|
9-Aminoacridine
9-Aminoacridine is a highly fluorescent dye used clinically as a topical antiseptic and experimentally as a mutagen, an intracellular pH indicator and a small molecule MALDI In mass spectrometry, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) is an ionization technique that uses a laser energy absorbing matrix to create ions from large molecules with minimal fragmentation. It has been applied to the analysis of b ... matrix. See also * 2-Aminoacridine * 3-Aminoacridine * 4-Aminoacridine References Aromatic amines Acridines DNA intercalaters {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Aminoacridine
2-Aminoacridine is an aminoacridine. See also * 3-Aminoacridine * 4-Aminoacridine * 9-Aminoacridine 9-Aminoacridine is a highly fluorescent dye used clinically as a topical antiseptic and experimentally as a mutagen, an intracellular pH indicator and a small molecule MALDI In mass spectrometry, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MAL ... Aromatic amines Acridines {{heterocyclic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Aminoacridine
3-Aminoacridine is an aminoacridine. See also * 2-Aminoacridine * 4-Aminoacridine * 9-Aminoacridine 9-Aminoacridine is a highly fluorescent dye used clinically as a topical antiseptic and experimentally as a mutagen, an intracellular pH indicator and a small molecule MALDI In mass spectrometry, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MAL ... {{heterocyclic-stub Aromatic amines Acridines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Aminoacridine
4-Aminoacridine is an aminoacridine. See also * 2-Aminoacridine * 3-Aminoacridine * 9-Aminoacridine 9-Aminoacridine is a highly fluorescent dye used clinically as a topical antiseptic and experimentally as a mutagen, an intracellular pH indicator and a small molecule MALDI In mass spectrometry, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MAL ... References {{reflist Aromatic amines Acridines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiseptic
An antiseptic (from Greek ἀντί ''anti'', "against" and σηπτικός ''sēptikos'', "putrefactive") is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's ability to safely destroy bacteria within the body, and from ''disinfectants'', which destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects. Antibacterials include antiseptics that have the proven ability to act against bacteria. Microbicides which destroy virus particles are called viricides or antivirals. Antifungals, also known as antimycotics, are pharmaceutical fungicides used to treat and prevent mycosis (fungal infection). Surgery The widespread introduction of antiseptic surgical methods was initiated by the publishing of the paper '' Antiseptic Principle of the Practice of Surgery'' in 1867 by Joseph Lister, which was inspired by Louis Pasteur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer in animals, such mutagens can therefore be carcinogens, although not all necessarily are. All mutagens have characteristic mutational signatures with some chemicals becoming mutagenic through cellular processes. The process of DNA becoming modified is called mutagenesis. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called "spontaneous mutations" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination. Discovery The first mutagens to be identified were carcinogens, substances that were shown to be linked to cancer. Tumors were described more than 2,000 years before the discovery of chromosomes and DNA; in 500 B.C., the Greek physician Hippocrates named tumors resembling a crab ''karkinos'' (from which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
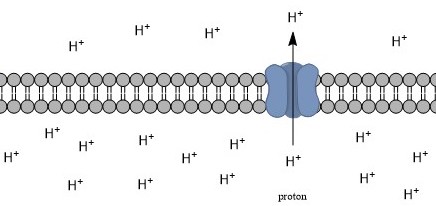
Intracellular PH
Intracellular pH (pHi) is the measure of the acidity or basicity (i.e., pH) of intracellular fluid. The pHi plays a critical role in membrane transport and other intracellular processes. In an environment with the improper pHi, biological cells may have compromised function. Therefore, pHi is closely regulated in order to ensure proper cellular function, controlled cell growth, and normal cellular processes. The mechanisms that regulate pHi are usually considered to be plasma membrane transporters of which two main types exist — those that are dependent and those that are independent of the concentration of bicarbonate (). Physiologically normal intracellular pH is most commonly between 7.0 and 7.4, though there is variability between tissues (e.g., mammalian skeletal muscle tends to have a pHi of 6.8–7.1). There is also pH variation across different organelles, which can span from around 4.5 to 8.0. pHi can be measured in a number of different ways. Homeostasis Intracel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MALDI
In mass spectrometry, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) is an ionization technique that uses a laser energy absorbing matrix to create ions from large molecules with minimal fragmentation. It has been applied to the analysis of biomolecules (biopolymers such as DNA, proteins, peptides and carbohydrates) and various organic molecules (such as polymers, dendrimers and other macromolecules), which tend to be fragile and fragment when ionized by more conventional ionization methods. It is similar in character to electrospray ionization (ESI) in that both techniques are relatively soft (low fragmentation) ways of obtaining ions of large molecules in the gas phase, though MALDI typically produces far fewer multi-charged ions. MALDI methodology is a three-step process. First, the sample is mixed with a suitable matrix material and applied to a metal plate. Second, a pulsed laser irradiates the sample, triggering ablation and desorption of the sample and matrix materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Amines
In organic chemistry, an aromatic amine is an organic compound consisting of an aromatic ring attached to an amine. It is a broad class of compounds that encompasses aniline Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starti ...s, but also many more complex aromatic rings and many amine substituents beyond . Such compounds occur widely. Aromatic amines are widely used as precursor to pesticides, pharmaceuticals, and dyes. Aromatic amines in textiles Since August 2012, the new standard EN 14362-1:2012 ''Textiles - Methods for determination of certain aromatic amines derived from azo colorants - Part 1: Detection of the use of certain azo colorants accessible with and without extracting the fibres'' is effective. It had been officially approved by the European Committee for Stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acridines
Acridine is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocycle with the formula C13H9N. Acridines are substituted derivatives of the parent ring. It is a planar molecule that is structurally related to anthracene with one of the central CH groups replaced by nitrogen. Like the related molecules pyridine and quinoline, acridine is mildly basic. It is an almost colorless solid, which crystallizes in needles. There are few commercial applications of acridines; at one time acridine dyes were popular, but they are now relegated to niche applications, such as with acridine orange. The name is a reference to the acrid odour and acrid skin-irritating effect of the compound. Isolation and syntheses Carl Gräbe and Heinrich Caro first isolated acridine in 1870 from coal tar. Acridine is separated from coal tar by extracting with dilute sulfuric acid. Addition of potassium dichromate to this solution precipitates acridine bichromate. The bichromate is decomposed using ammonia. Acridine an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |