|
7 Medical Battalion Group
7 Medical Battalion Group is the specialist Airborne Medical Unit of the South African Military Health Service. The Battalion's main task is to render medical support to the South African Airborne and Special Forces. Other specialties of the Battalion include Combat Search and Rescue, CBRNE detection, verification and decontamination, Diving and Aviation medicine and numerous other skills associated in supporting Special Forces. Little is publicly known of this elite medical unit primarily because of its association with the South African Special Forces. The unit's founder Commandant Wouter Basson led the research on the SADF Chemical and Biological Warfare program. Other tasks of the battalion include, but are not limited to, medical support to the South African Police Service Special Task Force and other elite units, the South African Air Force Combat Search and Rescue units and the Presidential Protection Services (particularly in the context of Joint VVIP Protection Operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Operations
Special operations (S.O.) are military activities conducted, according to NATO, by "specially designated, organized, selected, trained, and equipped forces using unconventional techniques and modes of employment". Special operations may include reconnaissance, unconventional warfare, and counter-terrorism actions, and are typically conducted by small groups of highly-trained personnel, emphasizing sufficiency, stealth, speed, and tactical coordination, commonly known as " special forces". History Australia In World War II following advice from the British, Australia began raising special forces. The first units to be formed were independent companies, which began training at Wilson's Promontory in Victoria in early 1941 under the tutelage of British instructors. With an establishment of 17 officers and 256 men, the independent companies were trained as "stay behind" forces, a role that they were later employed in against the Japanese in the South West Pacific Area during 1942 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Police Service Special Task Force
The Special Task Force (STF) is the elite police tactical unit of the South African Police Service (SAPS). The Special Task Force handles high risk operations that fall beyond the scope of classic policing which require specialised skills. History In 1967, about 2,000 members of the South African Police were deployed to guard the northern border of Rhodesia (modern day Zimbabwe) to assist the Rhodesian security forces as guerrilla attacks became more frequent during the Rhodesian Bush War. These police members proved to be ill-equipped and ineffective at dealing with guerrilla warfare and terrorism. As a result of these events the Security Branch of the Police began to envision a special police unit to deal with high-risk situations such as hostage situations. Captain J.J. de Swardt of the Security Branch of the Police as well as Sergeant Roelf de Plooy (a counter insurgency (COIN) instructor), both veterans of the deployments in Rhodesia against Zimbabwe African National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
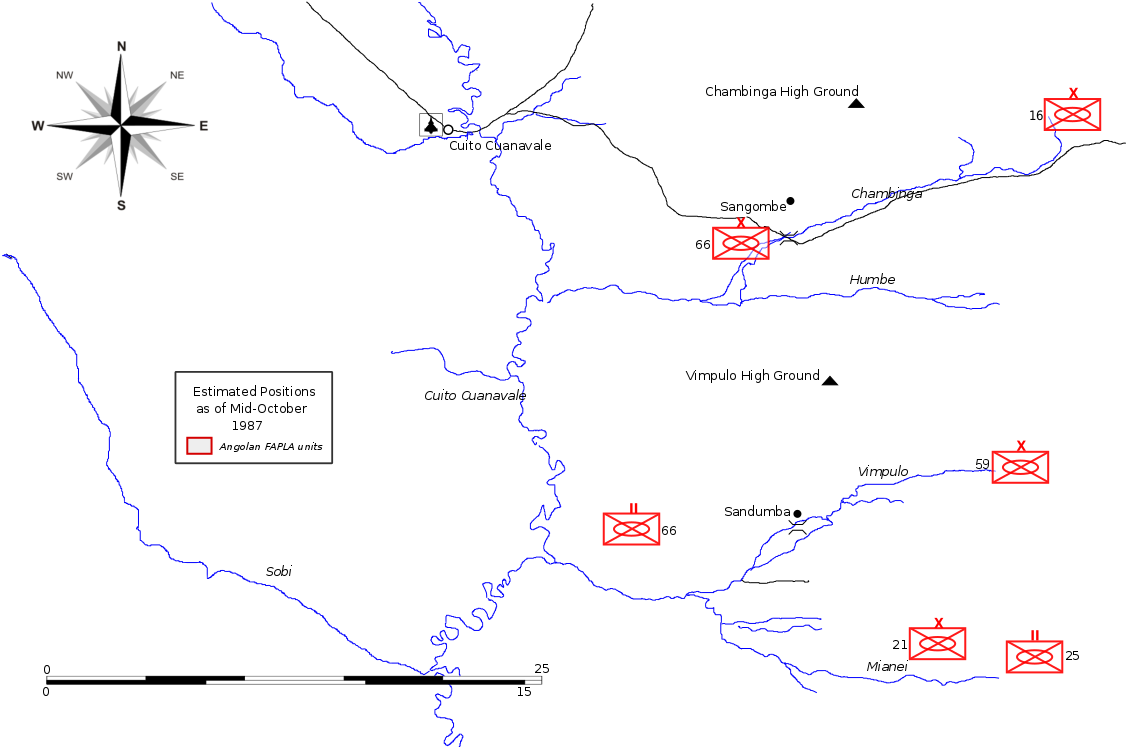
Operation Packer
Operation Packer was a military operation by the South African Defence Force (SADF) during the South African Border War and Angolan Civil War from March to April 1988. This operation forms part of what became known as the Battle of Cuito Cuanavale. Operation Packer was a continuation of Operation Hooper, using fresh troops and equipment. The Cubans' objective was still to secure the town of Cuito Cuanavale to the west of the river from capture. The SADF objective was once again to eliminate the remaining Angolan forces on the east side of the river, so as to ensure that the Angolans were no longer a threat to UNITA in the south-east. Although at the conclusion some Angolan units remained in positions east of the river, the Angolan advance against UNITA was permanently halted, and UNITA lived to fight on. The SADF never attempted to cross the river or to capture the town. Both sides again claimed victory. Background On the 29 February 1988, the SADF and UNITA launched a fourth att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Hooper
Operation Hooper was a military operation in 1987-88 by the South African Defence Force (SADF) during the South African Border War. This operation forms part of what has come to be called the Battle of Cuito Cuanavale. The Cubans' objective was securing the town of Cuito Cuanavale on the west of the river from capture. The SADF objective was to drive the People's Armed Forces for the Liberation of Angola (FAPLA) west across the river or to destroy them, so as to ensure that FAPLA was no longer a threat to the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA) in the south-east. The FAPLA advance was permanently halted, UNITA lived to fight on for another 15 years. The SADF never attempted to capture the town. Both sides claimed victory. Background Directly following on from Operation Moduler, by November 1987 the SADF had cornered the remnants of three FAPLA units on the east of the Cuito River, across from the town itself and was poised to destroy them. Gleijeses (2007) T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Modular
Operation Moduler (sometimes incorrectly called "Modular") was a military operation by the South African Defence Force (SADF) during the South African Border War. It formed part of what has come to be called the Battle of Cuito Cuanavale. The Angolan objective was to advance south-east to attack the UNITA (National Union for the Total Independence of Angola) at Mavinga. The SADF objective was to protect UNITA by stopping that advance. The advance was halted with heavy Angolan casualties. The South African forces and its UNITA allies then began offensive operations against the Angolan forces, who had retreated back to a defensive line east of the Cuito River with the objective of destroying them once and for all. Background During January 1987, the Angolans began to increase their air defence network in the Cuito Cuanavale region and by April they had begun to assemble a large force of tanks, APCs, trucks and a large number of helicopters and fighter and strike aircraft at the tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Border War
The South African Border War, also known as the Namibian War of Independence, and sometimes denoted in South Africa as the Angolan Bush War, was a largely asymmetric conflict that occurred in Namibia (then South West Africa), Zambia, and Angola from 26 August 1966 to 21 March 1990. It was fought between the South African Defence Force (SADF) and the People's Liberation Army of Namibia (PLAN), an armed wing of the South West African People's Organisation (SWAPO). The South African Border War resulted in some of the largest battles on the African continent since World War II and was closely intertwined with the Angolan Civil War. Following several years of unsuccessful petitioning through the United Nations and the International Court of Justice for Namibian independence from South Africa, SWAPO formed the PLAN in 1962 with material assistance from the Soviet Union, China, and sympathetic African states such as Tanzania, Ghana, and Algeria. Fighting broke out between PLAN and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Honours Of South Africa
South Africa follows the British system of awarding battle honours to military units, to recognise the battles, theatres and campaigns in which they have fought with distinction. History Before the unification of Union of South Africa in 1910, units were largely left to invent their own battle honours. Exceptions were the honours for the Anglo-Zulu War (1879) and the Natal Rebellion (1906), which were authorised by the Natal colonial government in 1909 and 1908 respectively, and the honours for the Anglo-Boer War (1899–1902), which were authorised by the British authorities. Many of these units were embodied in the Union Defence Force in 1913. The UDF did not acknowledge their self-assumed battle honours in official publications, e.g. the annual ''Officers List'', but did not prevent the units from displaying the honours on their Colours. Only in the 1960s were these honours reviewed: many were then approved, but some were disallowed. Battle honours for World War I (1914– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Honours
A battle honour is an award of a right by a government or sovereign to a military unit to emblazon the name of a battle or operation on its flags ("colours"), uniforms or other accessories where ornamentation is possible. In European military tradition, military units may be acknowledged for their achievements in specific wars or operations of a military campaign. In Great Britain and those countries of the Commonwealth which share a common military legacy with the British, battle honours are awarded to selected military units as official acknowledgement for their achievements in specific wars or operations of a military campaign. These honours usually take the form of a place and a date (e.g. " Cambrai 1917"). Theatre honours, a type of recognition in the British tradition closely allied to battle honours, were introduced to honour units which provided sterling service in a campaign but were not part of specific battles for which separate battle honours were awarded. Theatr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Aviation Medicine
An institute is an organisational body created for a certain purpose. They are often research organisations (research institutes) created to do research on specific topics, or can also be a professional body. In some countries, institutes can be part of a university or other institutions of higher education, either as a group of departments or an autonomous educational institution without a traditional university status such as a "university institute" (see Institute of Technology). In some countries, such as South Korea and India, private schools are sometimes referred to as institutes, and in Spain, secondary schools are referred to as institutes. Historically, in some countries institutes were educational units imparting vocational training and often incorporating libraries, also known as mechanics' institutes. The word "institute" comes from a Latin word ''institutum'' meaning "facility" or "habit"; from ''instituere'' meaning "build", "create", "raise" or "educate". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Coast
Project Coast was a 1980s top-secret chemical and biological weapons (CBW) program instituted by the apartheid-era government of South Africa. Project Coast was the successor to a limited postwar CBW program, which mainly produced the lethal agents CX powder and mustard gas; as well as non-lethal tear gas for riot control purposes. The program was headed by Wouter Basson, a cardiologist who was the personal physician of South African Prime Minister P. W. Botha. History From 1975 onwards, the South African Defence Force (SADF) found itself embroiled in conventional battles in Angola as a result of the South African Border War. The perception that its enemies had access to battlefield chemical and biological weapons led South Africa to begin expanding its own program, initially as a defensive measure and by carrying out research on vaccines. As the years went on, research was carried out on offensive uses of the newly found capability. Finally, in 1981, President P. W. Botha or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNITA
The National Union for the Total Independence of Angola ( pt, União Nacional para a Independência Total de Angola, abbr. UNITA) is the second-largest political party in Angola. Founded in 1966, UNITA fought alongside the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA) in the Angolan War for Independence (1961–1975) and then against the MPLA in the ensuing civil war (1975–2002). The war was one of the most prominent Cold War proxy wars, with UNITA receiving military aid initially from People's Republic of China from 1966 until October 1975 and later from the United States and apartheid South Africa while the MPLA received support from the Soviet Union and its allies, especially Cuba. Until 1996, UNITA was funded through Angolan diamond mines in both Lunda Norte and Lunda Sul along the Cuango River valley, especially the Catoca mine, which was Angola's only Kimberlite mine at that time. Valdemar Chidondo served as Chief of Staff in the government of UNITA, pro-W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Medical Service
The South African Medical Service (SAMS) was a branch of the South African Defence Force (SADF). In 1994 when the SADF was merged with various other military and armed resistance forces as part of the post-apartheid reforms the SAMS became the South African Military Health Service of the South African National Defence Force. The SAMS operated three hospitals, 1 Military Hospital in Pretoria, 2 Military Hospital in Cape Town, and 3 Military Hospital in Bloemfontein. It also had three specialist institutes; the Institute for Aviation Medicine, the Institute for Maritime Medicine, and the Military Psychological Institute. History The SA Defence Act Amendment Act, No. 22 of 1922 re-organised the Permanent Force. From 1 February 1923 the Permanent Force consisted a number of Corps, including the SA Medical Corps. By that time three Medical Corps were already in existence, the Transvaal Medical Corps (established in 1903), the Natal Volunteer Medical Corps (established in 1899 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |