|
9000 BC
The 9th millennium BC spanned the years 9000 BC to 8001 BC (11 to 10 thousand years ago). In chronological terms, it is the first full millennium of the current Holocene epoch that is generally reckoned to have begun by 9700 BC (11.7 thousand years ago). It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological and anthropological analysis, or by radiometric dating. In the Near East, especially in the Fertile Crescent, the transitory Epipalaeolithic age was gradually superseded by the Neolithic with evidence of agriculture across the Levant to the Zagros Mountains in modern-day Iran. The key characteristic of the Neolithic is agricultural settlement, albeit with wooden and stone tools and weapons still in use. It is believed that agriculture had begun in China by the end of the millennium. Elsewhere, especially in Europe, the Palaeolithic continued. Global environment In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
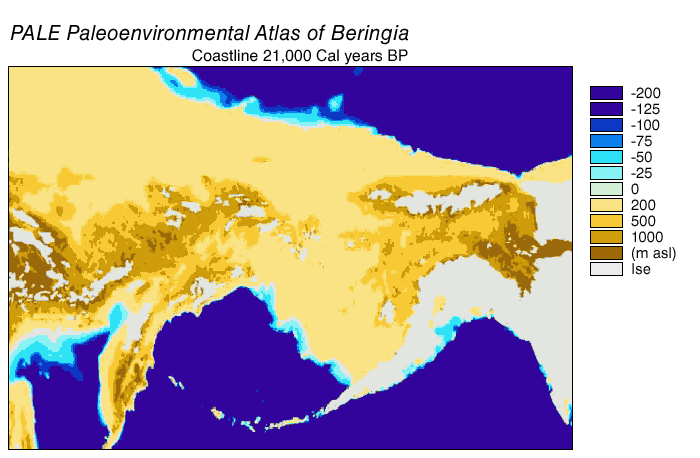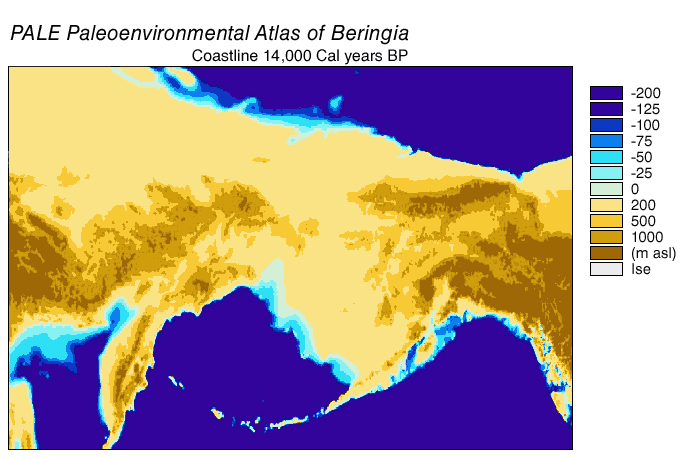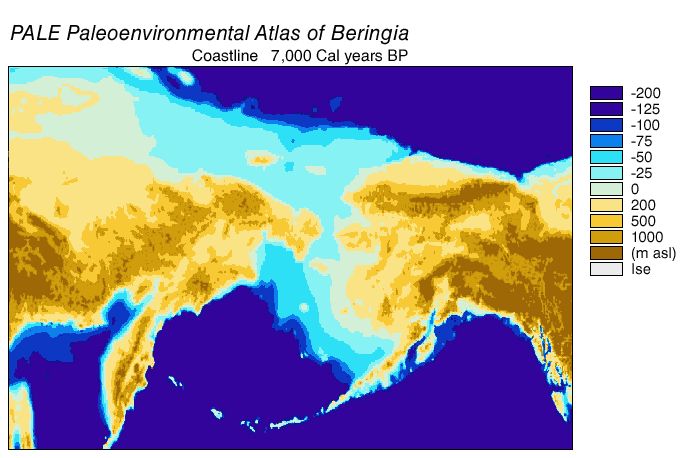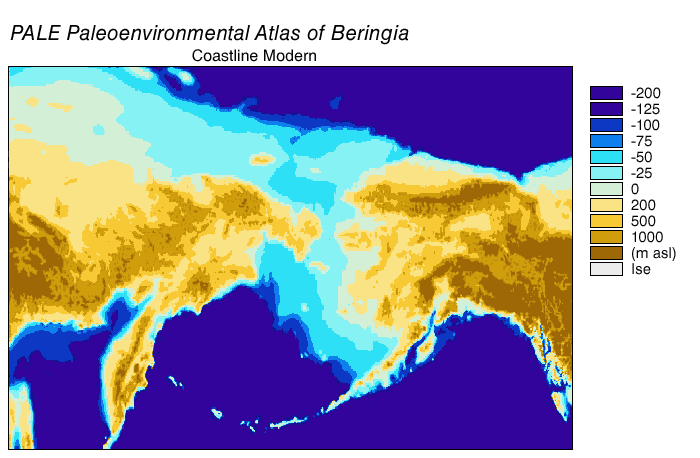
Bering Land Bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi Peninsula, Chukchi and Kamchatka Peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States and the Yukon in Canada. The area includes land lying on the North American Plate and Siberian land east of the Chersky Range. At certain times in prehistory, it formed a land bridge that was up to wide at its greatest extent and which covered an area as large as British Columbia and Alberta together, totaling approximately . Today, the only land that is visible from the central part of the Bering land bridge are the Diomede Islands, the Pribilof Islands of St. Paul and St. George, St. Lawrence Island, St. Matthew Island, and King Island (Alaska), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
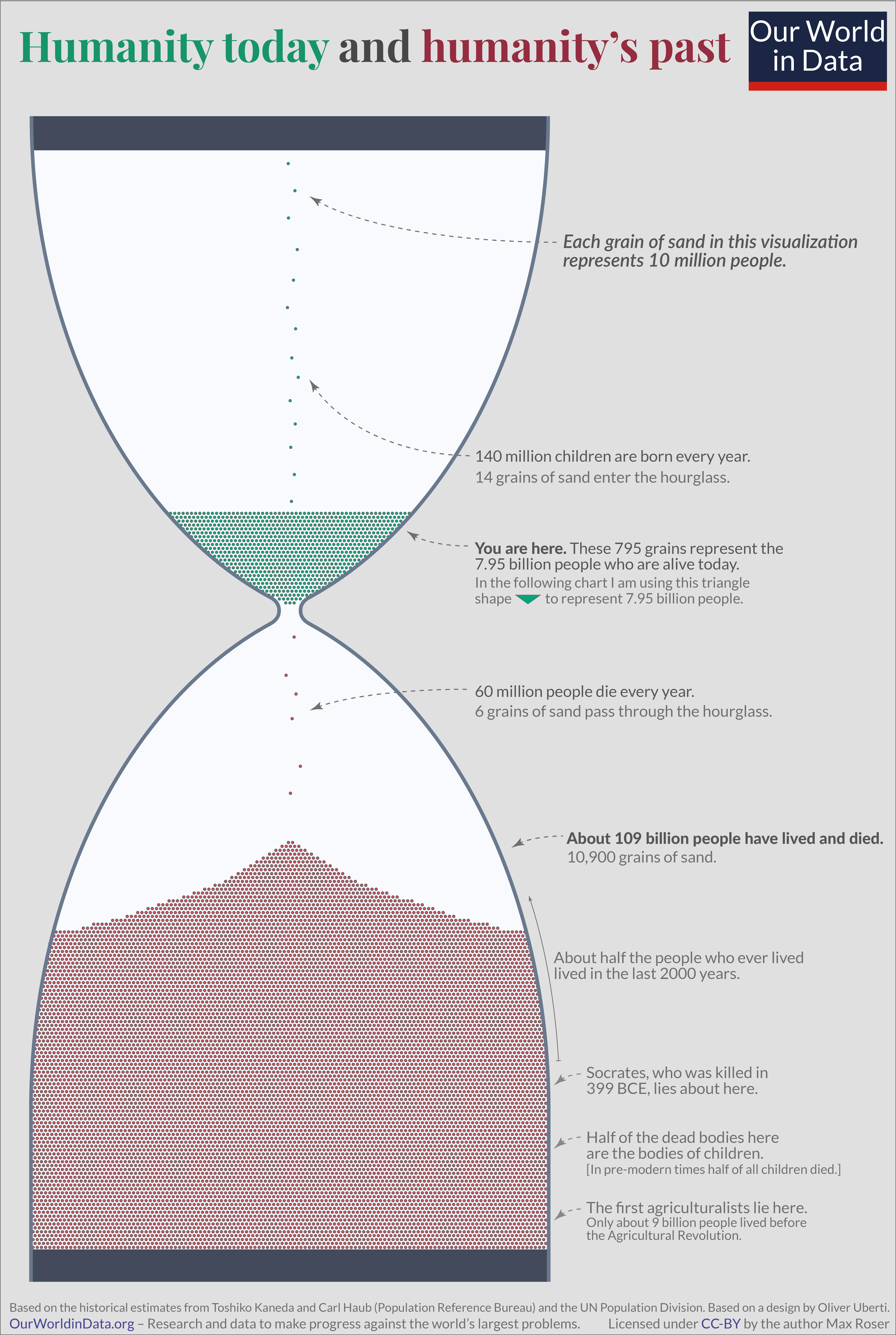
World Population Estimates
This article lists current estimates of the world population in history. In summary, estimates for the progression of world population since the Late Middle Ages are in the following ranges: Estimates for pre-modern times are necessarily fraught with great uncertainties, and few of the published estimates have confidence intervals; in the absence of a straightforward means to assess the error of such estimates, a rough idea of expert consensus can be gained by comparing the values given in independent publications. Population estimates cannot be considered accurate to more than two decimal digits; for example, the world population for the year 2012 was estimated at 7.02, 7.06, and 7.08 billion by the United States Census Bureau, the Population Reference Bureau, and the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, respectively, corresponding to a spread of estimates of the order of 0.8%. Deep prehistory As a general rule, the confidence of estimates on h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
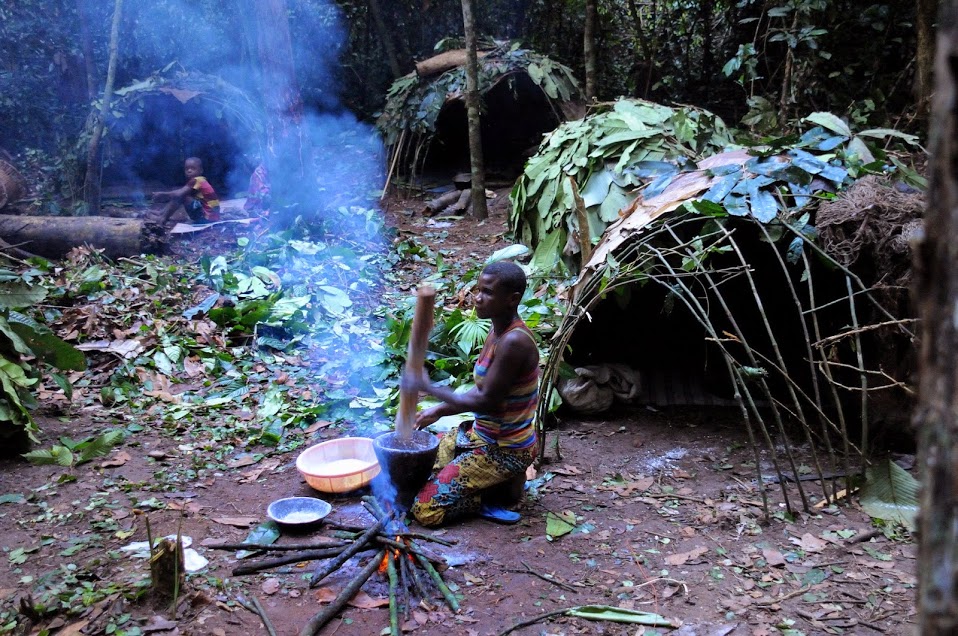
Hunting-gathering
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, honey, or anything safe to eat, and/or by hunting game (pursuing and/or trapping and killing wild animals, including catching fish), roughly as most animal omnivores do. Hunter-gatherer societies stand in contrast to the more sedentary agricultural societies, which rely mainly on cultivating crops and raising domesticated animals for food production, although the boundaries between the two ways of living are not completely distinct. Hunting and gathering was humanity's original and most enduring successful competitive adaptation in the natural world, occupying at least 90 percent of human history. Following the invention of agriculture, hunter-gatherers who did not change were displaced or conquered by farming or pastoralist groups in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism. Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they remain as tephra unless hot enough to fuse into pyroclastic rock or tuff. Tephrochronology is a geochronological technique that uses discrete layers of tephra—volcanic ash from a single eruption—to create a chronological framework in which paleoenvironmental or archaeological records can be placed. When a volcano explodes, it releases a variety of tephra including ash, cinders, and blocks. These layers settle on the land and, over time, sedimentation occurs incorporating these tephra layers into the geologic record. Often, when a volcano explodes, biological organisms are killed and their remains are buried within the tephra layer. These fossils are later dated by scientists to determine the age of the fossil and its place within the geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grímsvötn
Grímsvötn (; ''vötn'' = "waters", singular: ) is a volcano with a (partially subglacial) fissure system located in Vatnajökull National Park, Iceland. The volcano itself is completely subglacial and located under the northwestern side of the Vatnajökull ice cap. The subglacial caldera is at , at an elevation of . Beneath the caldera is the magma chamber of the Grímsvötn volcano. Grímsvötn is a basaltic volcano which has the highest eruption frequency of all the volcanoes in Iceland and has a southwest-northeast-trending fissure system. The massive climate-impacting Laki fissure eruption of 1783–1784 was a part of the same fissure system. Grímsvötn was erupting at the same time as Laki during 1783, but continued to erupt until 1785. Because most of the volcanic system lies underneath Vatnajökull, most of its eruptions have been subglacial and the interaction of magma and meltwater from the ice causes phreatomagmatic explosive activity. Jökulhlaup Eruptions in the cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic of Korea) comprising its southern half. Korea consists of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and several minor islands near the peninsula. The peninsula is bordered by China to the northwest and Russia to the northeast. It is separated from Japan to the east by the Korea Strait and the Sea of Japan (East Sea). During the first half of the 1st millennium, Korea was divided between three states, Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla, together known as the Three Kingdoms of Korea. In the second half of the 1st millennium, Silla defeated and conquered Baekje and Goguryeo, leading to the "Unified Silla" period. Meanwhile, Balhae formed in the north, superseding former Goguryeo. Unified Silla eventually collapsed into three separate states due to civi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulleungdo
Ulleungdo (also spelled Ulreungdo; Hangul: , ) is a South Korean island 120 km (75 mi) east of the Korean Peninsula in the Sea of Japan, formerly known as the Dagelet Island or Argonaut Island in Europe. Volcanic in origin, the rocky steep-sided island is the top of a large stratovolcano which rises from the seafloor, reaching a maximum elevation of at Seonginbong Peak. The island is in length and in width; it has an area of . It has a population of 10,426 inhabitants. The island makes up the main part of Ulleung County, North Gyeongsang Province, South Korea and is a popular tourist destination. The main city of Ulleung-do is the port of Dodong (), which serves as the main ferry port between Ulleung-do and the South Korean mainland. After tourism, the main economic activity is fishing, including its well-known harvest of squid, which can be seen drying in the sun in many places. History The island consists primarily of trachyandesite rock. A major explosive er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Quaternary Volcanic Eruptions
This article is a list of volcanic eruptions of approximately magnitude 6 or more on the Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) or equivalent sulfur dioxide emission during the Holocene, and Pleistocene eruptions of the Decade Volcanoes (Avachinsky-Koryaksky, Kamchatka; Colima, Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt; Mount Etna, Sicily; Galeras, Andes, Northern Volcanic Zone; Mauna Loa, Hawaii; Mount Merapi, Central Java; Mount Nyiragongo, East African Rift; Mount Rainier, Washington; Sakurajima, Kagoshima Prefecture; Santamaria/ Santiaguito, Central America Volcanic Arc; Santorini, Cyclades; Taal Volcano, Luzon Volcanic Arc; Teide, Canary Islands; Ulawun, New Britain; Mount Unzen, Nagasaki Prefecture; Mount Vesuvius, Naples); Campania, Italy; South Aegean Volcanic Arc; Laguna de Bay, Luzon Volcanic Arc; Mount Pinatubo, Luzon Volcanic Arc; Toba, Sunda Arc; Mount Meager massif, Garibaldi Volcanic Belt; Yellowstone hotspot, Wyoming; and Taupō Volcanic Zone, greater than VEI 4. The eruptions in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples. Many Indigenous peoples of the Americas were traditionally hunter-gatherers and many, especially in the Amazon basin, still are, but many groups practiced aquaculture and agriculture. While some societies depended heavily on agriculture, others practiced a mix of farming, hunting, and gathering. In some regions, the Indigenous peoples created monumental architecture, large-scale organized cities, city-states, chiefdoms, states, kingdoms, republics, confederacies, and empires. Some had varying degrees of knowledge of engineering, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, writing, physics, medicine, planting and irrigation, geology, mining, metallurgy, sculpture, and gold smithing. Many parts of the Americas are still populated by Indigenous peoples; some countries have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_2007.jpg)