efficient use of available organs regardless of ABO blood type, which would otherwise be unavailable due to hyperacute rejection.West, L. J., Karamlou, T., Dipchand, A. I., Pollock-Barziv, S. M., Coles, J. G., & McCrindle, B. W. (2006). Impact on outcomes after listing and transplantation, of a strategy to accept ABO blood group-incompatible donor hearts for neonates and infants. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 131(2), 455–461. Schmoeckel, M., Däbritz, S. H., Kozlik-Feldmann, R., Wittmann, G., Christ, F., Kowalski, C., et al. (2005). Successful ABO-incompatible heart transplantation in two infants. Transplant International, 18(10), 1210–1214. Primarily in use in infants and young toddlers, research is ongoing to allow for increased use of this capability in adult transplants. Normal ABO-compatibility rules may be observed for all recipients. This mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
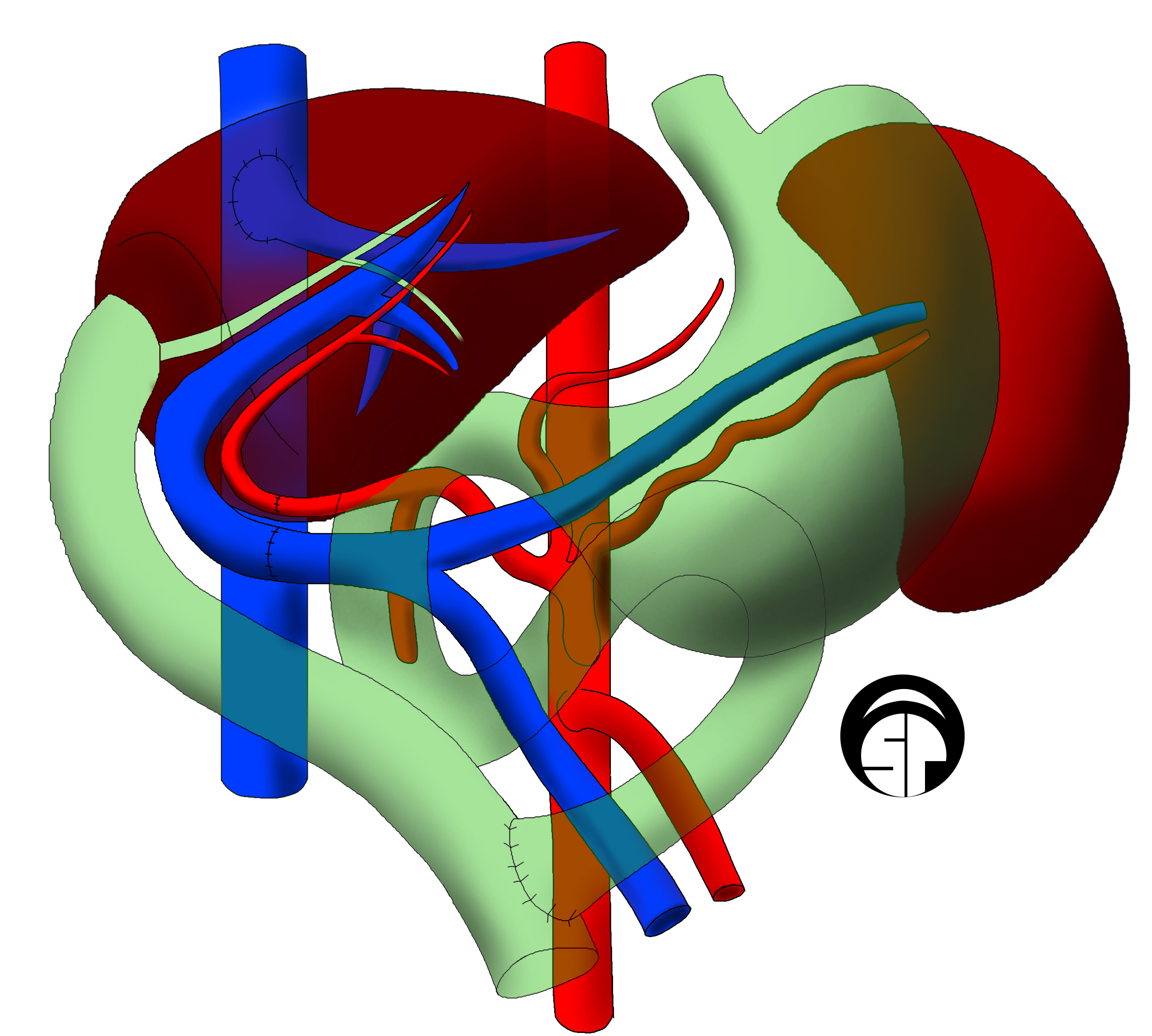
Organ Transplantation
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ (anatomy), organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a Organ donation, donor site to another location. Organ (anatomy), Organs and/or Tissue (biology), tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source. Organs that have been successfully transplanted include the Heart transplantation, heart, Kidney transplantation, kidneys, Liver transplantation, liver, Lung transplantation, lungs, Pancreas transplantation, pancreas, Intestinal transplant, intestine, Thymus transplantation, thymus and uterus transplantation, uterus. Tissues include Bone grafting, bones, tendons (both referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard L
Leonard or ''Leo'' is a common English masculine given name and a surname. The given name and surname originate from the Old High German ''Leonhard'' containing the prefix ''levon'' ("lion") from the Greek Λέων ("lion") through the Latin '' Leo,'' and the suffix ''hardu'' ("brave" or "hardy"). The name has come to mean "lion strength", "lion-strong", or "lion-hearted". Leonard was the name of a Saint in the Middle Ages period, known as the patron saint of prisoners. Leonard is also an Irish origin surname, from the Gaelic ''O'Leannain'' also found as O'Leonard, but often was anglicised to just Leonard, consisting of the prefix ''O'' ("descendant of") and the suffix ''Leannan'' ("lover"). The oldest public records of the surname appear in 1272 in Huntingdonshire, England, and in 1479 in Ulm, Germany. Variations The name has variants in other languages: * Leen, Leendert, Lenard (Dutch) * Lehnertz, Lehnert (Luxembourgish) * Len (English) * :hu:Lénárd (Hungarian) * Lenart ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus. Thrombosis may occur in veins (venous thrombosis) or in arteries (arterial thrombosis). Venous thrombosis (sometimes called DVT, deep vein thrombosis) leads to a blood clot in the affected part of the body, while arterial thrombosis (and, rarely, severe venous thrombosis) affects the blood supply and leads to damage of the tissue supplied by that artery (ischemia and necrosis). A piece of either an arterial or a venous thrombus can break off as an embolus, which could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
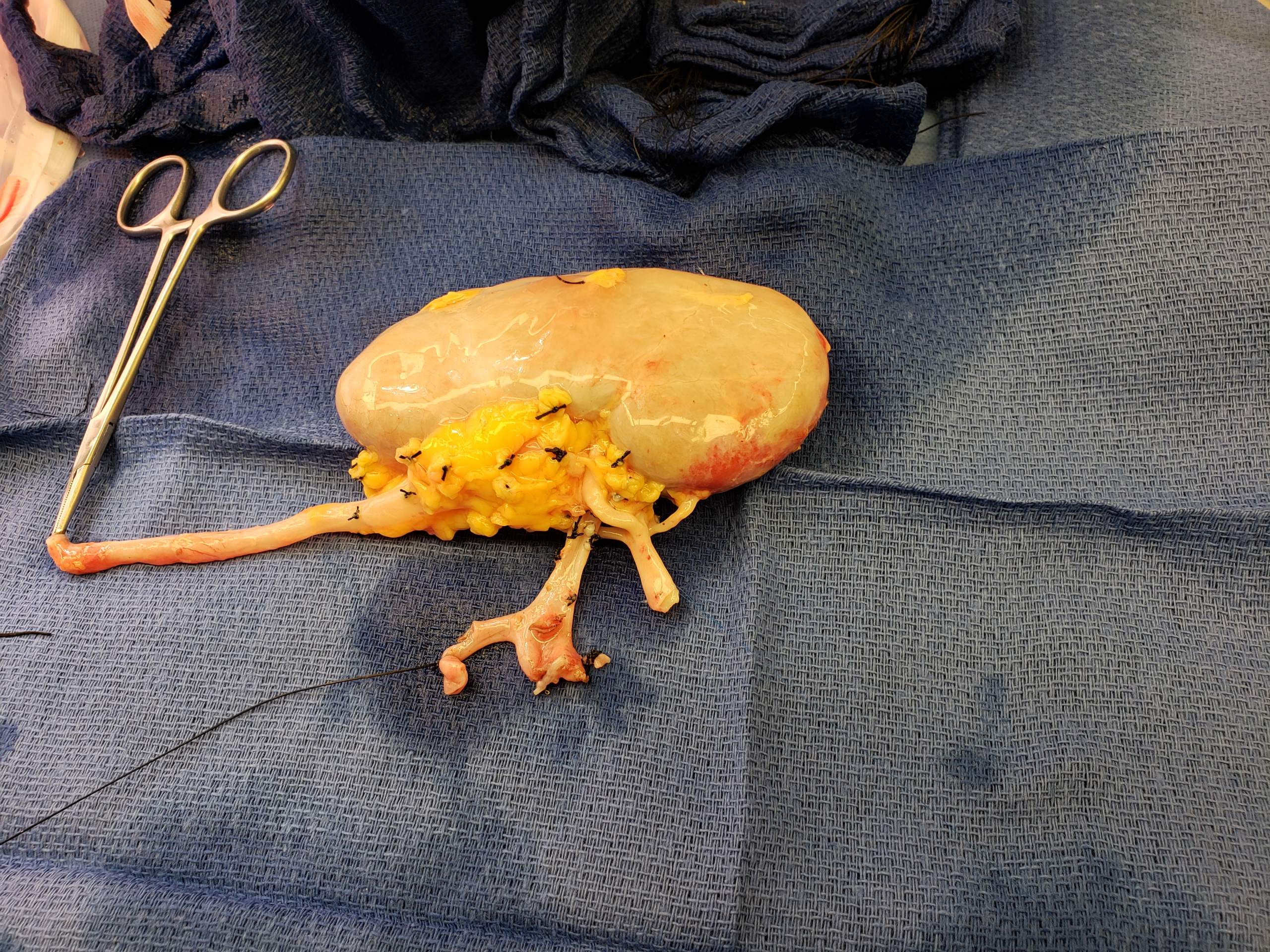
Kidney Transplantation
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor kidney transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. Before receiving a kidney transplant, a person with ESRD must undergo a thorough medical evaluation to make sure that they are healthy enough to undergo transplant surgery. If they are deemed a good candidate, they can be placed on a waiting list to receive a kidney from a deceased donor. Once they are placed on the waiting list, they can receive a new kidney very quickly, or they may have to wait many years; in the United States, the average waiting time is three t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, although availability of donor organs is a major limitation. The most common technique is orthotopic transplantation, in which the native liver is removed and replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomic position as the original liver. The surgical procedure is complex, requiring careful harvest of the donor organ and meticulous implantation into the recipient. Liver transplantation is highly regulated, and only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians and supporting medical team. The duration of the surgery ranges from 4 to 18 hours depending on outcome. Favorable outcomes require careful screening for eligible recipient, as well as a well-calibrated live or cadaveric donor match. Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,765,188 people (as of 2021) surrounding the western end of Lake Ontario, while the Greater Toronto Area proper had a 2021 population of 6,712,341. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, sports and culture, and is recognized as one of the most multicultural and cosmopolitan cities in the world. Indigenous peoples have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, located on a broad sloping plateau interspersed with rivers, deep ravines, and urban forest, for more than 10,000 years. After the broadly disputed Toronto Purchase, when the Mississauga surrendered the area to the British Crown, the British established the town of York in 1793 and later designat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hospital For Sick Children, Toronto
The Hospital for Sick Children (HSC), corporately branded as SickKids, is a major pediatric teaching hospital located on University Avenue in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Affiliated with the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Toronto, the hospital was ranked the top pediatric hospital in the world by Newsweek in 2021. The hospital's Peter Gilgan Centre for Research and Learning is believed to be the largest pediatric research tower in the world, at . History During 1875, an eleven-room house was rented for a year by a Toronto women's bible study group, led by Elizabeth McMaster. Opened on March 1, it set up six iron cots and "declared open a hospital 'for the admission and treatment of all sick children.'" The first patient, a scalding victim named Maggie, came in on April 3. In its first year, 44 patients were admitted to the hospital in its first year of operation, and 67 others were treated in outpatient clinics. In 1876, the hospital moved to larger facilities. In 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Privilege
Certain sites of the mammalian body have immune privilege, meaning they are able to tolerate the introduction of antigens without eliciting an inflammatory immune response. Tissue grafts are normally recognised as foreign antigen by the body and attacked by the immune system. However, in immune privileged sites, tissue grafts can survive for extended periods of time without rejection occurring. Immunologically privileged sites include: * the eyes * the placenta and fetus * the testicles * the central nervous system Immune privilege is also believed to occur to some extent or able to be induced in articular cartilage. This was once thought to also include the brain, but this is now known to be incorrect, as it has been shown that immune cells of the central nervous system contribute to the maintenance of neurogenesis and spatial learning abilities in adulthood.Ziv, Y.et al (2006). Nature Neuroscience, Immune cells contribute to the maintenance of neurogenesis and spatial learning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrian Kantrowitz
Adrian Kantrowitz (October 4, 1918 – November 14, 2008) was an American cardiac surgeon whose team performed the world's second heart transplant attempt (after Christiaan Barnard) at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York on December 6, 1967. McRae, Donald (2006). ''Every Second Counts: The Race to Transplant the First Human Heart'', New York: Penguin (Berkley/Putnam). The infant lived for only six hours. At a press conference afterwards, Kantrowitz emphasized that he considered the operation to have been a failure. Kantrowitz also invented the intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP), a left ventricular assist device (L-VAD), and an early version of the implantable pacemaker. In 1981, Kantrowitz became a founding member of the World Cultural Council. Early life and education Kantrowitz was born in New York City on October 4, 1918. His mother was a costume designer and his father ran a clinic in the Bronx, and his grandparents were from Vermont. Adrian told his mother as a thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABO Blood Group System
The ABO blood group system is used to denote the presence of one, both, or neither of the A and B antigens on erythrocytes. For human blood transfusions, it is the most important of the 43 different blood type (or group) classification systems currently recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusions (ISBT) as of June 2021. A mismatch (very rare in modern medicine) in this, or any other serotype, can cause a potentially fatal adverse reaction after a transfusion, or an unwanted immune response to an organ transplant. The associated anti-A and anti-B antibodies are usually IgM antibodies, produced in the first years of life by sensitization to environmental substances such as food, bacteria, and viruses. The ABO blood types were discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1901; he received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1930 for this discovery. ABO blood types are also present in other primates such as apes and Old World monkeys. History Discovery The ABO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. The term ''antigen'' originally referred to a substance that is an antibody generator. Antigens can be proteins, peptides (amino acid chains), polysaccharides (chains of monosaccharides/simple sugars), lipids, or nucleic acids. Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors, including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Diverse antigen receptors are made by cells of the immune system so that each cell has a specificity for a single antigen. Upon exposure to an antigen, only the lymphocytes that recognize that antigen are activated and expanded, a process known as clonal selection. In most cases, an antibody can only react to and bind one specific antigen; in some instances, however, antibodies may cross-react and bind more than one antigen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isohemagglutinin
The ABO blood group system is used to denote the presence of one, both, or neither of the A and B antigens on erythrocytes. For human blood transfusions, it is the most important of the 43 different blood type (or group) classification systems currently recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusions (ISBT) as of June 2021. A mismatch (very rare in modern medicine) in this, or any other serotype, can cause a potentially fatal adverse reaction after a transfusion, or an unwanted immune response to an organ transplant. The associated anti-A and anti-B antibodies are usually IgM antibodies, produced in the first years of life by sensitization to environmental substances such as food, bacteria, and viruses. The ABO blood types were discovered by Karl Landsteiner in 1901; he received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1930 for this discovery. ABO blood types are also present in other primates such as apes and Old World monkeys. History Discovery The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |