|
8A4 Class ROUV
The Chinese 8A4 class ROUV is a remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROUV) used to perform various underwater tasks, ranging from oil platform service to salvage and rescue missions. The 8A4 is a member of a series of related ROUVs developed by the Shenyang Institute of Automation (SIA) in the People's Republic of China (PRC). The predecessor to the 8A4 was the RECON-IV, an improved version of the American RECON-III. The 8A4 itself is an upgraded version of the American AMETEK 2006, and the 7B8 is an improved version of the 8A4. History The 8A4's origins trace back to the RECON-IV ROUV. China has operated ROUVs to support its offshore oil and salvage operations since the 1980s, such as Hysub 10 ROUVs and Hysub 40 ROUVs supplied by the Canadian firm International Submarine Engineering in British Columbia. The Shanghai Salvage Bureau deployed Hysub 40 ROUVs and proved them to be a successful platform for offshore oil drilling, salvage, and rescue missions. However, foreign-buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicle
A remotely operated underwater vehicle (technically ROUV or just ROV) is a tethered underwater mobile device, commonly called ''underwater robot''. Definition This meaning is different from remote control vehicles operating on land or in the air. ROVs are unoccupied, usually highly maneuverable, and operated by a crew either aboard a vessel/floating platform or on proximate land. They are common in deepwater industries such as offshore hydrocarbon extraction. They are linked to a host ship by a neutrally buoyant tether or, often when working in rough conditions or in deeper water, a load-carrying umbilical cable is used along with a tether management system (TMS). The TMS is either a garage-like device which contains the ROV during lowering through the splash zone or, on larger work-class ROVs, a separate assembly which sits on top of the ROV. The purpose of the TMS is to lengthen and shorten the tether so the effect of cable drag where there are underwater currents is minimize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SJT Class ROUV
SJT-class ROUVs are a series of Chinese remotely operated underwater vehicles (ROUVs) jointly developed by the Shenyang Institute of Automation of the Chinese Academy of Science and the Institute of Underwater Engineering of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SHJTU). The general designer of the SJT-class of ROUVs is Zhu Jimao (), a professor at SHJTU, who also was the general designer of the earlier Type 7103 DSRV. Many more ROUVs have been developed after the SJT series, based on experience gained from this series. HR-01 ROUV The origin of SJT-class ROUV begins with HR-01 (), one of the first indigenously developed ROUVs. Work began in 1982 and was completed in winter 1985, entering service the following year. In 1989, it won 2nd place in the Science and Technology Advance Award of the Chinese Academy of Science. Based on experience gained from HR-01, the three subsequent SJT-class ROUVs were jointly developed with a Canadian company from 1985 through June 1987. Specifications: *We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's own law" is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be defined from a human resources perspective, where it denotes a (relatively high) level of discretion granted to an employee in his or her work. In such cases, autonomy is known to generally increase job satisfaction. Self-actualized individuals are thought to operate autonomously of external expectations. In a medical context, respect for a patient's personal autonomy is considered one of many fundamental ethical principles in medicine. Sociology In the sociology of knowledge, a controversy over the boundaries of autonomy inhibited analysis of any concept beyond relative autonomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliary Ships Of The People's Liberation Army Navy
Auxiliary may refer to: * A backup site or system In language * Auxiliary language (other) * Auxiliary verb In military and law enforcement * Auxiliary police * Auxiliaries, civilians or quasi-military personnel who provide support of some kind to a military service ** Auxiliaries (Roman military) In religion * Auxiliary bishop, in the Roman Catholic Church * Auxiliary organization (LDS Church) In technology * Auxiliary input jack and auxiliary cable, generally for audio; frequently associated with mobile device audio * Aux-send of a mixing console * An auxiliary Port is a common port found on many Cisco routers for CLI access. Other uses * Auxiliary route, also known as "special route", in road transportation ** An auxiliary route of the Interstate Highway System in the United States * Auxiliary ship is a naval vessel designed to operate in support of combat ships and other naval operations * Auxiliary (fraternity or sorority) * A marching band color guard See als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
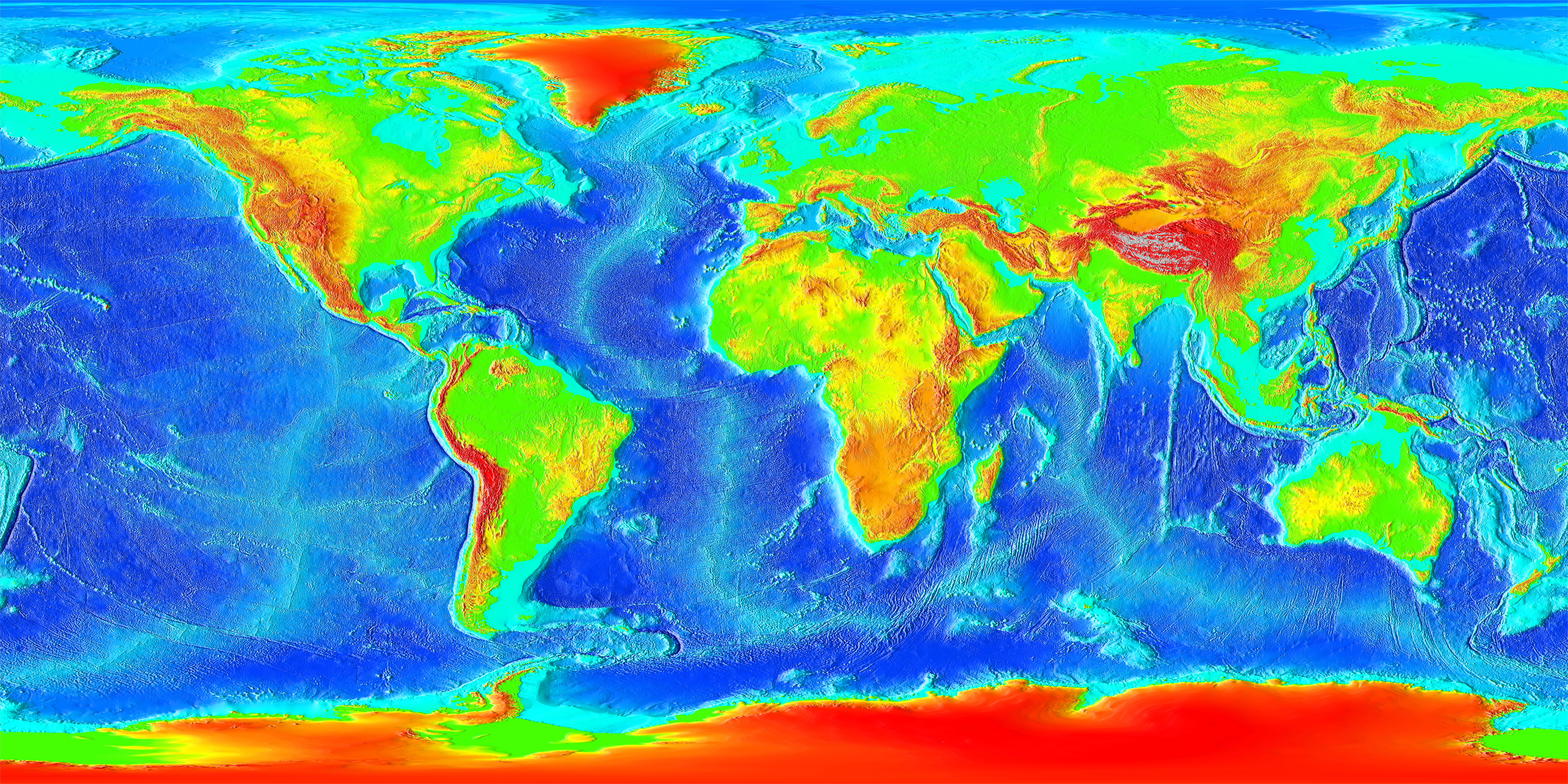
Seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'. The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of the ocean is very deep, where the seabed is known as the abyssal plain. Seafloor spreading creates mid-ocean ridges along the center line of major ocean basins, where the seabed is slightly shallower than the surrounding abyssal plain. From the abyssal plain, the seabed slopes upward toward the continents and becomes, in order from deep to shallow, the continental rise, slope, and shelf. The depth within the seabed itself, such as the depth down through a sediment core, is known as the “depth below seafloor.” The ecological environment of the seabed and the deepest waters are collectively known, as a habitat for creatures, as the “benthos.” Most of the seabed throughout the world's oceans is covered in layers of marine sediments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manipulator (device)
In robotics, a manipulator is a device used to manipulate materials without direct physical contact by the operator (profession), operator. The applications were originally for dealing with ionizing radiation, radioactive or biohazardous materials, using robotic arms, or they were used in inaccessible places. In more recent developments they have been used in diverse range of applications including welding automation, robotic surgery and in robotic arm, space. It is an arm-like mechanism that consists of a series of segments, usually sliding or jointed called cross-slides, which grasp and move objects with a number of degrees of freedom (mechanics), degrees of freedom. In industrial ergonomics a manipulator is a lift-assist device used to help workers lift, maneuver and place articles in process that are too heavy, too hot, too large or otherwise too difficult for a single worker to manually handle. As opposed to simply vertical lift assists (cranes, hoists, etc.) manipulators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remotely Operated Vehicle
A remotely operated underwater vehicle (technically ROUV or just ROV) is a tethered underwater mobile device, commonly called ''underwater robot''. Definition This meaning is different from remote control vehicles operating on land or in the air. ROVs are unoccupied, usually highly maneuverable, and operated by a crew either aboard a vessel/floating platform or on proximate land. They are common in deepwater industries such as offshore hydrocarbon extraction. They are linked to a host ship by a neutrally buoyant tether or, often when working in rough conditions or in deeper water, a load-carrying umbilical cable is used along with a tether management system (TMS). The TMS is either a garage-like device which contains the ROV during lowering through the splash zone or, on larger work-class ROVs, a separate assembly which sits on top of the ROV. The purpose of the TMS is to lengthen and shorten the tether so the effect of cable drag where there are underwater currents is minimize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proof Of Concept
Proof of concept (POC or PoC), also known as proof of principle, is a realization of a certain method or idea in order to demonstrate its feasibility, or a demonstration in principle with the aim of verifying that some concept or theory has practical potential. A proof of concept is usually small and may or may not be complete. These collaborative trials aim to test feasibility of business concepts and proposals to solve business problems and accelerate business innovation goals. A proof of value (PoV) is sometimes used along proof of concept, and differs by focusing more on demonstrating the potential customers use case and value, and is usually less in-depth than a proof of concept. Usage history The term has been in use since 1967. In a 1969 hearing of the Committee on Science and Astronautics, Subcommittee on Advanced Research and Technology, ''proof of concept'' was defined as following: One definition of the term "proof of concept" was by Bruce Carsten in the context o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottom Crawler
A bottom crawler is an underwater exploration and recovery vehicle. It is designed to sink to the bottom of a body of water, where it moves about using traction against the bottom with wheels or tracks. It is usually tethered to a surface ship by cables providing power, control, video, and lifting capabilities, but this is not essential. Such devices have been proposed for use in recovering deep seabed minerals, such as manganese nodules. These also have been considered since the late 1960s for use in offshore oil exploration and production in extremely deep water, but practical devices have used other technologies from the sea surface, such as moored barges and tension leg platform __NOTOC__ A tension-leg platform (TLP) or extended tension leg platform (ETLP) is a vertically moored floating structure normally used for the offshore production of oil or gas, and is particularly suited for water depths greater than 300 metres ...s. References Oceanography {{Ocean-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'. The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of the ocean is very deep, where the seabed is known as the abyssal plain. Seafloor spreading creates mid-ocean ridges along the center line of major ocean basins, where the seabed is slightly shallower than the surrounding abyssal plain. From the abyssal plain, the seabed slopes upward toward the continents and becomes, in order from deep to shallow, the continental rise, slope, and shelf. The depth within the seabed itself, such as the depth down through a sediment core, is known as the “depth below seafloor.” The ecological environment of the seabed and the deepest waters are collectively known, as a habitat for creatures, as the “benthos.” Most of the seabed throughout the world's oceans is covered in layers of marine sediments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiaolong (submersible)
''Jiaolong'' ( flood dragon) is a Chinese crewed deep-sea research submersible that can dive to a depth of over . It has the second-greatest depth range of any crewed research vehicle in the world; the only crewed expeditions to have gone deeper were the dives of the ''Trieste'' bathyscaphe () in 1960, ''Archimède'' () in 1962, ''Deepsea Challenger'' () in 2012, and ''DSV Limiting Factor'' () in 2019 (with three diving to Challenger Deep). The general designer is Xu Qinan (徐芑南), a former professor at the School of Naval Architecture, Ocean and Civil Engineering (船舶与海洋工程学院) of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SJTU), who also designed many other Chinese submersibles and uncrewed underwater vehicles. Xu is now an academician for the Chinese Academy of Engineering. The first deputy general designer is Cui Weicheng (崔维成), and the deputy general designer was Zhu Weiqing (朱维庆). On June 27, 2012, the ''Jiaolong'' with two oceanauts reached a depth of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |