|
74th Parallel North
The 74th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 74 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane, in the Arctic. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Europe, Asia, the Arctic Ocean, and North America. At this latitude the sun is visible for 24 hours, 0 minutes during the summer solstice and nautical twilight during the winter solstice. Around the world Starting at the Prime Meridian and heading eastwards, the parallel 74° north passes through: : See also *73rd parallel north The 73rd parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 73 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane, in the Arctic. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Europe, Asia, the Arctic Ocean and North America. At this latitude the sun is visible for ... * 75th parallel north {{geographical coordinates, state=collapsed n74 Geography of the Arctic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Of Latitude
A circle of latitude or line of latitude on Earth is an abstract east–west small circle connecting all locations around Earth (ignoring elevation) at a given latitude coordinate line. Circles of latitude are often called parallels because they are Parallel (geometry), parallel to each other; that is, planes that contain any of these circles never Intersection, intersect each other. A location's position along a circle of latitude is given by its longitude. Circles of latitude are unlike circles of longitude, which are all great circles with the centre of Earth in the middle, as the circles of latitude get smaller as the distance from the Equator increases. Their length can be calculated by a common sine or cosine function. The 60th parallel north or 60th parallel south, south is half as long as the Equator (disregarding Earth's minor flattening by 0.335%). On the Mercator projection or on the Gall-Peters projection, a circle of latitude is perpendicular to all meridian (geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territorial waters.World Wildlife Fund, 2008. It was known among Russians in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea ("Norse Sea"); the current name of the sea is after the historical Netherlands, Dutch navigator Willem Barentsz. The Barents Sea is a rather shallow Continental shelf, shelf sea, with an average depth of , and it is an important site for both fishing and hydrocarbon exploration.O. G. Austvik, 2006. It is bordered by the Kola Peninsula to the south, the shelf edge towards the Norwegian Sea to the west, and the archipelagos of Svalbard to the northwest, Franz Josef Land to the northeast and Novaya Zemlya to the east. The islands of Novaya Zemlya, an extension of the northern end of the Ural Mountains, separate the Barents Sea from the Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Siberian Sea
The East Siberian Sea ( rus, Восто́чно-Сиби́рское мо́ре, r=Vostochno-Sibirskoye more) is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukotka, and Wrangel Island to the east. This sea borders on the Laptev Sea to the west and the Chukchi Sea to the east. This sea is one of the least studied in the Arctic area. It is characterized by severe climate, low water salinity, and a scarcity of flora, fauna and human population, as well as shallow depths (mostly less than 50 m), slow sea currents, low tides (below 25 cm), frequent fogs, especially in summer, and an abundance of ice fields which fully melt only in August–September. The sea shores were inhabited for thousands of years by indigenous tribes of Yukaghirs, Chukchi and then Evens and Evenks, which were engaged in fishing, hunting and reindeer husbandry. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
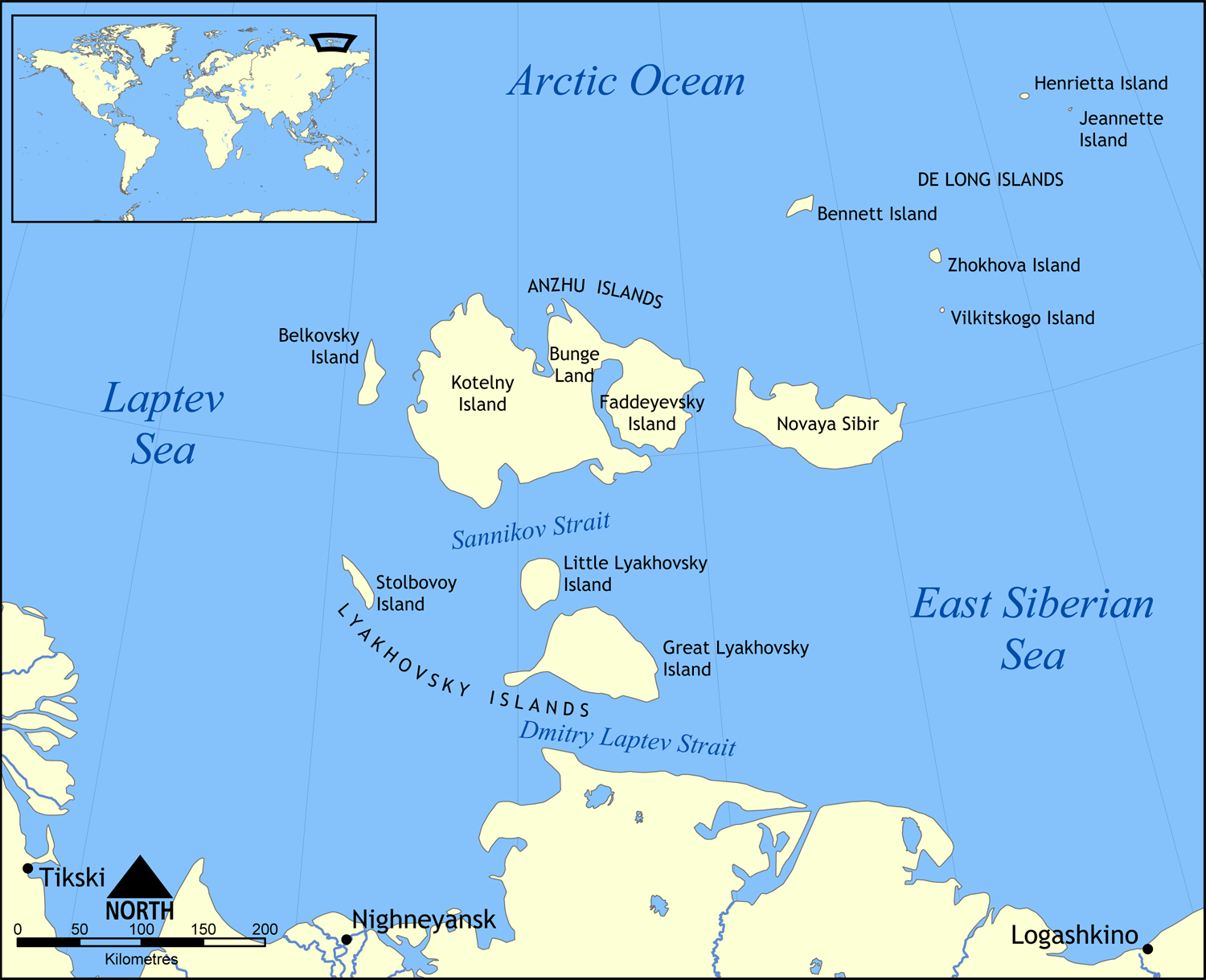
Little Lyakhovsky Island
Maly Lyakhovsky Island (russian: Малый Ляховский) is the second largest of the Lyakhovsky Islands belonging to the New Siberian Islands archipelago in Laptev Sea in northern Russia. It has an area of . The Lyakhovsky Islands are named in honour of Ivan Lyakhov, who explored them in 1773. Geology Maly Lyakhovsky Island consists of Upper Jurassic to lower Cretaceous turbidites, also known as ''flysch'', covered by a thin veneer of Pliocene to Pleistocene sediments. These Mesozoic rocks consist of sandstones, argillites, and shales deformed into east-northeast striking folds about wide. The Mesozoic rocks are covered by a relatively thin layer of Pliocene to Pleistocene sandy and clayey sediments of colluvial and alluvial origin. Near the coast, the alluvial sediments grade into nearshore marine sediments containing fossil marine mollusks and lignitized wood. Thick permafrost characterized by massive ice wedges has developed in these sediments.Fujita, K., and D.B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stolbovoy Island
Stolbovoy Island (russian: Столбовой остров) is a long and narrow island off the southwest side of the New Siberian archipelago in the eastern part of the Laptev Sea. It is located 184 km away from the Siberian coast and 100 km southwest of Kotelny Island, being thus quite detached from the New Siberian island group, although it belongs to the Lyakhov Islands subgroup of the New Siberian Islands. History According to Russian tradition in 1690 the Boyar Maxim Mukhoplev visited the island and found a number of crosses, the tombs of Russian seafarers who had previously been there. Stolbovoy was first charted by Yakov Sannikov in 1800. There was a meteorological station located on the north-west coast of the island at the time of the USSR. In 2012 an automatic GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System) monitoring facility was installed in the same spot. Presently the island belongs to the Sakha Republic administrative division of the Russian Federation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Siberian Islands
The New Siberian Islands ( rus, Новосиби́рские Oстрова, r=Novosibirskiye Ostrova; sah, Саҥа Сибиир Aрыылара, translit=Saña Sibiir Arıılara) are an archipelago in the Extreme North of Russia, to the north of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha (Yakutia) Republic. History The first news about the existence of the New Siberian Islands was brought by a Cossack, Yakov Permyakov, in the beginning of the 18th century. In 1712, a Cossack unit led by M. Vagin reached the Great Lyakhovsky Island. In 1809–10 Yakov Sannikov and Matvei Gedenschtrom went to the New Siberian Islands on a cartographic expedition. Sannikov reported the sighting of a "new land" north of Kotelny in 1811. This became the myth of ''Zemlya Sannikova'' or ''Sannikov Land''.Markham, Albert Hastings ''Arctic Exploration'', 1895 In 1886, Russian polar explorer and scientist Eduard Toll, during his first visit to the New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolshoy Begichev Island
Bolshoy Begichev (russian: Большой Бегичев, translation= Big Begichev) is an island in the Laptev Sea, in the Sakha Republic, Russia. Geography The area of the island is . Bolshoy Begichev is located within the Khatanga Gulf (russian: Хатангский залив), splitting the gulf into two straits. Adjacent Islands Maliy Begichev Only west of Bolshoy Begichev lies the much smaller island known as Maliy Begichev Island. Its size is only . The border between administrative divisions of the Russian Federation runs between the two Begichev islands, so that while Maliy Begichev is in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Bolshoy Begichev is in the Sakha republic. Both Bolshoy Begichev and Maliy Begichev are named after Russian polar explorer Nikifor Begichev. Preobrazheniya North of Bolshoy Begichev lies small Preobrazheniya Island. This elongated granitic island was useful as a landmark for ships plying the Northern Sea Route in the past. History A NAVTEX Coast Station used to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea ( rus, мо́ре Ла́птевых, r=more Laptevykh; sah, Лаптевтар байҕаллара, translit=Laptevtar baỹğallara) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy Cape. The Kara Sea lies to the west, the East Siberian Sea to the east. The sea is named after the Russian explorers Dmitry Laptev and Khariton Laptev; formerly, it had been known under various names, the last being Nordenskiöld Sea (russian: link=no, мо́ре Норденшёльда), after explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld. The sea has a severe climate with temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F) over more than nine months per year, low water salinity, scarcity of flora, fauna and human population, and low depths (mostly less than 50 meters) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Taymyr
Lake Taymyr (russian: Таймыр, Таймырское озеро, Taymyr, Taymyrskoye ozero) is a lake of the central regions of the Taymyr Peninsula in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russian Federation. It is located south of the Byrranga Mountains. Geography Lake Taymyr is large, with a length of 165 km roughly east-to-west. It has an irregular shape with many arms projecting in different directions that cover a wide region. Its maximum width, however, is only about 23 km in its broadest area which is towards the eastern end of the lake. Lake Taymyr is covered with ice from late September until June. The main river flowing into its basin, from the west, is the Upper Taymyra. Other rivers flowing into it are the Zapadnaya, Severnaya, Bikada-Nguoma, Yamu-Tarida and Kalamissamo. The Lower Taymyra flows out of the lake northwards across the Byrranga mountain region. The tundra areas south of Lake Taymyr are full of smaller lakes and marshes. There are two quite large lakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taymyr Peninsula
The Taymyr Peninsula (russian: Таймырский полуостров, Taymyrsky poluostrov) is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of the mainland of Eurasia. Administratively it is part of the Krasnoyarsk Krai Federal subject of Russia. Geography The Taymyr Peninsula lies between the Yenisei Gulf of the Kara Sea and the Khatanga Gulf of the Laptev Sea. Lake Taymyr and the Byrranga Mountains are located within the vast Taymyr Peninsula. Cape Chelyuskin, the northernmost point of the Afro-Eurasian continent, is located at the northern end of the Taymyr Peninsula. Population The Nenets people, also known as ''Samoyeds'', are an indigenous people in northern arctic Russia, and some live at the Taymyr Peninsula. The Nganasan people are an indigenous Samoyedic people inhabiting central Siberia, including the Taymyr Peninsula. In the Russian Federation, they are recognized as being one of the Indigenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyasina Bay
The Pyasina Bay , also known as Pyasina Gulf, (russian: Пясинский залив; ''Pyasinsky Zaliv'') is a bay at the mouth of the river Pyasina in the Kara Sea. It is limited on its western side by the Kamennyye Islands and on its northeastern side by the Minina Skerries. The Pyasina Bay is surrounded by tundra coast. It is full of islands and island groups, foremost of which are the Zveroboy group (Zapadnyy, Malyy, Severnyy), the small Trio Island group and the Ptich'i Islands, the Labyrintovyye Islands, right at the large mouth of the river, the Begichevskaya Kosa string of islands and Farvaternyy Island. The climate in the area is severe, with long and bitter winters and frequent blizzards and gales. The bay is frozen for about nine months in a year and even in summer it is never quite free of ice floes. The Pyasina Bay was explored by Baron Eduard von Toll during his last venture, the Russian Arctic Expedition of 1900–1903. References * William Barr Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rastorguyev Island
Rastorguyev Island or Rastorguyeva Island (russian: остров Расторгуева, ''ostrov Rastorguyeva'') is an island in the Kara Sea, Russian Federation. Geography It is the third largest island of the Kamennyye Islands. It is located close to the shores of the Taymyr Peninsula, about from the coast. A narrow and bent landspit projects northwards of the norther shore. There are two hills on the island, the highest of which is Mount Kolomeitsev ''(Gora Kolomeitseva)'' —named after Nikolai Kolomeitsev— in the eastern part. Winters are long, cold and bitter, and the surrounding sea freezes solid about ten months every year. History The whole area around Rastorguyev Island was explored by Russian geologist Baron Eduard von Toll during his last venture, the Russian Arctic Expedition of 1900–1903. This large island was named by him after Stepan Innokentyevich Rastorguyev, an Imperial Russian Cossack officer accompanying him. Toll sent Rastorguyev along with the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)