|
7F-5-MeO-MET
5-MeO-7-F-MET (5-MeO-7F-MET, 5-Methoxy-7-fluoro-''N''-methyl-''N''-ethyltryptamine) is a tryptamine derivative which acts as a serotonin receptor agonist selective for the 5-HT2 subtypes, with a pEC50 of 8.71 at 5-HT2A, vs 8.25 at 5-HT2B and 7.69 at 5-HT2C. In animal tests it produced the most potent head-twitch response of a range of related fluorinated tryptamine derivatives tested, though still with slightly lower potency than psilocybin. See also * 5-MeO-MET * 4-Fluoro-5-methoxy-DMT * 5-Methoxy-7,N,N-trimethyltryptamine * 7-Chloro-AMT 7-Chloro-α-methyltryptamine (7-Cl-AMT) is a tryptamine derivative with stimulant effects, invented in the 1960s. It is a weak monoamine oxidase inhibitor but its pharmacology has not otherwise been studied by modern techniques, though several c ... References {{Hallucinogens Designer drugs Psychedelic tryptamines Serotonin receptor agonists Tryptamines Fluoroarenes Methoxy compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7-Chloro-AMT
7-Chloro-α-methyltryptamine (7-Cl-AMT) is a tryptamine derivative with stimulant effects, invented in the 1960s. It is a weak monoamine oxidase inhibitor but its pharmacology has not otherwise been studied by modern techniques, though several closely related compounds are known to act as serotonin–dopamine releasing agents and agonists of the 5-HT2A receptor. See also * 5-Chloro-AMT * 5-Chloro-DMT * 5-Fluoro-AMT * 5-Fluoro-AET * 5-Fluoro-DMT * 6-Fluoro-AMT * 7-Methyl-DMT * 7-Methyl-AET * 7F-5-MeO-MET * O-4310 O-4310 (1-isopropyl-6-fluoro-psilocin) is a tryptamine derivative developed by Organix Inc which acts as a serotonin receptor agonist. It is claimed to have an EC50 of 5nM at 5-HT2A with 89% efficacy vs 5-HT, and 100x selectivity over 5-HT2C, ... References Designer drugs Psychedelic tryptamines Serotonin receptor agonists Chloroarenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
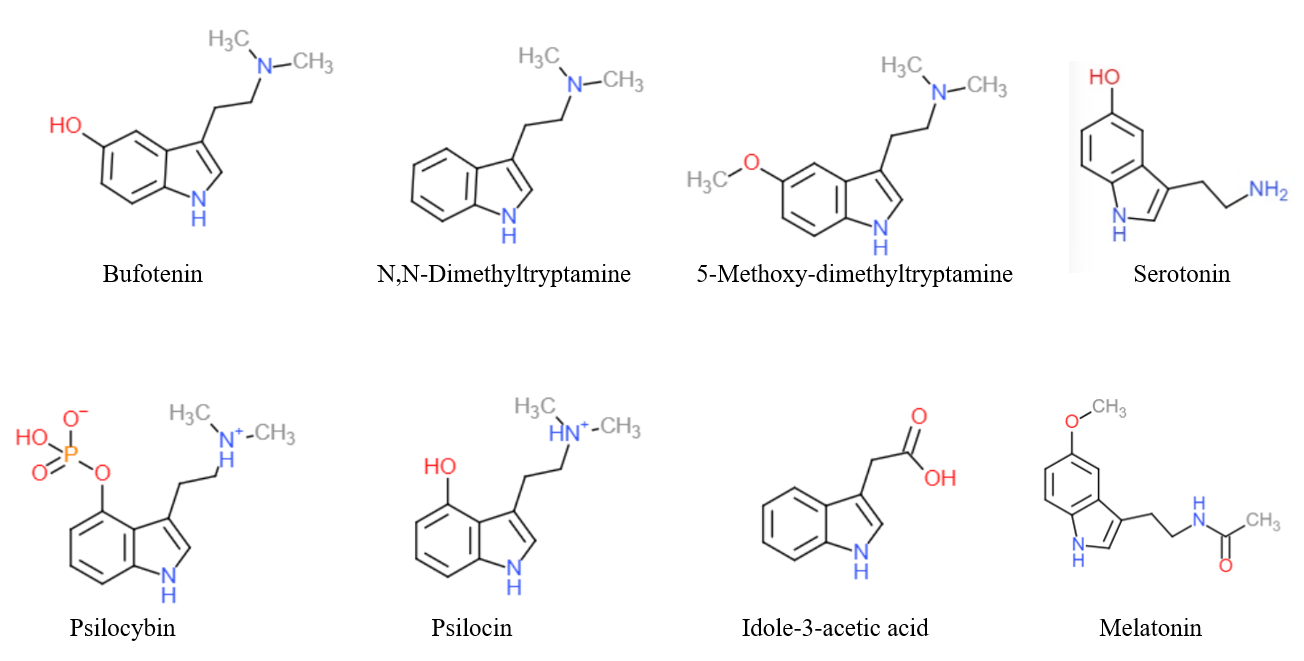
Tryptamines
Substituted tryptamines, or serotonin analogues, are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (−CH2–CH2−) sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms. Well-known tryptamines include serotonin, an important neurotransmitter, and melatonin, a hormone involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Tryptamine alkaloids are found in fungi, plants and animals; and sometimes used by humans for the neurological or psychotropic effects of the substance. Prominent examples of tryptamine alkaloids include psilocybin (from "psilocybin mushrooms") and DMT. In South America, dimethyltryptamine is obtained from numerous plant sources, like chacruna, and it is often used in ayahuasca brews. Many synthetic tryptamines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-Methoxy-7,N,N-trimethyltryptamine
5-Methoxy-7,N,N-trimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-7,N,N-TMT, 5-MeO-7-TMT), is a tryptamine derivative which acts as an agonist at the 5-HT2 serotonin receptors. In animal tests, both 7,N,N-TMT and 5-MeO-7,N,N-TMT produced behavioural responses similar to those of psychedelic drugs such as DMT and 5-MeO-DMT, but compounds with larger 7-position substituents such as 7-ethyl-DMT and 7-bromo-DMT did not produce psychedelic-appropriate responding despite high 5-HT2 receptor binding affinity, suggesting these may be antagonists or weak partial agonists for the 5-HT2 receptors. The related compound 7-MeO-MiPT (cf. 5-MeO-MiPT) was also found to be inactive, suggesting that the 7-position has poor tolerance for bulky groups at this position, at least if agonist activity is desired. See also * 5-MeO-2-TMT * 7F-5-MeO-MET 5-MeO-7-F-MET (5-MeO-7F-MET, 5-Methoxy-7-fluoro-''N''-methyl-''N''-ethyltryptamine) is a tryptamine derivative which acts as a serotonin receptor agonist selective for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin Receptor Agonists
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychedelic Tryptamines
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips").Pollan, Michael (2018). ''How to Change Your Mind: What the New Science of Psychedelics Teaches Us About Consciousness, Dying, Addiction, Depression, and Transcendence'' Sometimes, they are called classic hallucinogens, serotonergic hallucinogens, or serotonergic psychedelics, and the term ''psychedelics'' is used more broadly to include all hallucinogens; this article uses the narrower definition of ''psychedelics''. Psychedelics cause specific psychological, visual, and auditory changes, and often a substantially altered state of consciousness.Leary, Timothy; Metzner, Ralph (1964). ''The Psychedelic Experience: A Manual Based on The Tibetan Book of the Dead'' Psychedelic states are often compared to meditative, psychodynamic or transcendental types of alterations of mind. The "classical" psychedelics, the psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designer Drugs
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects, and shorter duration (and possibly also because it is easier to apply for patents for new molecules) and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human trials, the use of some of these drugs may result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-MeO-MET
5-MeO-MET (5-Methoxy-N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine) is a relatively rare designer drug from the substituted tryptamine family, related to compounds such as N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine and 5-MeO-DMT. It was first synthesised in the 1960s and was studied to a limited extent, but was first identified on the illicit market in June 2012 in Sweden. It was made illegal in Norway in 2013, and is controlled under analogue provisions in numerous other jurisdictions. See also * 4-HO-MET * 5-HO-DiPT * 5-EtO-DMT * 5-Fluoro-MET * 5-MeO-EPT * 5-MeO-MALT * 5-MeO-MiPT 5-MeO-MiPT is a psychedelic and hallucinogenic drug, used by some as an entheogen. It has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to the drugs 5-MeO-DiPT, DiPT, and MiPT. It is commonly used as a "substitute" for 5-MeO-DiPT because ... References Tryptamines Methoxy compounds Substances discovered in the 1960s {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin Receptor
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand. The serotonin receptors modulate the release of many neurotransmitters, including glutamate, GABA, dopamine, epinephrine / norepinephrine, and acetylcholine, as well as many hormones, including oxytocin, prolactin, vasopressin, cortisol, corticotropin, and substance P, among others. Serotonin receptors influence various biological and neurological processes such as aggression, anxiety, appetite, cognition, learning, memory, mood, nausea, sleep, and thermoregulation. They are the target of a variety of pharmaceutical and recreational drugs, including many antidepressants, antipsychotics, anorectics, antiemetics, gast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocybin
Psilocybin ( , ) is a naturally occurring psychedelic prodrug compound produced by more than 200 species of fungi. The most potent are members of the genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P. cyanescens'', but psilocybin has also been isolated from about a dozen other genera. Psilocybin is itself biologically inactive but is quickly converted by the body to psilocin, which has mind-altering effects similar, in some aspects, to those of LSD, mescaline, and DMT. In general, the effects include euphoria, visual and mental hallucinations, changes in perception, a distorted sense of time, and perceived spiritual experiences. It can also cause adverse reactions such as nausea and panic attacks. Imagery found on prehistoric murals and rock paintings of modern-day Spain and Algeria suggests that human usage of psilocybin mushrooms predates recorded history. In Mesoamerica, the mushrooms had long been consumed in spiritual and div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-twitch Response
The head-twitch response (HTR) is a rapid side-to-side head movement that occurs in mice and rats after the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor is activated. The prefrontal cortex may be the neuroanatomical locus mediating the HTR. Many serotonergic hallucinogens, including lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), induce the head-twitch response, and so the HTR is used as a behavioral model of hallucinogen effects. However while there is generally a good correlation between compounds that induce head twitch in mice and compounds that are hallucinogenic in humans, it is unclear whether the head twitch response is primarily caused by 5-HT2A receptors, 5-HT2C receptors or both, though recent evidence shows that the HTR is mediated by the 5-HT2A receptor and modulated by the 5-HT2C receptor. Also, the effect can be non-specific, with head twitch responses also produced by some drugs that do not act through 5-HT2 receptors, such as phencyclidine, yohimbine, atropine and cannabinoid receptor antagonists. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |